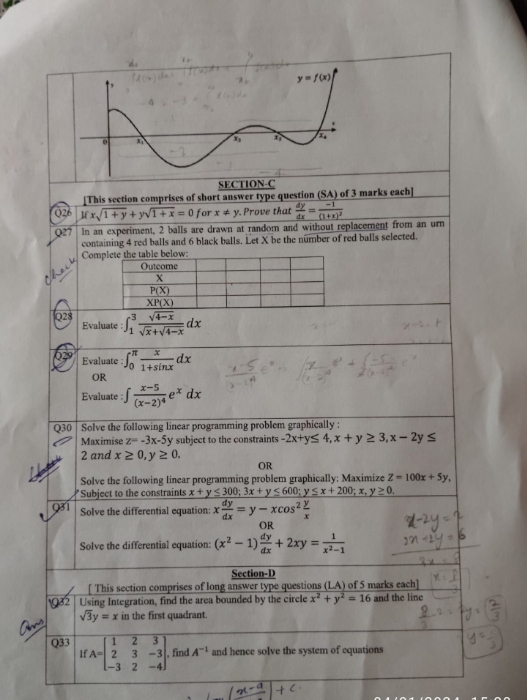
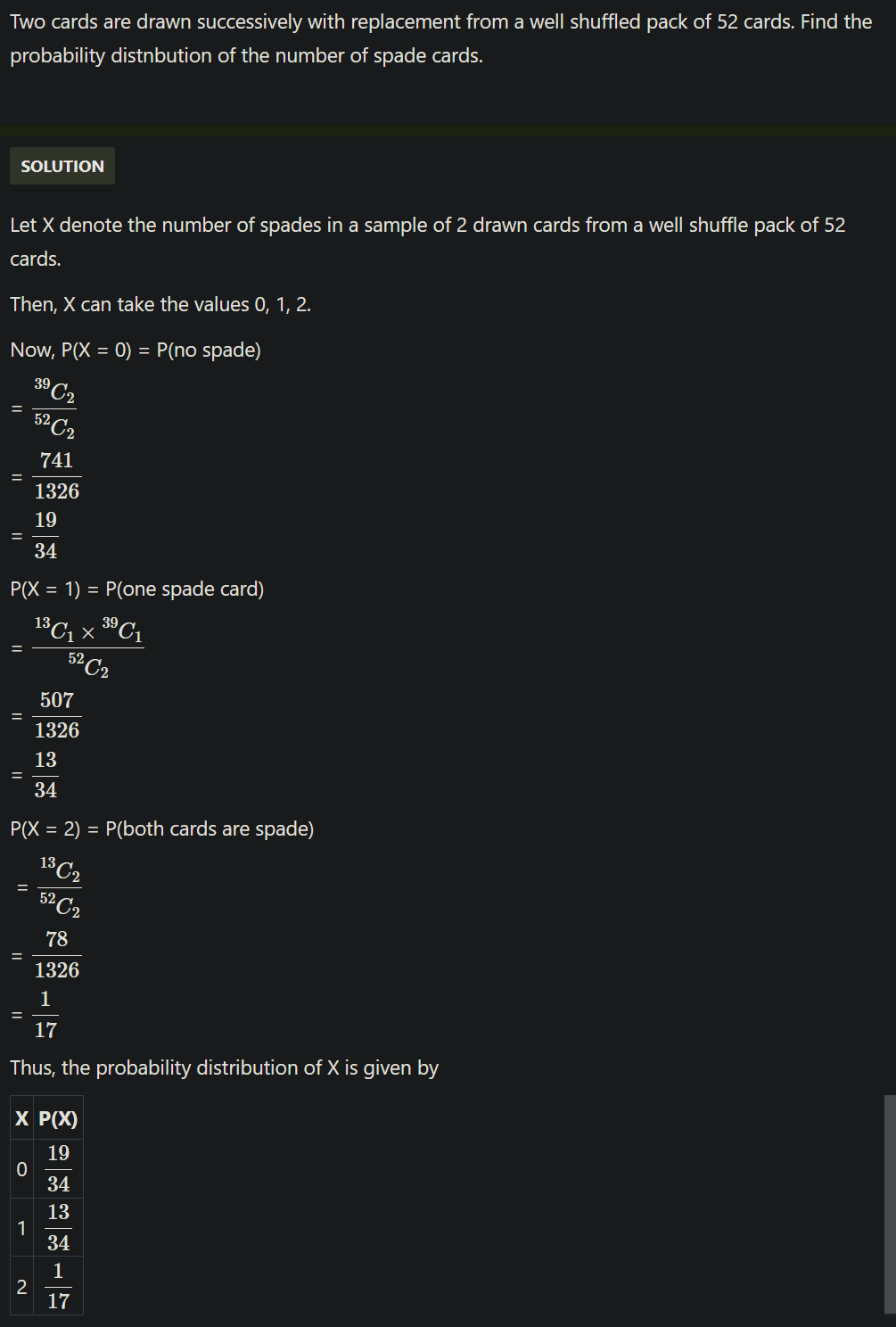
CBSE Class 12-science Answered
If A and B are two events such that 2P(A) = P(B) = 4/13 and P(A | B) = 3/7, then P(A  B) = ……
B) = ……
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 13:23: PM
Here, 2P(A) = P(B) = 4/13 and P(A | B) = 3/7
Or P(A) = 2/13, P(B) = 4/13 and P(A | B) = 3/7

Answered by | 04 Jun, 2014, 15:23: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by khushisjkvm | 04 Jan, 2024, 19:14: PM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by ashwinskrishna2006 | 26 Dec, 2023, 19:34: PM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by arjunsah797 | 03 May, 2022, 10:04: AM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by lovemaan5500 | 07 Feb, 2020, 09:47: AM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by lovemaan5500 | 08 Oct, 2019, 21:43: PM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by lovemaan5500 | 03 Oct, 2019, 05:47: AM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by lovemaan5500 | 03 Oct, 2019, 05:46: AM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by J.Jeya | 26 Jul, 2019, 09:29: AM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 13:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Maths
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 13:23: PM