Class 9 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 16: Digestive System
Understand the concept of digestion effectively with TopperLearning’s Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 16 Digestive System. Learn about the enzymes of pancreatic juice and how they help in the process of digestion. Also, revise answers about the enzymes secreted by ileum, salivary glands and stomach.
To help you practice your knowledge about the digestive system, the Frank textbook includes MCQs. You can also find answers for these questions in our chapter solutions. In addition, you can glance through our other ICSE Class 9 Biology study materials such as Selina solutions, practice tests and more for a thorough exam preparation.
151
Digestive System Exercise 151
Solution 1
Nutrition can be defined as the process which involves the utilization of food by an animal to obtain energy for growth and development. There are two types of nutrition - autotrophic and heterotrophic.
Solution 2
(a) Autotrophs: These are the organisms which prepare organic food in their body from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water, etc. Example - green plants and certain protests.
(b) Heterotrophs: The organisms which cannot prepare their own food and depends on ready-made food synthesized by green plants are called heterotrophs. Examples - animals and human beings.
(c) Carnivores: The organisms which feed upon other animals and animal products. Examples - tiger, lion, cat, etc.
(d) Omnivores: The organisms which feed on all kinds of plant and animal food are called omnivores. Examples - Cockroach and human beings.
(e) Herbivores: The organisms that feed on plants only are termed as herbivores. Examples - sheep, cow, goat, etc.
(b) Heterotrophs: The organisms which cannot prepare their own food and depends on ready-made food synthesized by green plants are called heterotrophs. Examples - animals and human beings.
(c) Carnivores: The organisms which feed upon other animals and animal products. Examples - tiger, lion, cat, etc.
(d) Omnivores: The organisms which feed on all kinds of plant and animal food are called omnivores. Examples - Cockroach and human beings.
(e) Herbivores: The organisms that feed on plants only are termed as herbivores. Examples - sheep, cow, goat, etc.
Solution 3
(a) Parasites are the organisms that live in or on the body of another organism called host, and obtain nourishment from its body whereas saprophyte is an organism that absorbs soluble organic nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter.
(b) Autotroph is an organism which prepares organic food in their body from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water, etc. whereas heterotroph is an organism which cannot prepare its own food and depends on ready-made food synthesized by green plants.
(c) Holozoic nutrition is a nutrition in which animals survive by consuming other organisms whereas saprozoic nutrition is the nutrition in which the animals absorbs soluble organic nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter.
(d) Holophytic nutrition is the nutrition in which organisms prepare organic food in their body from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water, etc. whereas in holozoic nutrition, the animals survive by consuming other organisms.
(b) Autotroph is an organism which prepares organic food in their body from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water, etc. whereas heterotroph is an organism which cannot prepare its own food and depends on ready-made food synthesized by green plants.
(c) Holozoic nutrition is a nutrition in which animals survive by consuming other organisms whereas saprozoic nutrition is the nutrition in which the animals absorbs soluble organic nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter.
(d) Holophytic nutrition is the nutrition in which organisms prepare organic food in their body from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water, etc. whereas in holozoic nutrition, the animals survive by consuming other organisms.
Solution 4
The steps involved in animal nutrition are:
(a) Ingestion - It means taking solid or liquid food inside the body.
(b) Digestion - It is the breaking down of complex insoluble food components into simple soluble substances.
(c) Absorption - It is the process by which soluble soluble digested food passes from alimentary canal into blood and lymph through intestinal villi.
(d) Assimilation - Utilization of absorbed food by different body cells is called assimilation.
(e) Egestion - Elimination of undigested food as faeces is called egestion.
(a) Ingestion - It means taking solid or liquid food inside the body.
(b) Digestion - It is the breaking down of complex insoluble food components into simple soluble substances.
(c) Absorption - It is the process by which soluble soluble digested food passes from alimentary canal into blood and lymph through intestinal villi.
(d) Assimilation - Utilization of absorbed food by different body cells is called assimilation.
(e) Egestion - Elimination of undigested food as faeces is called egestion.
Solution 5
There are four types of teeth:
(a) Incisors - These are used for cutting.
(b) Canines - These teeth are used for tearing.
(c) Premolars - For masticating the food.
(d) Molars - For grinding and masticating the food.
(a) Incisors - These are used for cutting.
(b) Canines - These teeth are used for tearing.
(c) Premolars - For masticating the food.
(d) Molars - For grinding and masticating the food.
Solution 6

