CBSE Class 9 Maths Types and Angle Sum Property
- each side of square field ABCD is 50 m long, length of diagonal field is (route 2 =1.414
- diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD bisects ?A . i . it biseets ?C also ii . ABCD is a rhombus
- Why is'nt the angle sum property true for a concave quadrilateral even when we can divide it into two triangles
- what is quadrilaterals
- Why is the angle sum property not applicable to concave quadrilateral?(please explain briefly and if possible with proof and example) Thank you.
-
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the line segments bisecting
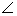 C and
C and 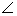 D meet at E. Prove that
D meet at E. Prove that 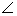 A +
A +  B = 2
B = 2  CED.
CED. 
-
In the given figure, PQRS is a quadrilateral in which PQ is the longest side and RS is the shortest side. Prove that
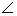 R >
R >  P.
P. 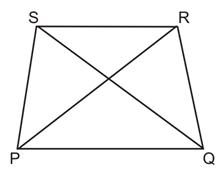
- The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 5: 9: 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral.
-
In the given figure, LMNQ is a parallelogram in which
 L = 75o and
L = 75o and  QMN = 60o. Find
QMN = 60o. Find 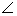 NQM and
NQM and 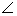 LQM.
LQM. 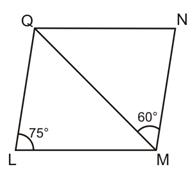
-
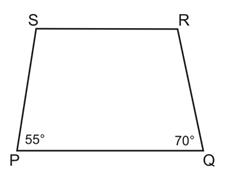
In the figure, PQRS is a trapezium in which PQ
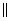 SR. if
SR. if 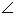 P = 55o and
P = 55o and 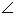 Q = 70o, find
Q = 70o, find 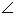 R and
R and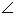 S.
S.