Class 9 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 20: Health: Causes of Diseases
Learn in detail about health issues with TopperLearning’s Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 20 Health: Causes of Diseases. Our expert solutions will give you detailed explanations on infectious diseases - diphtheria, measles and more. Also, use our solutions to learn the basics treatment of diseases.
Our Frank solutions ICSE Class 9 Biology will support you with answers for different question types including ‘Match the items,’ ‘True of False’ and more. Our study portal also provides online practice tests, sample question papers, videos and other learning materials to give you maximum learning support and score top marks.
191
192
Health: Causes of Diseases Exercise 191
Solution 1
(a) Disease is the stage when body or any part of it shows some disturbance in normal functions.
(b) Pathogen refers to any disease causing organism.
(c) Infection refers to the pathological state resulting from the invasion of the body by pathogenic microorganisms.
(d) Incubation period refers to the period between exposure to an infection and the appearance of the first symptoms.
(b) Pathogen refers to any disease causing organism.
(c) Infection refers to the pathological state resulting from the invasion of the body by pathogenic microorganisms.
(d) Incubation period refers to the period between exposure to an infection and the appearance of the first symptoms.
Health: Causes of Diseases Exercise 192
Solution 2
(a) Communicable diseases are the diseases which spread by different organisms such as bacteria, virus and fungi. These are transmitted from one person to another. Example - Flu, malaria, syphilis.
(b) Non-communicable diseases - These diseases are not transferred from one person to another. They are of different types like allergy, nutritional deficiencies, degenerated diseases, cancer and mental diseases. Example - Arthritis, hypertension
(c) Epidemic diseases - These diseases spread rapidly and affect a large number of people at a time. Example - Spread of plague in Surat in 1994.
(d) Sporadic diseases - This refers to a type when there are scattered individual cases of a disease.
(b) Non-communicable diseases - These diseases are not transferred from one person to another. They are of different types like allergy, nutritional deficiencies, degenerated diseases, cancer and mental diseases. Example - Arthritis, hypertension
(c) Epidemic diseases - These diseases spread rapidly and affect a large number of people at a time. Example - Spread of plague in Surat in 1994.
(d) Sporadic diseases - This refers to a type when there are scattered individual cases of a disease.
Solution 3
Pneumonia - Diplococcus pneumonia
Tetanus - Clostridium tetani
Whooping cough - Haemophilus pertussis
Tetanus - Clostridium tetani
Whooping cough - Haemophilus pertussis
Solution 4
(i) Influenza -
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
(ii) Polio -
Symptoms - Symptoms commence 7-12 days after infection. These include infection of throat and intestines, muscle stiffness in neck and back.
Treatment - Vaccine of polio is more effective in children. Oral polio drops are also given to children.
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
(ii) Polio -
Symptoms - Symptoms commence 7-12 days after infection. These include infection of throat and intestines, muscle stiffness in neck and back.
Treatment - Vaccine of polio is more effective in children. Oral polio drops are also given to children.
Solution 5
Infectious diseases are the diseases which spread by different organisms such as bacteria, virus and fungi. These are transmitted from one person to another.
Influenza is a highly infectious viral disease. This disease spreads quickly from one person to the next. The virus is transmitted from the patient to the other person while the patient is coughing, sneezing, laughing or speaking. This is also transmitted by contaminated towel and handkerchief.
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
Influenza is a highly infectious viral disease. This disease spreads quickly from one person to the next. The virus is transmitted from the patient to the other person while the patient is coughing, sneezing, laughing or speaking. This is also transmitted by contaminated towel and handkerchief.
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
Solution 6
(a) Tuberculosis: It is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It affects bones, intestine, brain and other organs. Symptoms include restlessness in the beginning, loss of appetite, pain in chest and increase in heart beat. Treatment includes taking medicines like P.A.S. and thioacetazone.
(b) Diptheria: It is a communicable disease caused by Corynebacterium diptheriae. In most of the people, this is caused by droplet infection, coughing and spitting. Symptoms are high fever, weakness and swelling in the throat. Patients should be treated with anti-toxin injection. Children should be vaccinated with DPT.
(c) Influenza: Influenza is a highly infectious viral disease. This disease spreads quickly from one person to the next. The virus is transmitted from the patient to the other person while the patient is coughing, sneezing, laughing or speaking. This is also transmitted by contaminated towel and handkerchief.
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
(d) Measles: It is a highly infectious viral disease. It usually affects children. Symptoms include - suddenly high fever, red eyes and oozing of water from eyes. Fever, cough and rashes appear on the third day. After 2 to 3 days temperature goes down. Treatment includes complete rest, clothes and towels should be washed in boiling water. Endomonstan B-vaccine is the best treatment.
(e) Malaria: This disease is caused by parasitic protozoa, Plasmodium. The disease is transmitted from one person to another by female anopheles mosquitoes. The symptoms are followed by high fever, temperature rises on alternate days. Sweating is followed by lowering of body temperature. Besides this patient feels headache, nausea and vomit.
This disease is treated by medicines like chloroquine, deraprin, etc.
(f) Filaria: It is caused by filarial worm, Wuchereria bancrofti. This disease is transmitted by mosquito. Symptoms include - irritation, blockage of lymphatic ducts and fever. This disease can be treated with an arsenic medicine for adult worms.
(b) Diptheria: It is a communicable disease caused by Corynebacterium diptheriae. In most of the people, this is caused by droplet infection, coughing and spitting. Symptoms are high fever, weakness and swelling in the throat. Patients should be treated with anti-toxin injection. Children should be vaccinated with DPT.
