Class 9 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 3: The Cell - A Unit of Life
Revise the different types of cells with TopperLearning’s Frank solutions for ICSE Class 9 Biology The Cell - A Unit of Life. Understand the functions of plastids, chloroplast and mitochondria with the reference answer created by our experts. Learn to draw and explain the structure of a chromosome or a plant cell with the support of well-prepared solutions by experienced science teachers.
Enjoy learning your ICSE Class 9 Biology lessons with TopperLearning’s ready-reference free Frank textbook solutions. Prepare for your exam with model answers for different types of textbook questions. These reference answers will help you gain a thorough understanding of the chapter concepts and boost your marks.
The Cell - A Unit of Life Exercise 25
Solution 1
Solution 2
(i) All living organisms are composed of cell. Hence cell is the structural unit of living organisms.
(ii) All cells arise from pre-existing cells of the similar kind by cell division.
(iii) The chemical composition and metabolism of all cells is basically alike.
Solution 3
The two types of cells are:
(i) Prokaryotic cells - These cells lack a well-organised nucleus and membrane bound organelles. They are usually found in unicellular organisms, which are referred to as prokaryotes. Example of prokaryotes are bacteria and blue-green algae.
(ii) Eukaryotic cells - These cells possess a well-organised nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Organisms made up of eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. Examples of eukaryotes are plants and animals.
Solution 4
(i) Mitochondria
(ii) Endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) Plastid
(iv) Golgi body
(v) Vacuoles
(vi) Lysosomes
(vii) Centrosomes
(Write any 5)
Solution 5
(b) Virchow stated that new cells originate only from pre-existing cells (omnis cellula e cellula).
(c) Schleiden found that all plant cells have essentially similar structure.
(d) Schwann observed that all animal cells are basically similar and lack cell wall.
Solution 6
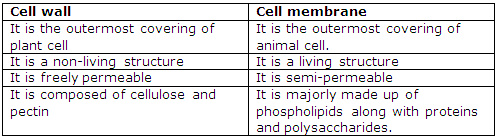
Solution 7
(b) Ribosomes - It is the site of protein synthesis.
(c) Cell membrane - It gives definite shape to the cell, protects the internal cell contents and allows entry and exit of specific substances into and out of the cell.
The Cell - A Unit of Life Exercise 26
Solution 8
(i) Chloroplast - Green coloured plastids (due to presence of chlorophyll)
(ii) Chromoplast- Coloured plastids (except green colour)
(iii) Leucoplast - Colourless plastids
The main functions of plastids are:
(i) Chloroplasts trap solar energy and use it to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water by the process of photosynthesis.
(ii) Chromoplasts attract insects and other animals to ensure pollination and dispersal of fruits.
(iii) Leucoplasts store starch, proteins or lipids in cell.
(Write any 2 functions)
Solution 9
Solution 10
SER - Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
RER - Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
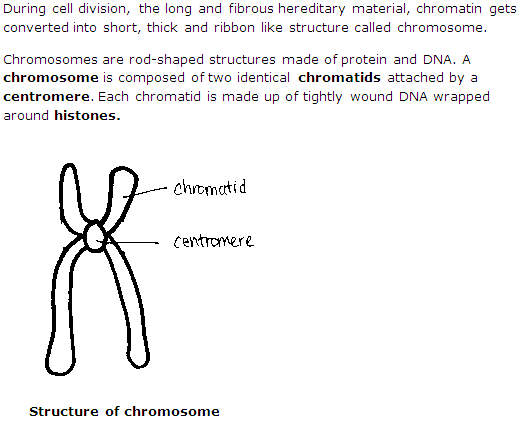
Solution 14
(b) Chromosomes are the hereditary material of the nucleus, concerned with the transmission of hereditary traits from parents to offspring.
(c) Endoplasmic Reticulum increases the surface area of the cytoplasm for different metabolic activities of the cell.
Solution 15
(b) Deoxyribonucleic acid
(c) Theory
(d) Ostrich
(e) Nucleus
Solution 16
Power house of cells - Mitochondria
Help in formation of cell plate during cell division - Golgi complex
Site for photosynthesis - Chloroplast
Control tower of cell - Nucleus
Structure bearing genes - Chromosomes
Solution 17
b - Nucleus
c - Chromatin
d - Nuclear membrane
e - SER
f - Mitochondria
g - Golgi vesicles
h - Golgi complex
i - RER
j - Ribosomes
Solution 18
(b) Schleiden and Schwann
(c) Nerve cell
(d) Fibres of ramie
(e) ATP
(f) The cell of Mycoplasma laidlawii
(g) Cell lacking a well-organised nucleus and membrane bound organelles is called prokaryotic cell.
The Cell - A Unit of Life Exercise 27
Solution 19
b - Nucleolus
c - Mitochondria
d - Golgi apparatus
e - Chloroplast
f - cell membrane
g - cell membrane
h - ER
i - Microtubule
Solution 20
(ii) (a) DNA
(iii) (c) plastid
(iv) (a) nucleus membrane
(v) (b) Altman
(vi) (b) Robert Hooke
(vii) (a) Robert Hooke
