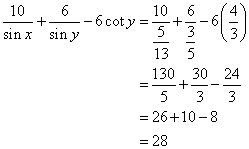Class 9 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 22: Trigonometrical Ratios [Sine, Consine, Tangent of an Angle and their Reciprocals]
Trigonometrical Ratios [Sine, Consine, Tangent of an Angle and their Reciprocals] Exercise Ex. 22(A)
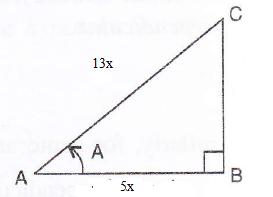
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) ![]()
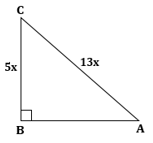
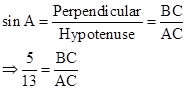
∴ If length of BC = 5x, length of AC = 13x
Now,
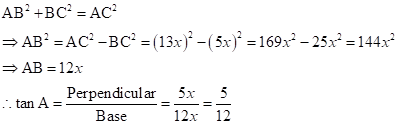
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (ii) 1
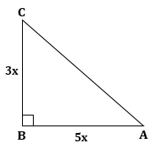
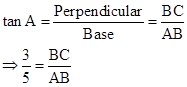
∴ If length of BC = 3x, length of AB = 5x
Now,
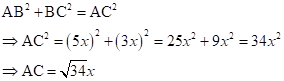
So,
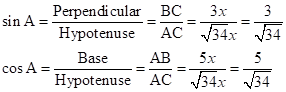
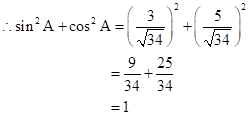
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (iv) -1
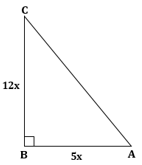
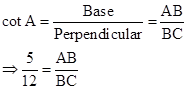
∴ If length of AB = 5x, length of BC = 12x
Now,
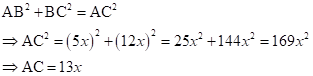
So,
![]()
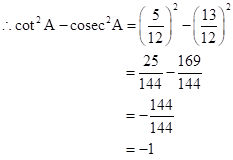
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iii)
![]()
In right-angled ΔADB,
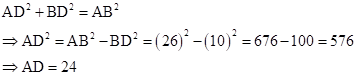
Now,
![]()
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (i) 1
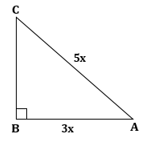
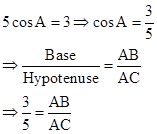
∴ If length of AB = 3x, length of AC = 5x
Now,
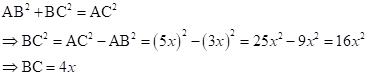
So,
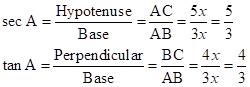
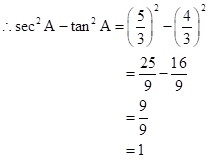
Solution 2
Given angle ![]()
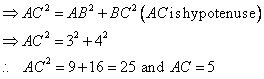
(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
(iv)
![]()
(v)
![]()
(vi)
![]()
Solution 3
Given angle ![]()
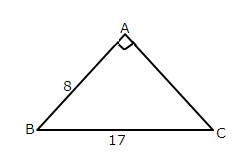
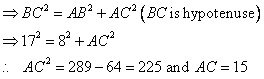
(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
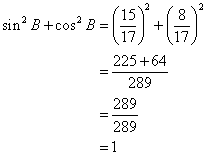
(iv)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
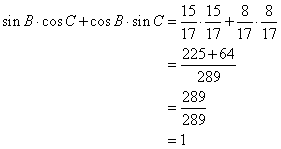
Solution 4
Consider the diagram as
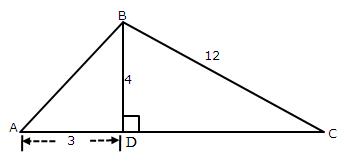
Given angle ![]() and
and ![]()


(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
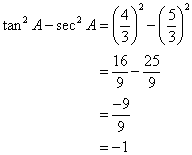
(iv)
![]()
(v)
![]()
(vi)
![]()
![]()

