Class 9 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 2: Being Alive - What is its Meaning?
Revision of your Biology lessons becomes easier with Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Being Alive – What is its meaning? Our textbook solutions include details about the characteristics of living organisms. You can revise the examples of movement in non-living things, and also revise the definitions of locomotion, life, nutrition and more.
With our ICSE Class 9 Biology Frank textbook solutions, it is easy to understand concepts. Explore TopperLearning’s online learning portal and you can even use our Selina solutions, video lessons, mock tests, and other online resources.
13
14
Being Alive - What is its Meaning? Exercise 13
Solution 1
Characteristics of living organisms are:
(i) All living organisms exhibit a definite shape and size. For example - Mango trees can be identified among all the other tress. Also tigers can be identified among other animals.
(ii) All living beings show some type of body organization. Their body may be made of one cell in case of unicellular organisms or many cells in case of multicellular organisms. In multicellular organisms, cells are further organized into tissues, organs and organ systems.
(iii) Living organisms show autotrophic or heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
(iv) All living organisms respire continuously. During respiration, most organisms use up oxygen from environment and release carbon dioxide. This oxygen oxidizes food materials to release energy which is used to carry out the various life processes of the organism.
(v) In all living organisms, many chemical processes occur in order to maintain life and this is called metabolism. Some of these processes are constructive called anabolic processes whereas others are destructive called catabolic processes.
(vi) All living organisms show the characteristic feature of growth. From a small size at birth, living organisms grow due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells. Example - A seedling growing into a small plant and then into a big tree.
(vii) Reproduction helps in producing offsprings similar to parents and thus helps in maintaining continuity of race.
(viii) All living organisms show some form of movement or another. This may be movement of the entire body from one place to another as seen in most animals, few plants and certain plant organs, or movement of a part of the body only.
(ix) All living organisms excrete waste products of metabolism from their body.
(x) Every living organism shows a definite life-cycle including four stages i.e. birth, growth, maturity and death. Every living organism has a definite life-span.
(i) All living organisms exhibit a definite shape and size. For example - Mango trees can be identified among all the other tress. Also tigers can be identified among other animals.
(ii) All living beings show some type of body organization. Their body may be made of one cell in case of unicellular organisms or many cells in case of multicellular organisms. In multicellular organisms, cells are further organized into tissues, organs and organ systems.
(iii) Living organisms show autotrophic or heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
(iv) All living organisms respire continuously. During respiration, most organisms use up oxygen from environment and release carbon dioxide. This oxygen oxidizes food materials to release energy which is used to carry out the various life processes of the organism.
(v) In all living organisms, many chemical processes occur in order to maintain life and this is called metabolism. Some of these processes are constructive called anabolic processes whereas others are destructive called catabolic processes.
(vi) All living organisms show the characteristic feature of growth. From a small size at birth, living organisms grow due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells. Example - A seedling growing into a small plant and then into a big tree.
(vii) Reproduction helps in producing offsprings similar to parents and thus helps in maintaining continuity of race.
(viii) All living organisms show some form of movement or another. This may be movement of the entire body from one place to another as seen in most animals, few plants and certain plant organs, or movement of a part of the body only.
(ix) All living organisms excrete waste products of metabolism from their body.
(x) Every living organism shows a definite life-cycle including four stages i.e. birth, growth, maturity and death. Every living organism has a definite life-span.
Solution 2
Organisms capable of performing all the vital activities of life like nutrition, growth, respiration, digestion and excretion etc. are called living organisms. Example - man, bird, fish, trees.
Things which do not perform any vital life activities are called non-living things. Example - pen, table, stone, water, car etc. Non-living things require external energy for their movement (car, train etc.) or addition of particles from outside for increase in size (eg. increase in size of alum crystals in their concentrated solutions).
Growing of the crystal of copper sulphate is not a living character. This is because the increase in its size is due to deposition of new material externally and not from within. This is known as extrinsic growth. In living organisms, growth occurs due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells.
Things which do not perform any vital life activities are called non-living things. Example - pen, table, stone, water, car etc. Non-living things require external energy for their movement (car, train etc.) or addition of particles from outside for increase in size (eg. increase in size of alum crystals in their concentrated solutions).
Growing of the crystal of copper sulphate is not a living character. This is because the increase in its size is due to deposition of new material externally and not from within. This is known as extrinsic growth. In living organisms, growth occurs due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells.
Solution 3
A motor car requires external energy for its movement and also it does not perform the vital life activities on its own, hence it is not a living organism. A living organism has internal energy which is used for carrying out all its vital life activities.
Solution 4
(a) Irritability is a feature shown by living beings, but not non-living things. It refers to the ability of the organism to respond in accordance with internal or external environmental stimuli. Irritability is well-developed in animals due to the evolution of nervous system. An example is the immediate removal of hand from a hot object. Irritability is also shown by plants but it is not very prominent.
(b) Metabolism - In all living organisms, many chemical processes occur constantly in order to maintain life and this is called metabolism. Metabolism includes two types of processes i.e. constructive and destructive. Only living organisms show metabolism.