(c) Influenza: Influenza is a highly infectious viral disease. This disease spreads quickly from one person to the next. The virus is transmitted from the patient to the other person while the patient is coughing, sneezing, laughing or speaking. This is also transmitted by contaminated towel and handkerchief.
Symptoms - Symptoms begin with headache, cold, sneezing, nose clogging, pain in hands, feet and waist. Watery discharge from nose and eyes makes patient restless and weak.
Method of treatment - Increased immunity is the best remedy. Penicillin, streptopenicillin and gamma globulin lower the effect of this disease. Eucalyptus oil should be applied on nose. During high fever, ice fermenting should be done as well as liquid food given.
(d) Measles: It is a highly infectious viral disease. It usually affects children. Symptoms include - suddenly high fever, red eyes and oozing of water from eyes. Fever, cough and rashes appear on the third day. After 2 to 3 days temperature goes down. Treatment includes complete rest, clothes and towels should be washed in boiling water. Endomonstan B-vaccine is the best treatment.
(e) Malaria: This disease is caused by parasitic protozoa, Plasmodium. The disease is transmitted from one person to another by female anopheles mosquitoes. The symptoms are followed by high fever, temperature rises on alternate days. Sweating is followed by lowering of body temperature. Besides this patient feels headache, nausea and vomit.
This disease is treated by medicines like chloroquine, deraprin, etc.
(f) Filaria: It is caused by filarial worm, Wuchereria bancrofti. This disease is transmitted by mosquito. Symptoms include - irritation, blockage of lymphatic ducts and fever. This disease can be treated with an arsenic medicine for adult worms.
Solution 7
The symptoms of diabetes insipidus are:
(i) Excessive urination, but urine does not contain sugar at all
(ii) Increased frequency in urination
(iii) Progressive weakness
(iv) Increased appetite
(v) Loss of weight
(vi) Excessive thirst
(i) Excessive urination, but urine does not contain sugar at all
(ii) Increased frequency in urination
(iii) Progressive weakness
(iv) Increased appetite
(v) Loss of weight
(vi) Excessive thirst
Solution 8
Diplococcus pneumonia, Clostridium tetani, Ascaris lumbricoides, Plasmodium species, HIV virus
Solution 9
The main causes of human heart diseases are:
(i) Body overweight
(ii) Birth defects of the heart
(iii) Deposition of cholesterol resulting in arteriosclerosis
(iv) Severe infections
(v) Excessive use of coffee, tobacco etc.
(vi) Malfunctioning of some of the endocrine glands
(i) Body overweight
(ii) Birth defects of the heart
(iii) Deposition of cholesterol resulting in arteriosclerosis
(iv) Severe infections
(v) Excessive use of coffee, tobacco etc.
(vi) Malfunctioning of some of the endocrine glands
Solution 10
Full form of AIDS is Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome.
It is caused by Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
AIDS is transmitted in the following ways:
(i) Sexual intercourse with the suffering from AIDS.
(ii) Transfusion of the AIDS infected blood.
(iii) New born child born from the infected mother.
It is caused by Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
AIDS is transmitted in the following ways:
(i) Sexual intercourse with the suffering from AIDS.
(ii) Transfusion of the AIDS infected blood.
(iii) New born child born from the infected mother.
Solution 11
Degenerative diseases - Rheumatic
Diabetes - Insulin
AIDS - HIV virus
Cholera - Bacterial disease
Influenza - Viral disease
Mosquito - Vector
Elephantiasis - Filaria
Diabetes - Insulin
AIDS - HIV virus
Cholera - Bacterial disease
Influenza - Viral disease
Mosquito - Vector
Elephantiasis - Filaria
Solution 12
(a) allergy
(b) Plasmodium
(c) virus, bacteria
(d) caused by virus
(e) Wuchereria bancrofti
(b) Plasmodium
(c) virus, bacteria
(d) caused by virus
(e) Wuchereria bancrofti
Solution 13
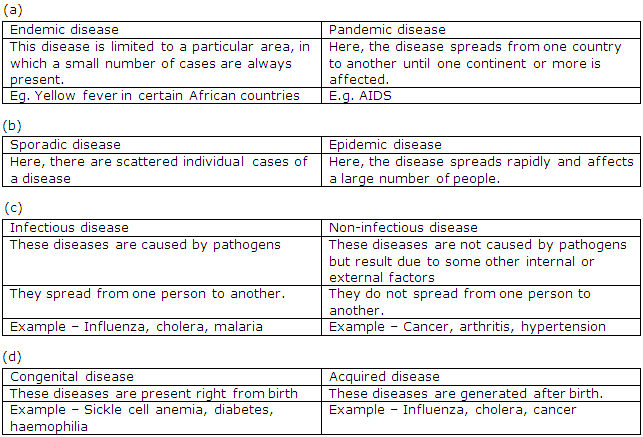
Solution 14
(a) Typhoid, cholera, tetanus
(b) Viruses
(c) Rabies
(d) Filariasis, Ascariasis
(e) Arthritis, diabetes
(b) Viruses
(c) Rabies
(d) Filariasis, Ascariasis
(e) Arthritis, diabetes
Solution 15
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) True
(e) False
(f) True
(b) False
(c) True
(d) True
(e) False
(f) True
Solution 16
(i) (a) Diabetes
(ii) (d) Cholera
(iii) (b) filarial
(iv) (b) Smallpox
(v) (d) yellow fever
(vi) (c) Uncontrolled division of cells
(ii) (d) Cholera
(iii) (b) filarial
(iv) (b) Smallpox
(v) (d) yellow fever
(vi) (c) Uncontrolled division of cells
