JEE Class main Answered
.

Asked by swayamagarwal2114 | 25 Jul, 2022, 14:34: PM
Mass of liquid in calorimeter = volume × density = 100 × 0.88 = 88 gram
electrical power of coil = voltage × current = 6.3 × 2 = 12.6 W = 12.6 J/s
while heating, at steady state, we have
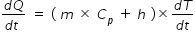 .......................................(1)
.......................................(1)where dQ/dt is heat absorbed by liquid and calorimeter that is same as electrical power of coil.
m is mass of liquid, Cp is specific heat, h is water equivalent of calorimeter and
dT/dt is rate of change of temeperature
( 88 × 10-3 × Cp + 13 × 10-3 ) × (3.6/60) = 12.6
From above expression, we get Cp = 2386 J/kg
------------------------------------------
By Newtons law of cooling , we have
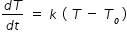
where k is constant and To is room temperature
From above expression we get , k = (3.6/60) / ( 55 - 10) = 1.333 × 10-3 J s-1 K-1
if room temeperature is 26o C , then rate of loss of heat by cooling is calcultaed as
(dT/dt ) = 1.333 × 10-3 × ( 55 - 26 ) = 3.867 × 10-2 J/s
Hence electrical power required for heating coil to get steady state is determined from eqn.(1)
= ( 88 × 10-3 × 2386 + 13 × 10-3 ) × 3.867