(c) Respiration - All living organisms respire continuously. During respiration, most organisms use up oxygen from environment and release carbon dioxide.
(d) Cellular structure -All living organisms are made up of one or many cells. Each cell contains protoplasm wherein all the life activities are carried out. Protoplasm is surrounded by a thin, elastic plasma membrane. Plant cells possess an additional cell wall to provide rigidity to the cells.
(e) Growth - All living organisms show the characteristic feature of growth.From a small size at birth, living organisms grow due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells. Example - A seedling growing into a small plant and then into a big tree.
(b) Metabolism - In all living organisms, many chemical processes occur constantly in order to maintain life and this is called metabolism. Metabolism includes two types of processes i.e. constructive and destructive. Only living organisms show metabolism.
(c) Respiration - All living organisms respire continuously. During respiration, most organisms use up oxygen from environment and release carbon dioxide.
(d) Cellular structure -All living organisms are made up of one or many cells. Each cell contains protoplasm wherein all the life activities are carried out. Protoplasm is surrounded by a thin, elastic plasma membrane. Plant cells possess an additional cell wall to provide rigidity to the cells.
(e) Growth - All living organisms show the characteristic feature of growth.From a small size at birth, living organisms grow due to formation of new cells and building up of protoplasm within cells. Example - A seedling growing into a small plant and then into a big tree.
Solution 5
The characters of living organisms are:
(i) Growth
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Metabolism
(iv) Respiration
(v) Nutrition
(vi) Movement and locomotion
(vii) Definite form and size
(viii) Reproduction
(ix) Excretion
(x) Irritability
(Write any four)
(i) Growth
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Metabolism
(iv) Respiration
(v) Nutrition
(vi) Movement and locomotion
(vii) Definite form and size
(viii) Reproduction
(ix) Excretion
(x) Irritability
(Write any four)
Solution 6
A rolling stone just rolls down due to gravitational force acting on it. It will stop rolling once it reaches a hurdle or plain ground. Then it cannot roll or move on its own. It needs some external force to cause its movement. Hence it is a non-living object. A living organism would be able to move by itself using its own energy, without depending on external force.
Solution 7
Living - Egg, protoplasm, cactus, flower, seed
Non-living - Table, glass, iron, car, nail
Dead - Coral, leather, cork
Non-living - Table, glass, iron, car, nail
Dead - Coral, leather, cork
Solution 8
Examples of movement in living things -
(i) Running of a lion
(ii) Drooping of leaves
Examples of movement in non-living things -
(i) Running of train or car
(ii) Rolling down of a stone
(i) Running of a lion
(ii) Drooping of leaves
Examples of movement in non-living things -
(i) Running of train or car
(ii) Rolling down of a stone
Solution 9
(a) Life is the condition that distinguishes organisms from inorganic objects and dead organisms.
(b) Death is the cessation of all life activities in a living being due to weakening and losing of energy from them after completing their life span
(c) Locomotion is the movement of the entire organism from one place to another.
(d) Reproduction is the ability of living organisms to produce young ones that are similar to parents.
(b) Death is the cessation of all life activities in a living being due to weakening and losing of energy from them after completing their life span
(c) Locomotion is the movement of the entire organism from one place to another.
(d) Reproduction is the ability of living organisms to produce young ones that are similar to parents.
Solution 10
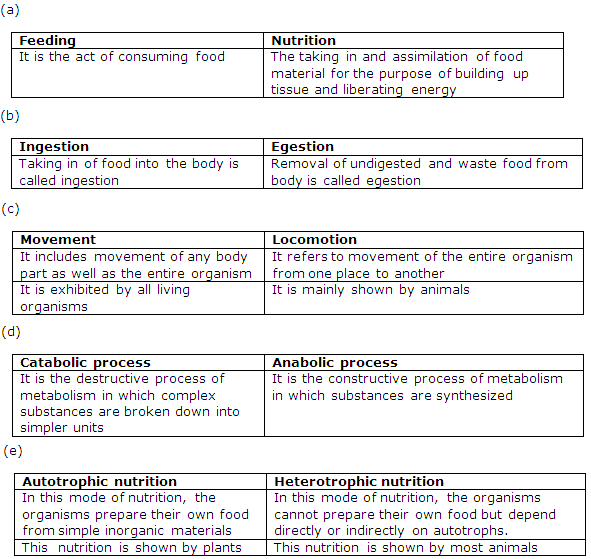
Solution 11
(a) False
(b) False
(c) False
(d) False
(e) True
(f) True
(g) True
(b) False
(c) False
(d) False
(e) True
(f) True
(g) True
Being Alive - What is its Meaning? Exercise 14
Solution 12
(i) (a) Protoplasm
(ii) (b) Dried bone
(iii) (a) Living
(iv) (d) The capacity to respond to the stimuli
(v) (a) Cell
(vi) (c) Reproduction
(ii) (b) Dried bone
(iii) (a) Living
(iv) (d) The capacity to respond to the stimuli
(v) (a) Cell
(vi) (c) Reproduction
