CBSE Class 12-science Answered
why is it so that for biasing a transistor the reverse bias voltage should be greater than the forward bias volatage?
Asked by Nishtha Sardana | 02 Dec, 2014, 07:53: AM
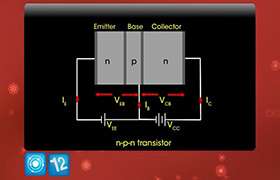
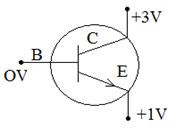
In a transistor, the emitter junction will be always forward biased with low battery voltage and the collector juction will be reverse biased with high battery voltage. We know that the function of an emitter is to provide charge carriers and that of the collector is to collect or attract the charge carriers.
If the forward bias voltage is made large, the majority carriers in the emitter will move towards the collector through the base region with great velocity. As large number of charge carriers flow, large heat gets produced which breaks the covalent bonds and this destroys the transistor.
On the other hand if the reverse bias voltage applied to the collector is large the collector will attract the majority carriers coming form the emitter through base without any heating effect or breaking of covalent bond in the transistor.
Hence the reverse bias voltage is always kept greater than the forward bias voltage in a transistor.
Answered by Jyothi Nair | 02 Dec, 2014, 09:11: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 23 Jun, 2014, 11:08: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 10 Jul, 2014, 10:25: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 23 Jun, 2014, 02:16: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Nov, 2014, 07:38: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 10 Jul, 2014, 11:09: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 23 Jun, 2014, 02:11: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 10 Jul, 2014, 01:13: PM