Solution 5
Given angle ![]() and
and ![]()
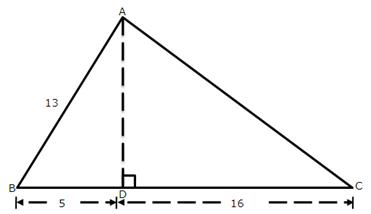


(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
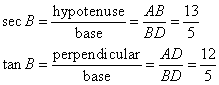
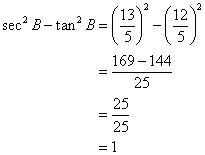
(iv)

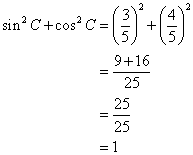
Solution 6
Consider the diagram below:
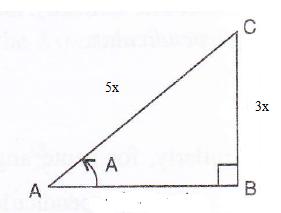
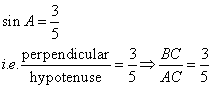
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
Solution 7
Given angle ![]() in the figure
in the figure

Now
(i)![]()
(ii)![]()
(iii)![]()
![]()
Solution 8
Consider the diagram below:
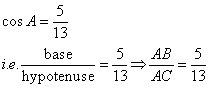
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
![]()
(i)
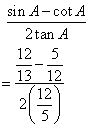
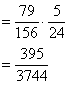
(ii)
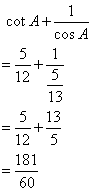
Solution 9
Consider the diagram below:
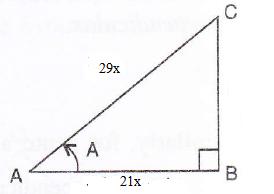
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
Solution 10
Consider the diagram below:
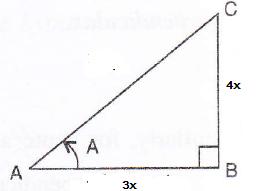
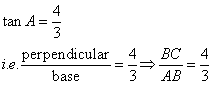
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore
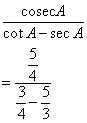
![]()
![]()
Solution 11
Consider the diagram below:
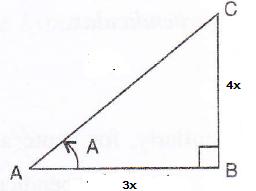
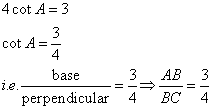
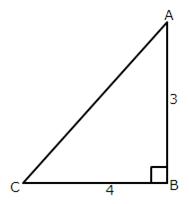
Therefore if length of AB = 3x, length of BC = 4x
Since

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
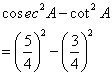
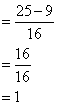
Solution 12
Consider the diagram below:
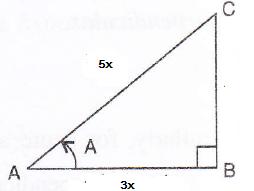
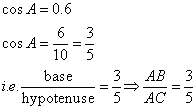
Therefore if length of AB = 3x, length of AC = 5x
Since

Now all other trigonometric ratios are
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 13
Consider the diagram below:
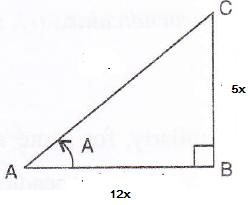
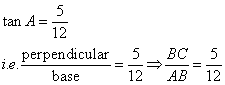
Therefore if length of AB = 12x, length of BC = 5x
Since

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
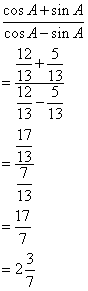
Solution 14
Consider the diagram below:
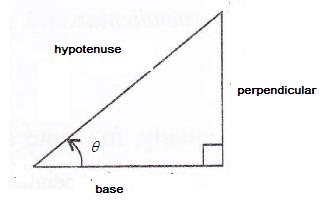
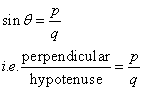
Therefore if length of perpendicular = px, length of hypotenuse = qx
Since

Now
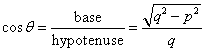
Therefore
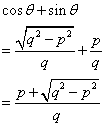
Solution 15
Consider the diagram below:
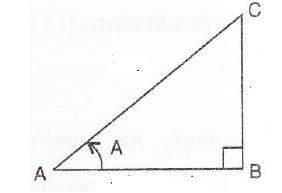
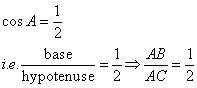
Therefore if length of AB = x, length of AC = 2x
Since

