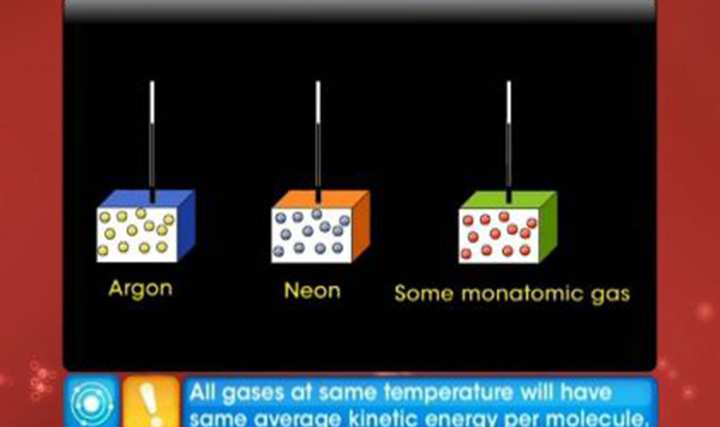
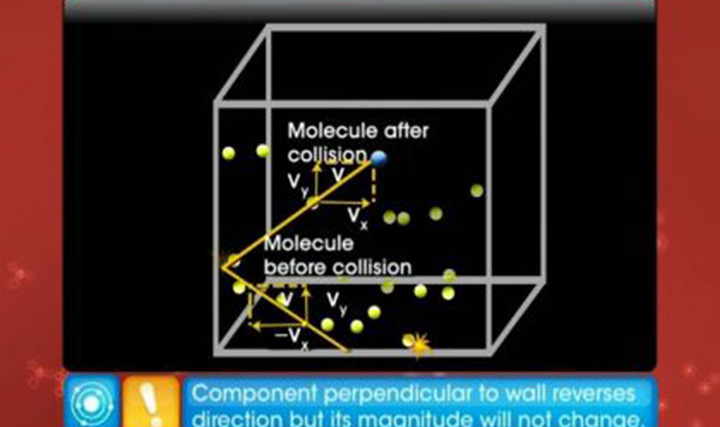
CBSE Class 11-science - Kinetic Theory of Gases Videos
Kinetic Theory of Gases
This video explains the kinetic theory of gases, ideal gas law and behaviour of an ideal gas.
More videos from this chapter
View All- an ideal gas is enclosed in a cylinder at pressure 2 atm and temperature 300k the mean time between two successive collisions is 6×10–?s if the pressure is doubled and temperature is increased to 500k the mean time between two successive collisions will be close to
- Derive allotropic constant in terms of degree of freedom and hence find it's value for monotonic diatomic and polyatomic gases . 4. Derive the expression for mean free path for a gas .
- Kinetic and calculus method
-
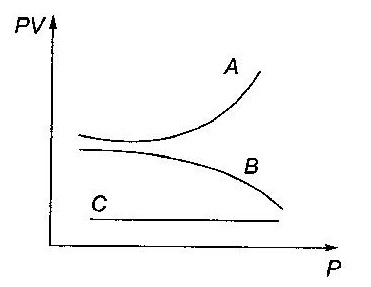
The graph shows the variation of PV with P of given masses of three gases A, B and C. The temperature is kept constant. Which of these is ideal graph?
- Is the r.m.s speed same as the average speed?
- When a gas is suddenly compressed, its temperature rises. Why?
- The volume of a gas sample is increased. Why does the pressure, which is exerted by the gas, decrease?
- In terms of the kinetic theory of gases, explain why the pressure of a gas in a closed container increases when the gas is heated?
- If three molecules have velocities 0.5, 1 and 2 km/s respectively, calculate the ratio of the root mean square speed and average speed.
- Calculate the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules at 27oC. Take the density of oxygen to be 0.001424 g/cc.