Solution 7
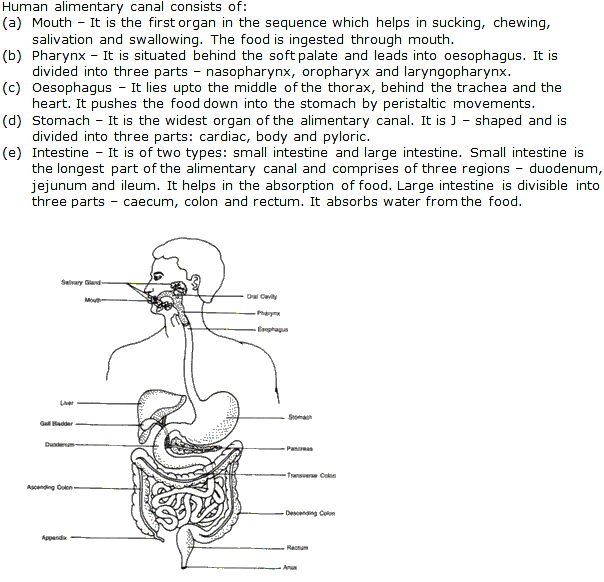
Solution 8
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) False
Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12
Salivary Glands - Three pairs in man and secrete 1000 to 1500 cc saliva per day.
Saliva is slightly acidic and its pH is 6.8.
There are three types of salivary glands:
(a) Parotid glands: It is the largest salivary gland and situated near the ears. It opens into oral cavity by Stenoson's duct.
(b) Sublingual glands: It is located beneath the tongue. It opens into the floor of oral cavity by duct of Rivinus.
(c) Submadibular or sub-maxillary glands: It is situated at the angles of the lower jaws. It opens inot oral cavity by Whartson's duct.
Each gland secret secretes saliva which is transported to the mouth cavity. At the time secrete saliva.
Saliva is slightly acidic and its pH is 6.8.
There are three types of salivary glands:
(a) Parotid glands: It is the largest salivary gland and situated near the ears. It opens into oral cavity by Stenoson's duct.
(b) Sublingual glands: It is located beneath the tongue. It opens into the floor of oral cavity by duct of Rivinus.
(c) Submadibular or sub-maxillary glands: It is situated at the angles of the lower jaws. It opens inot oral cavity by Whartson's duct.
Each gland secret secretes saliva which is transported to the mouth cavity. At the time secrete saliva.
Solution 13
(a) Lipase
(b) Lungs
(c) Rectum
(b) Lungs
(c) Rectum
Solution 14

Solution 15
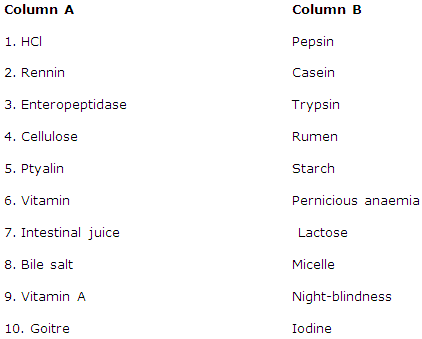
Solution 16

Solution 17
(a) Carboxypeptidase
(b) Rennin
(c) Caecum
(d) HCl
(e) Pepsin
(f) Digestion
(g) Protein
(h) Bilirubin
(b) Rennin
(c) Caecum
(d) HCl
(e) Pepsin
(f) Digestion
(g) Protein
(h) Bilirubin
Solution 18

Solution 19
(a) Stomach - Pepsin
(b) Salivary glands - Salivary amylase/Ptyalin
(c) Pancreas - Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxy peptidase, Pancreatic amylase and Pancreatic lipase.
(d) Ileum - Enterokinase, Endokinase, Aminopeptidase and Dipeptidase.
(b) Salivary glands - Salivary amylase/Ptyalin
(c) Pancreas - Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxy peptidase, Pancreatic amylase and Pancreatic lipase.
(d) Ileum - Enterokinase, Endokinase, Aminopeptidase and Dipeptidase.
Solution 20