Consider the diagram below:
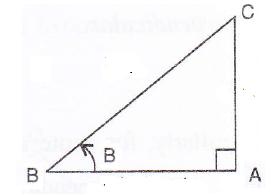
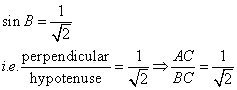
Therefore if length of AC = x, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
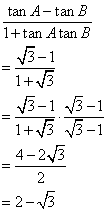
Trigonometrical Ratios [Sine, Consine, Tangent of an Angle and their Reciprocals] Exercise Ex. 22(B)
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) ![]()
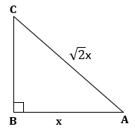
∴ If length of AB =
x, length of AC = ![]() x
x
Now,
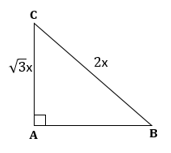
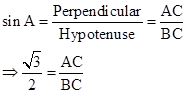
∴ If length of AC =
![]() x, length of BC = 2x
x, length of BC = 2x
Now,
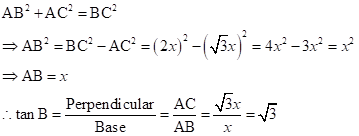
![]()
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (iii)
![]()
In right-angled ΔADC,
![]()
In right-angled ΔACB,
![]()
Now,
![]()
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (i) ![]()
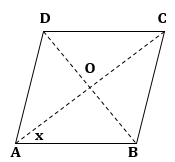
Let the diagonals BD and AC of a rhombus intersect each other at O.
Given, BD = 12 cm, AC = 16 cm.
Diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
⇒ OB = OD = 6 cm, OA = OC = 8 cm and ∠AOB = 90o
In right-angled ΔAOB,
![]()
Now,
![]()
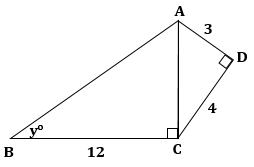
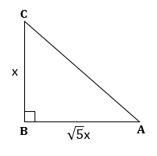
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iv) 6
In right-angled ΔADB,
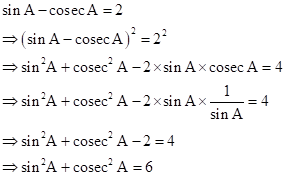
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (ii)
![]()
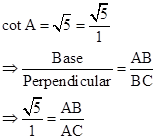
∴ If length of AB =
![]() x, length of BC = x
x, length of BC = x
Now,
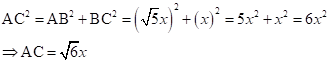
So,
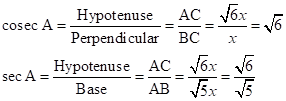
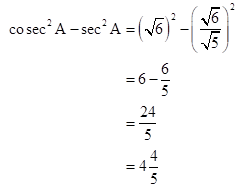
Solution 2
Consider the given figure
(i)
Since the triangle is a right angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem
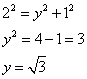
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
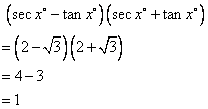
Solution 3
Consider the given figure
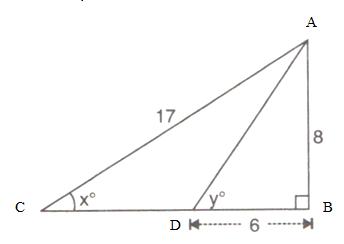
Since the triangle is a right angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem
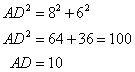
Also
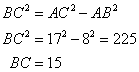
(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore
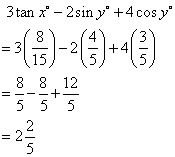
Solution 4
Consider the given figure
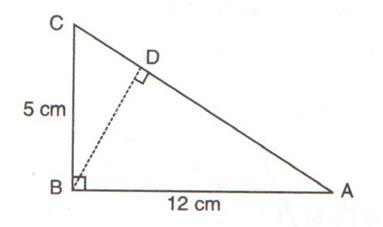
Since the triangle is a right angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem
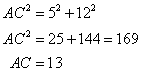
In ![]() and
and ![]() , the
, the ![]() is common to both the triangles,
is common to both the triangles, ![]() so therefore
so therefore![]() .
.
Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() are similar triangles according to AAA Rule
are similar triangles according to AAA Rule
So
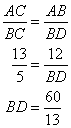
(i)
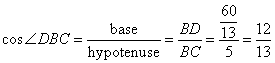
(ii)
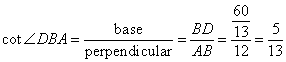
Solution 5
Consider the given figure
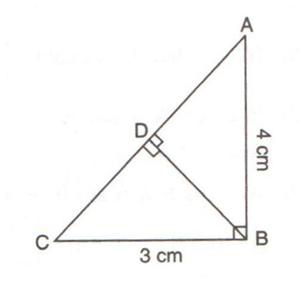
Since the triangle is a right angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem
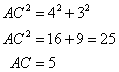
In ![]() and
and ![]() , the
, the ![]() is common to both the triangles,
is common to both the triangles, ![]() so therefore
so therefore![]() .
.
Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() are similar triangles according to AAA Rule
are similar triangles according to AAA Rule
So
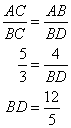
Now using Pythagorean Theorem
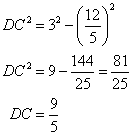
Therefore
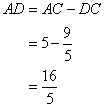
(i)
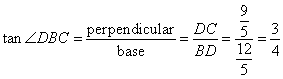
(ii)
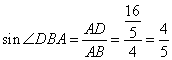
Solution 6
Consider the figure below
In the isosceles ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() the perpendicular drawn from angle
the perpendicular drawn from angle ![]() to the side
to the side ![]() divides the side
divides the side ![]() into two equal parts
into two equal parts ![]()
![]()
Solution 7
Consider the figure below
In the isosceles ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() the perpendicular drawn from angle
the perpendicular drawn from angle ![]() to the side
to the side ![]() divides the side
divides the side ![]() into two equal parts
into two equal parts ![]()
Since ![]()

