JEE Class main Answered
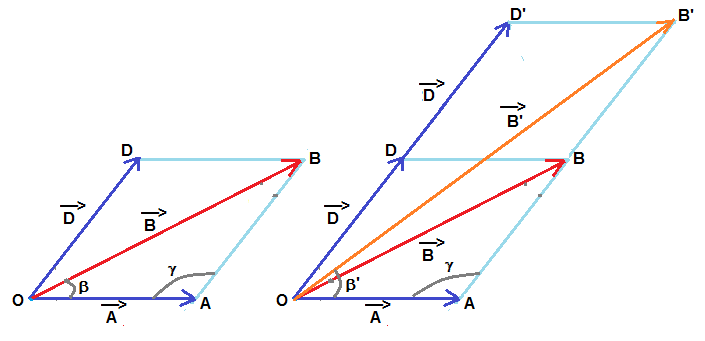
Consider three vectors vector A, vector B, vector C. It is given that vector A and vector B lie in the x-y plane and the direction of vector C is along (+k^). Also, it is known that |vector A|=10 and |vector B|=6 units and the three vectors are related by the relation vector A=vector B - alpha(vector B X vector C), where alpha is some postive constant.
Now, if only the magnitude of vector C is doubled, then what should the magnitude of vector B be, for which vector A remains unchanged (both in magnitude and direction)?
Asked by sd8022567 | 09 Jun, 2022, 13:02: PM
It is given that  and
and  are in x-y plane and
are in x-y plane and  is along z-axis .
is along z-axis .
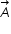 and
and 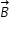 are in x-y plane and
are in x-y plane and 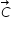 is along z-axis .
is along z-axis .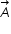 ,
, 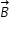 and
and 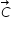 are related as
are related as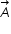 =
= 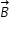 - α (
- α ( 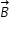 ×
× 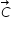 ) ...................... (1)
) ...................... (1)let 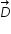 = α (
= α ( 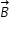 ×
× 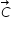 ) .........................(2)
) .........................(2)
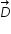 = α (
= α ( 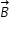 ×
× 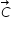 ) .........................(2)
) .........................(2)Hence we get , 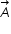 +
+ 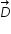 =
= 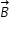 .......................(3)
.......................(3)
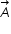 +
+ 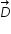 =
= 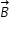 .......................(3)
.......................(3) From the given orientaion of vectors , we can see that 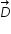 is in x-y plane .
is in x-y plane .
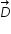 is in x-y plane .
is in x-y plane . Hence 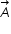 ,
, 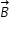 and
and 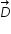 are coplanar .
are coplanar . 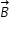 is resultant of
is resultant of
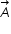 ,
, 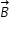 and
and 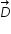 are coplanar .
are coplanar . 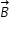 is resultant of
is resultant of 