CBSE Class 12-science Answered
by starting sign conventions and assumptions used derive the relation between u,v and f in case of concave mirror
Asked by upasonamandal7 | 28 Jan, 2022, 10:15: AM
Sign convention in the case of concave mirror:
- Since, object is always placed in front of the mirror hence the sign of object is taken as negative.
- Since, the centre of curvature and focus lie in front of the concave mirror, so signs of radius of curvature and focal length are taken as negative in the case of concave mirror.
- When image is formed in front of the mirror, the distance of image is taken as – (negative) and when image is formed behind the mirror, the distance of image is taken as + (positive).
- Height of image is taken as positive in the case of erect image and taken as negative in the case of inverted image.
Derivation: -
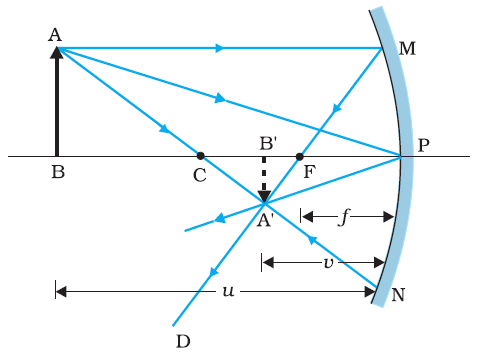 Figure shows the ray diagram considering three rays. It shows the image A′B′ (in this case, real) of an object AB formed by a concave
Figure shows the ray diagram considering three rays. It shows the image A′B′ (in this case, real) of an object AB formed by a concave
mirror. Thus, point A′ is image point of A if every ray originating at point A and falling on the concave mirror after reflection passes
through the point A′.
We now derive the mirror equation or the relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length ( f ).
From Figure, the two right-angled triangles A′B′F and MPF are similar. (For paraxial rays, MP can be considered to be a straight line
perpendicular to CP.) Therefore,
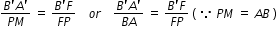 ......................................(1)
......................................(1)
since 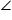 APB =
APB = 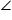 A'PB' , the right angled triangles A′B′P and ABP are also similar. Therefore,
A'PB' , the right angled triangles A′B′P and ABP are also similar. Therefore,
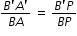 ...........................................(2)
...........................................(2)
Comparing eqns.(1) and (2), we get
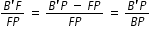 .........................................(3)
Equation (3) is a relation involving magnitude of distances. We now apply the sign convention. We note that light travels from the object to
.........................................(3)
Equation (3) is a relation involving magnitude of distances. We now apply the sign convention. We note that light travels from the object to
the mirror MPN. Hence this is taken as the positive direction.
To reach the object AB, image A′B′ as well as the focus F from the pole P, we have to travel opposite to the direction of incident light.
Hence, all the three will have negative signs. Thus,
B'P = -v, FP = -f , BP = -u
using these convention in eqn.(3), we get
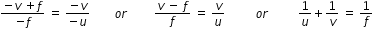 .............................(4)
Eqn.(4) is known as mirror formula
.............................(4)
Eqn.(4) is known as mirror formula

mirror. Thus, point A′ is image point of A if every ray originating at point A and falling on the concave mirror after reflection passes
From Figure, the two right-angled triangles A′B′F and MPF are similar. (For paraxial rays, MP can be considered to be a straight line
perpendicular to CP.) Therefore,
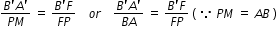 ......................................(1)
......................................(1) APB =
APB = 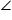 A'PB' , the right angled triangles A′B′P and ABP are also similar. Therefore,
A'PB' , the right angled triangles A′B′P and ABP are also similar. Therefore,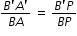 ...........................................(2)
...........................................(2)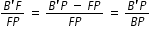 .........................................(3)
.........................................(3)the mirror MPN. Hence this is taken as the positive direction.
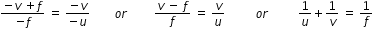 .............................(4)
.............................(4)
Answered by Shiwani Sawant | 28 Jan, 2022, 12:16: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by advssdrall | 30 Oct, 2022, 10:06: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by upasonamandal7 | 31 Jan, 2022, 10:35: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by upasonamandal7 | 28 Jan, 2022, 10:15: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by mridulabarua05 | 08 Feb, 2019, 10:04: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 21 May, 2014, 13:45: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 09 May, 2014, 12:59: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 09 May, 2014, 13:35: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 May, 2014, 13:44: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 09 May, 2014, 15:46: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Mohdabrar | 19 Feb, 2016, 02:27: AM