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
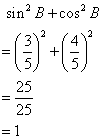
(iv)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
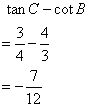
Solution 8
Consider the figure
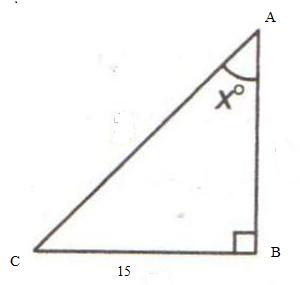
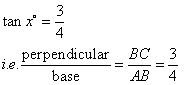
Therefore if length of base = 4x, length of perpendicular = 3x
Since
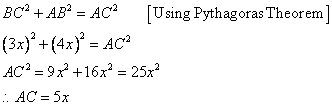
Now
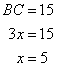
Therefore
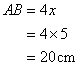
And
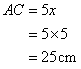
Solution 9
Consider the figure
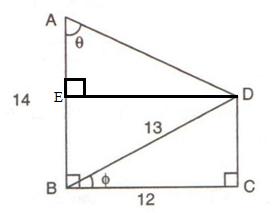
A perpendicular is drawn from D to the side AB at point E which makes BCDE is a rectangle.
Now in right angled triangle BCD using Pythagorean Theorem

Since BCDE is rectangle so ED 12 cm, EB = 5 and AE = 14 - 5 = 9
(i)
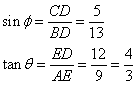
(ii)
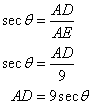
Or
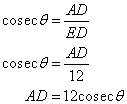
Solution 10
Given
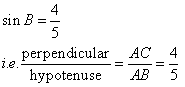
Therefore if length of perpendicular = 4x, length of hypotenuse = 5x
Since
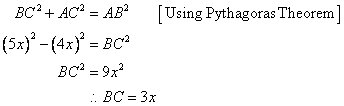
Now
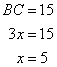
(i)
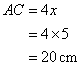
And
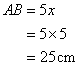
(ii)
Given
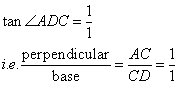
Therefore if length of perpendicular = x, length of hypotenuse = x
Since
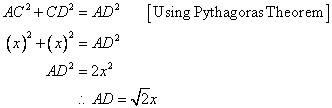
Now
![]()
So
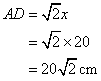
And
![]()
Now
![]()
![]()
So
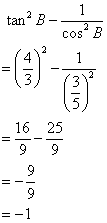
Solution 11
![]()
Squaring both sides

