CBSE Class 12-science Answered
The diagram of AC generator:
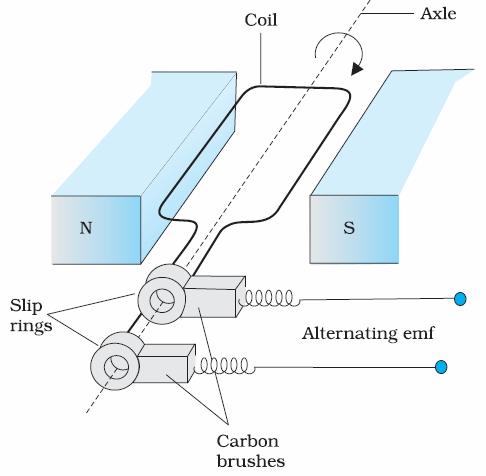
Basic parts of the AC generator:
i. Rectangular coil mounted on a rotor shaft. The coil also called armature is mechanically rotated in the uniform magnetic field by some external means.
ii. The axis of rotation of the coil is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. The rotation of the coil causes the magnetic flux through it to change, so an emf is induced in the coil.
iii. The ends of the coil are connected to an external circuit by means of slip rings and brushes.
iv. N and S are two permanent magnets which provide a constant magnetic field region in which the coil rotates.
Principle of working:
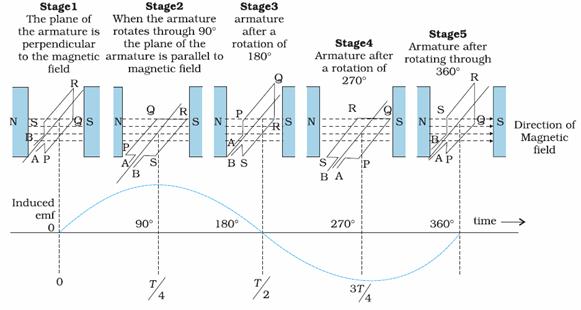
A wire loop of area A is free to rotate about an axis which is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. If the normal to the loop makes an angle θ with ![]() then, flux through the loop,Φ=cos θ.
then, flux through the loop,Φ=cos θ.
If this loop rotates with a constant angular velocity ![]()
The flux through it changes at the rate,
![]()
where Co is a constant
![]() emf is induced between ends A and B given by:
emf is induced between ends A and B given by:
![]()
V = Vm sin 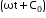 , here Vm =B A
, here Vm =B A ![]() Peak value of emf generated.
Peak value of emf generated.
Since the emf induced in the coil is varying as a function of sine, it is alternating in value and direction.
OR
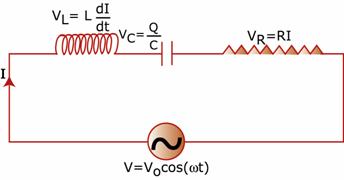
If I is the instantaneous current through LCR circuit, the instantaneous voltage across
the resistor is VR = RI , across the inductor is 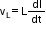 and across the capacitor is
and across the capacitor is 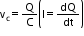
From conservation of energy, when all of them are connected in series, the total work required is just the sum of these.
So, V =![]()
The current will have the same frequency as V, but in general will not be in phase
with V.
The current can be written as
I =I0cos (![]() )
)
with the peak value 0 I and the relative phase ![]() fixed by equation.
fixed by equation.
Hence the voltage equations across each of the components will be

In the phasor diagram, the external source of EMF is V = Vο(peak value), which is
the x component of the phasor V , this vector will be along the X axis.
The current phasor I will be at an angle Φrelative to this.
So, since VR =RI, it will be parallel to this current phasor I, at angle Φrelative to V.
VL will make an angle+π/2 and VC will make angle -π/2 relative to VR.
This also implies that VL and VC will lie in opposite directions, as the following figure shows.
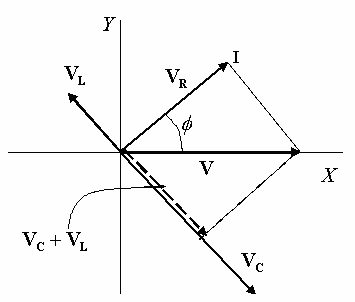
The vector VR is perpendicular to the vector VC + VL , and also, of course,
V=VR + (VL + VL)
Taking the dot product V![]() V gives
V gives

The factor Z is the analog of resistance in a purely resistive circuit, and is called
Impedance.
The phase angle is found as
![]()
Condition for resonance:
The amplitude or peak value of the current through the circuit will be
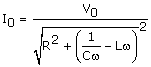
The expression clearly shows that 0 I is maximum if the term inside the bracket in the denominator is zero, since then the denominator is minimum and the impedance is completely resistive.
This means that the current is maximum at frequency ???, such that
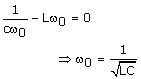
The maximum current is (I0)max ![]() as if the reactive elements are not there at all!
as if the reactive elements are not there at all!
This phenomenon, in which the peak value of current shoots up at this particular frequency is called 'resonance'.
The condition for resonance is hence:
![]()
Power factor:
Average power dissipated per cycle, is given by
![]()
The factor ![]() is called the 'Power Factor', since the power crucially depends on it. This factor depends on the applied frequency, apart from circuit parameters like L,C and R.
is called the 'Power Factor', since the power crucially depends on it. This factor depends on the applied frequency, apart from circuit parameters like L,C and R.
At resonance, XL = XC, so that ![]() . This implies that
. This implies that![]() , or that the power factor attains its maximum value, equal to unity.
, or that the power factor attains its maximum value, equal to unity.
For the (ii) capacitive and (iii) inductive circuits, the current and voltage differ in phase by ![]() so either way, it is minimum i.e. zero.
so either way, it is minimum i.e. zero.




