Class 9 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 23: Safe Disposal of Wastes
Understand waste management with TopperLearning’s Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 23 Safe Disposal of Wastes. Read about the benefits of garbage incineration with our detailed chapter solutions. Also, learn how an electrostatic precipitator works thanks to the answers prepared by our subject experts.
Revise your ICSE Class 9 Biology lessons easily with our Frank textbook solutions. Our experts have created well-prepared answers for short answer questions, MCQs and other question types from your textbook. In addition to these solutions, you can 24x7 access to video lessons, online practice tests, doubts and solutions and more to improve your knowledge of Biology concepts.
Safe Disposal of Wastes Exercise 212
Solution 1
(i) Dematerialization of production by reducing the amount of raw materials use and energy used in production.
(ii) Recycling wastes back into the production process.
(iii) Recovery of some ingredients and / or treatment of wastes.
(iv) Dispersal, dumping or storage.
Solution 2
Solution 3
(i) Incineration reduces the weight and volume of the waste by as much as 95%.
(ii) It helps in the treatment of clinical wastes and toxic pathogens.
(iii) It is designed in such a way that it can be also used to produce electricity.
(Write any two)
Solution 4
The processes involves in composting are :
Solution 5
(i) Primary treatment - In this, the coarse and fine suspended , solids are removed by sedimentation, coagulation and precipitation.
(ii) Secondary treatment - It is essentially a biological treatment process which involves the removal of colloidal and dissolved organic substances and some toxic chemicals.
(iii) Tertiary treatment - Here, excess nutrients are removed to allow the reuse of that water.
Solution 6
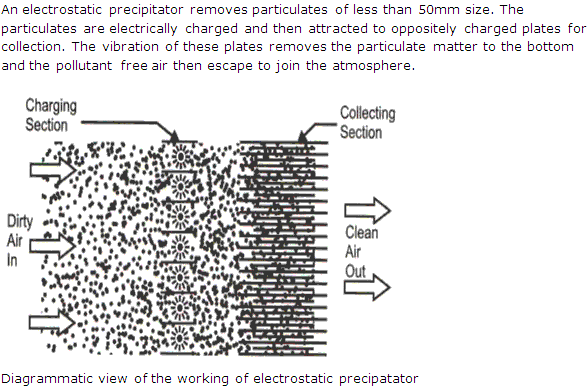
Solution 7
Household wastes consist of organic biodegradable matter as well as non-biodegradable matter. They should be segregated from each other using separate bins. Wherever possible, the non-biodegradable matter is recycled and used.
The organic biodegradable matter i.e. wet waste must be separated from other dry wastes. They are collected by municipal workers and transported to a landfill.
Solution 8
(i) Incineration reduces the weight and volume of the waste by as much as 95%.
(ii) It helps to destroy pathogens and toxins using high temperature, thereby playing role in the treatment of clinical wastes and certain hazardous wastes.
Solution 9
Sewage water is treated in three steps:
(i) Primary treatment - In this, the coarse and fine suspended solids are removed by sedimentation, coagulation and precipitation.
(ii) Secondary treatment - It is essentially a biological treatment process which involves removal of colloidal and dissolved organic substances and some toxic chemicals.
(iii) Tertiary treatment - Here, excess nutrients are removed to allow the reuse of that water.
Solution 10
1. Composting
2. Segregation of wet and dry waste.
Solution 11
(i) It is an eco-friendly method of disposing wet garbage from households and biomass wastes from gardens.
(ii) The compost obtained acts as rich organic manure for the garden plants.
Solution 12
(ii) (d) garbage and sewage sludge
(iii) (c) both (a) and (b)
(iv) (b) secondary treatment