Solution 12
![]()
Squaring both sides

Solution 13
Consider the diagram below:
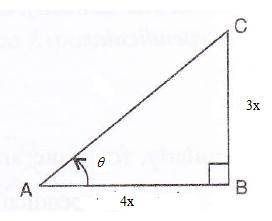

Therefore if length of BC = 3x, length of AB = 4x
Since

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
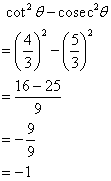
(iv)
Solution 14
Consider the diagram below:
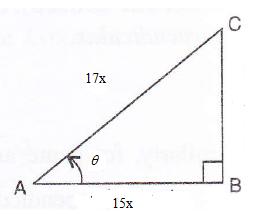
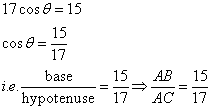
Therefore if length of AB = 15x, length of AC = 17x
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
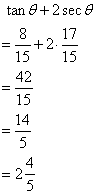
Solution 15
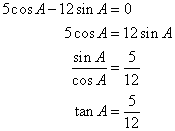
Now
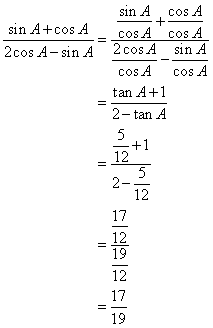
Trigonometrical Ratios [Sine, Consine, Tangent of an Angle and their Reciprocals] Exercise Test Yourself
Solution 1
Consider the diagram below:
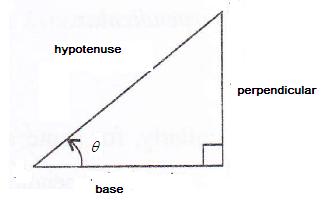
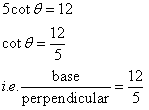
Therefore if length of base = 12x, length of perpendicular = 5x
Since
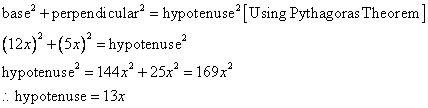
Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
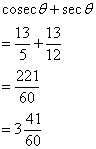
Solution 2
Consider the diagram below:
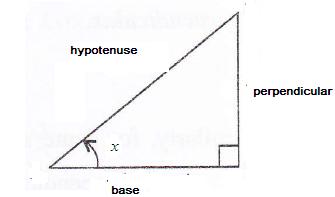
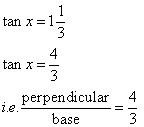
Therefore if length of base = 3x, length of perpendicular = 4x
Since
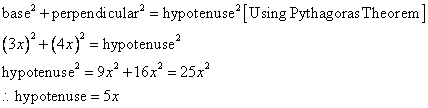
Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
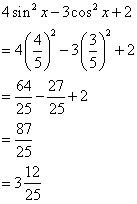
Solution 3
Consider the diagram below:
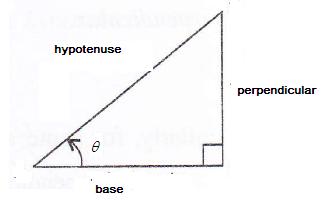
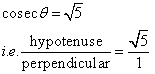
Therefore if length of hypotenuse ![]() , length of perpendicular = x
, length of perpendicular = x
Since
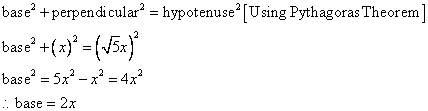
Now
![]()
![]()
(i)
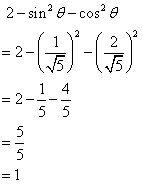
(ii)
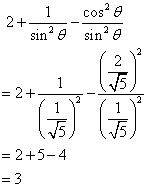
Solution 4
Consider the diagram below:
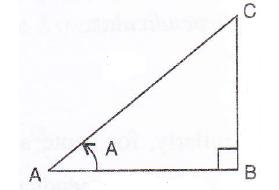
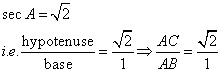
Therefore if length of AB = x, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore

Solution 5
Consider the diagram below:
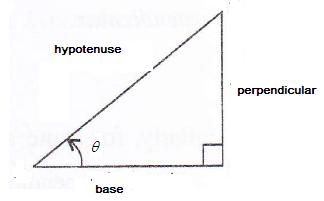
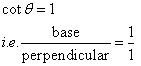
Therefore if length of base = x, length of perpendicular = x
Since
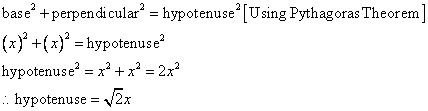
Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore

Solution 6
Given angle ![]() and
and ![]() in the figure
in the figure
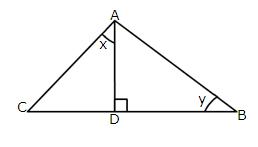

Again

Now
(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
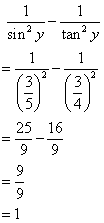
(iii)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore
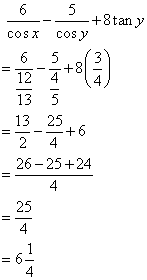
Solution 7
Since ![]() is mid-point of
is mid-point of ![]() so
so ![]()
(i)
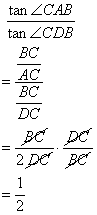
(ii)
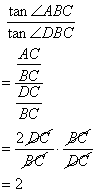
Solution 8
Consider the diagram below:
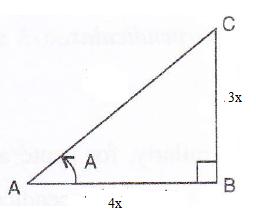
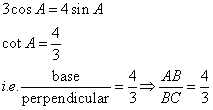
Therefore if length of AB = 4x, length of BC = 3x
Since

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
Therefore
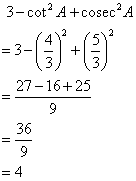
Solution 9
Consider the figure
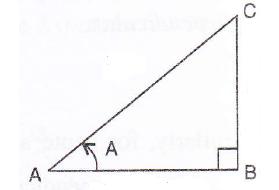
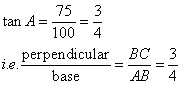
Therefore if length of base = 4x, length of perpendicular = 3x
Since
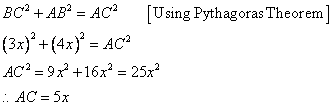
Now
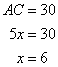
Therefore
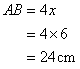
And
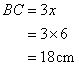
Solution 10
Consider the figure
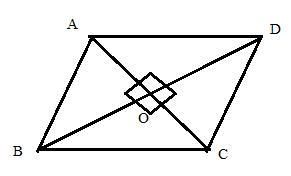
The diagonals of a rhombus bisects each other perpendicularly
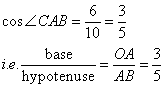
Therefore if length of base = 3x, length of hypotenuse = 5x
Since

Now
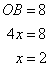
Therefore
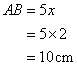
And
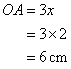
Since the sides of a rhombus are equal so the length of the side of the rhombus ![]()
The diagonals are
Solution 11
Consider the figure below
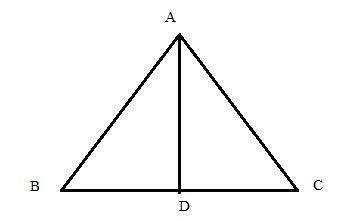
In the isosceles ![]() , the perpendicular drawn from angle
, the perpendicular drawn from angle ![]() to the side
to the side ![]() divides the side
divides the side ![]() into two equal parts
into two equal parts ![]()
Since ![]()

(i)
![]()
(ii)
![]()
(iii)
![]()
![]()
Therefore
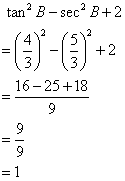
Solution 12
Consider the figure below
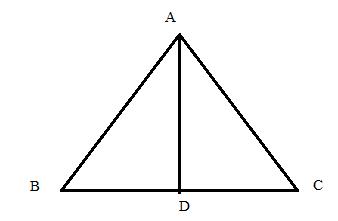
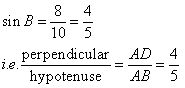
Therefore if length of perpendicular = 4x, length of hypotenuse = 5x
Since

Now
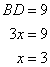
Therefore
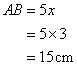
And
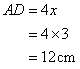
Again
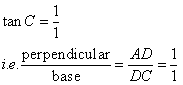
Therefore if length of perpendicular = x, length of base = x
Since

Now
![]()
Therefore
![]()
And
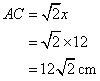
Solution 13
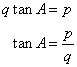
Now
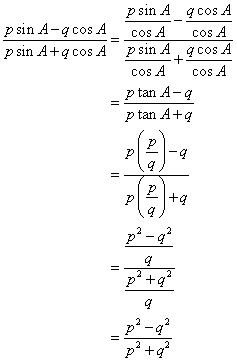
Solution 14
Consider the figure
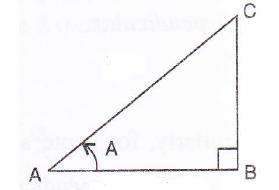
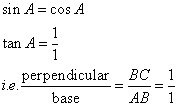
Therefore if length of perpendicular = x, length of base = x
Since

Now
![]()
Therefore
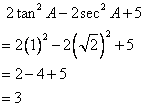
Solution 15
Consider the diagram
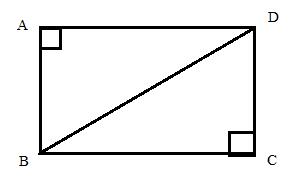
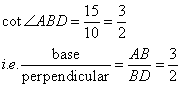
Therefore if length of base = 3x, length of perpendicular = 2x
Since

Now
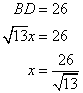
Therefore
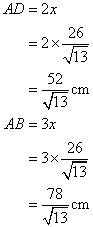
Now
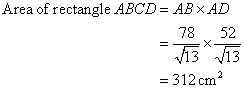

Solution 16
Consider the figure
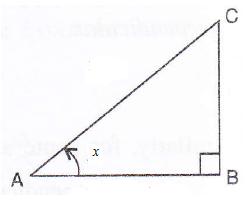
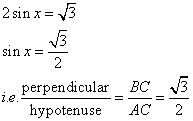
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
(i)
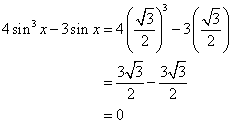
(ii)
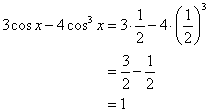
Solution 17
Consider the diagram below:
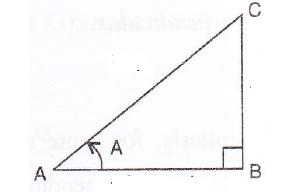
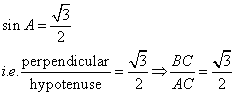
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since
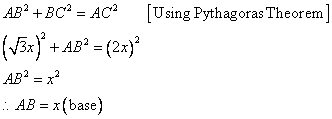
Consider the diagram below:
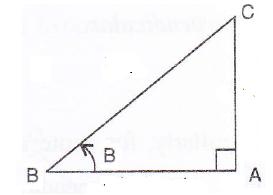
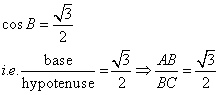
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
Therefore
Solution 18
Consider the figure
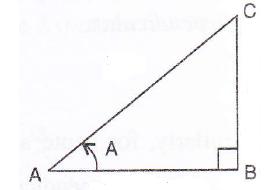
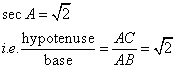
Therefore if length of ![]() , length of
, length of ![]()
Since

Now
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore

Solution 19
![]()
Now
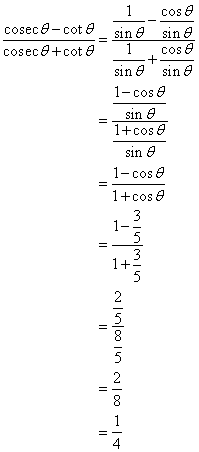
Solution 20
![]()
Squaring both sides

Solution 21
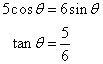
Now
(i)
![]()
(ii)
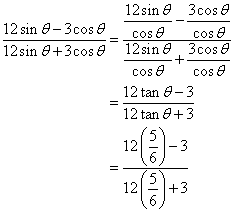
![]()
Solution 22
Consider the given diagram as
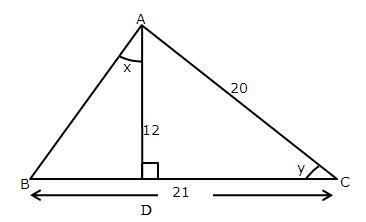
Using Pythagorean Theorem
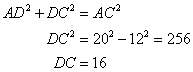
Now
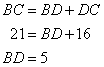
Again using Pythagorean Theorem
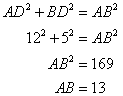
Now
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore