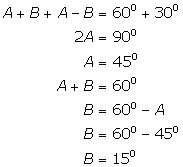Class 9 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 23 - Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios]
Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios] Exercise Ex. 23(A)
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) sin 60o
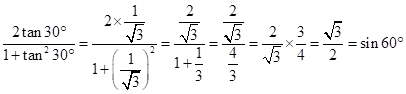
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (ii) 20o
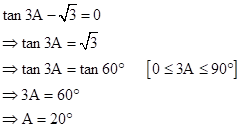
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (iii) 45o
![]()
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iii) 3
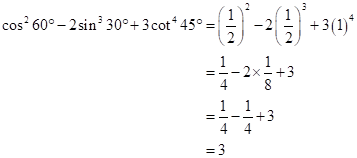
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (i) ![]()
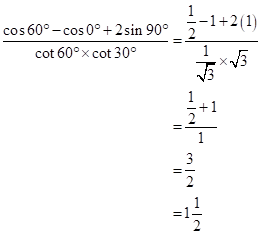
Solution 2
(i)![]()
(ii)![]()
(iii)![]()
(iv)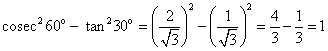
(v)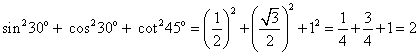
(vi)
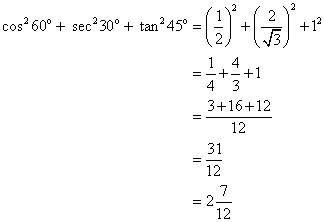
Solution 3
(i) 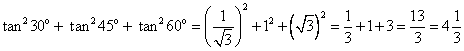
(ii) ![]()
![]()
(iii) 3 sin2 30o + 2 tan2 60o - 5 cos2 45o
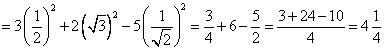
Solution 4
(i)LHS=sin 60o cos 30o + cos 60o. sin 30o
=![]()
(ii)LHS=cos 30o. cos 60o - sin 30o. sin 60o
=![]() =RHS
=RHS
(iii)LHS= cosec2 45o - cot2 45o
=![]() =RHS
=RHS
(iv)LHS= cos2 30o - sin2 30o
=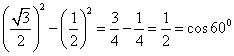 =RHS
=RHS
(v)LHS= 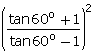
=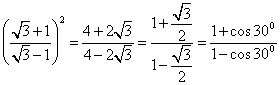 =RHS
=RHS
(vi)LHS= ![]()
=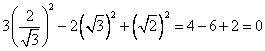 =RHS
=RHS
Solution 5
(i)
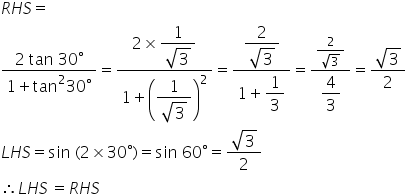
(ii)
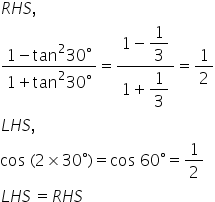
(iii)
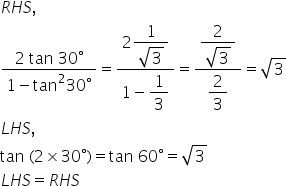
Solution 6
Given that AB = BC = x
![]()
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
(iii) ![]()
Solution 7
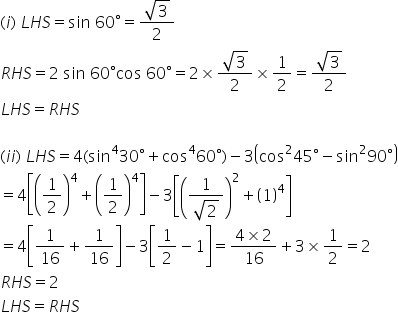
Solution 8
(i)
The angle, x is acute and hence we have, 0 < x
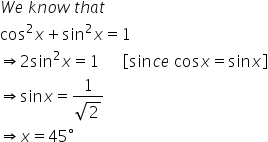
(ii)
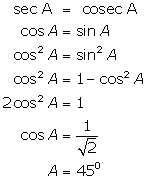
(iii)
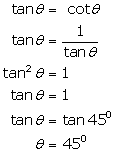
(iv)
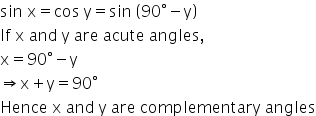
Solution 9
(i)
![]()
if x and y are acute angles,
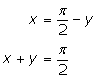
![]()
![]() is false.
is false.
(ii)
![]()
Sec![]() . Cot
. Cot ![]() = cosec
= cosec ![]() is true
is true
(iii)
![]()
Solution 10
(i)
For acute angles, remember what sine means: opposite over hypotenuse. If we increase the angle, then the opposite side gets larger. That means "opposite/hypotenuse" gets larger or increases.
(ii)
For acute angles, remember what cosine means: base over hypotenuse. If we increase the angle, then the hypotenuse side gets larger. That means "base/hypotenuse" gets smaller or decreases.
(iii)
For acute angles, remember what tangent means: opposite over base. If we decrease the angle, then the opposite side gets smaller. That means "opposite /base" gets decreases.
Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios] Exercise Ex. 23(B)
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) cot A
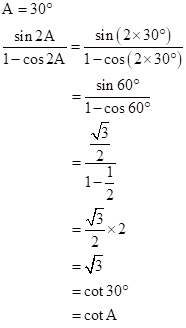
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (i) cot A
![]()
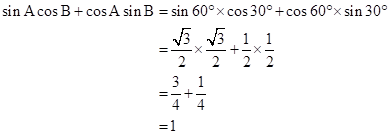
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (iii) sin 3A
![]()
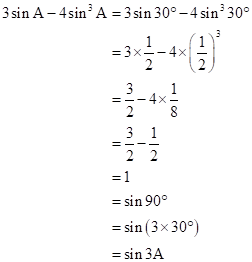
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iv) cos 60o
![]()
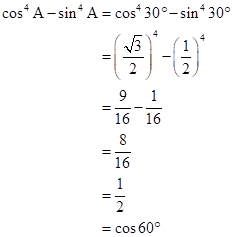
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (i) 1
![]()
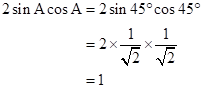
Solution 2
Given A = 60o and B = 30o
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

(iv)
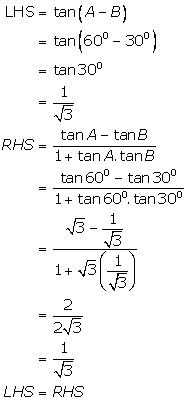
Solution 3
Given A=![]()
(i)
![]()
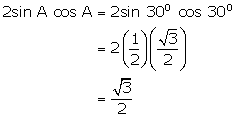
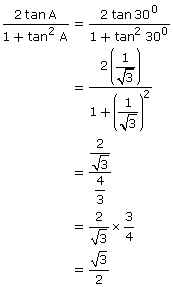
![]()
(ii)
![]()
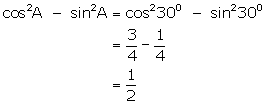
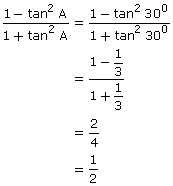
![]()
(iii)
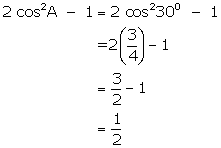
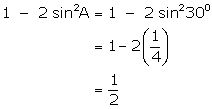
![]()
(iv)
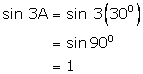
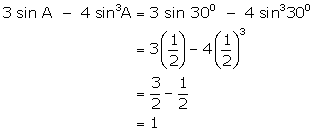
![]()
Solution 4
Given that A = B = 45o
(i)

(ii)

Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios] Exercise Ex. 23(C)
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) 30o
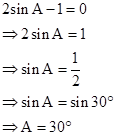
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (i) 90o or 0o
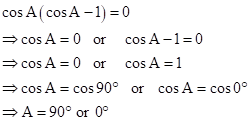
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (ii) 45o
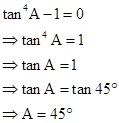
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iii) 10o
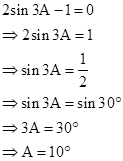
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (iv) 30o
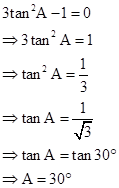
Solution 2
(i)
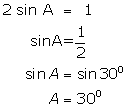
(ii)
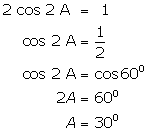
(iii)
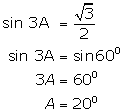
(iv)
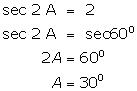
(V)
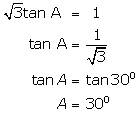
(vi)
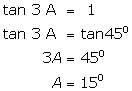
(vii)
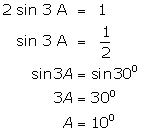
(viii)
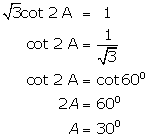
Solution 3
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

(iv)
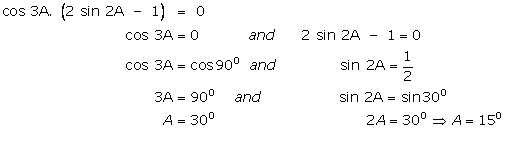
(v)

Solution 4
(i)
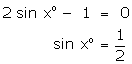
(ii)
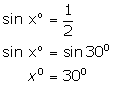
(iii)
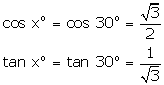
Solution 5
(i)
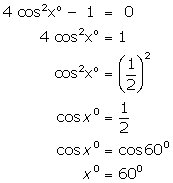
(ii)
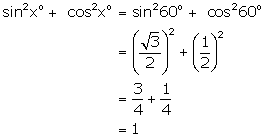
(iii)

Solution 6
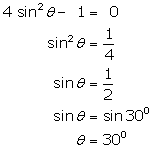
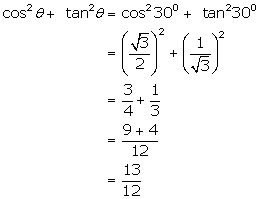
Solution 7
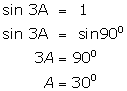
(i)
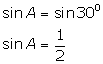
(ii)
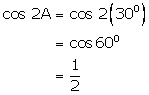
(iii)
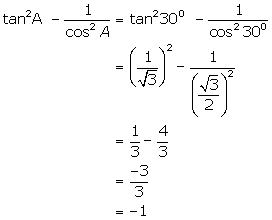
Solution 8
(i)
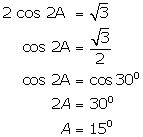
(ii)

(iii)

Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios] Exercise Test Yourself
Solution 1
(i)![]()
(ii)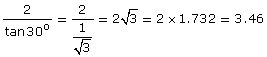
Solution 2
(i) Given that A=![]()

(ii) Given that B=![]()

Solution 3
Given that A = 30o
(i)

(ii)

(iii)
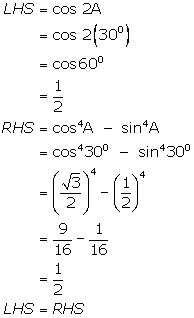
(iv)

(v)
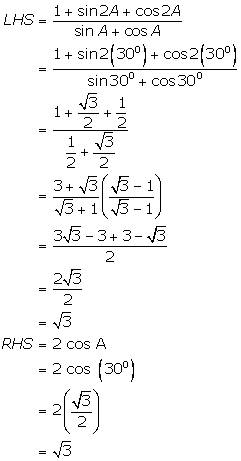
(vi)

(vii)

Solution 4
(i)
Given that x = 30o
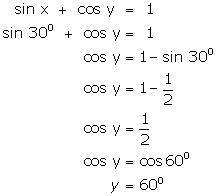
(ii)
Given that B = 90o
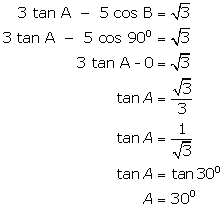
Solution 5
(i)
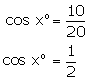
(ii)
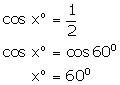
(iii)

(iv)
![]()
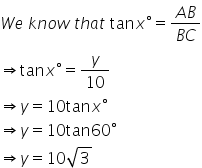
Solution 6
(i)
![]()
(ii)
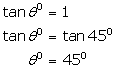
(iii)
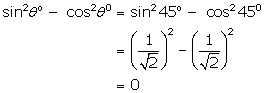
(iv)
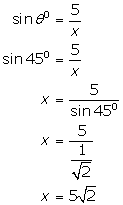
Solution 7
(i)

(ii)
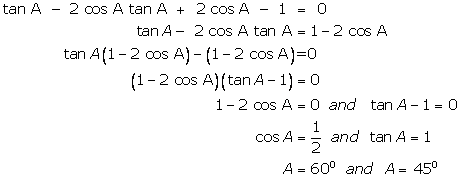
(iii)
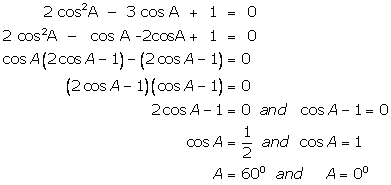
(iv)

Solution 8
(i)
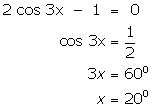
(ii)
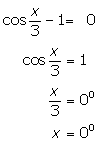
(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(vi)

(vii)

(viii)
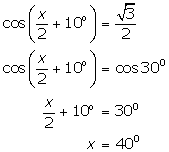
(ix)
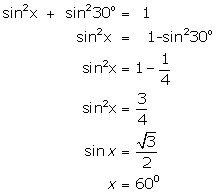
(x)
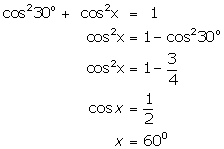
(xi)
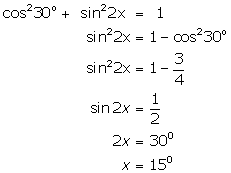
(xii)

Solution 9
(i)
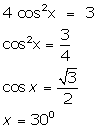
(ii)
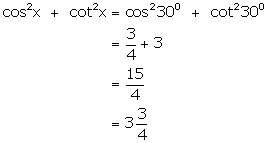
(iii)
![]()
(iv)
![]()
Solution 10
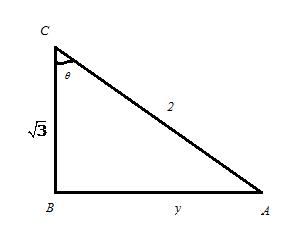
(i)
From![]()
![]()
(ii)
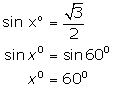
(iii)
![]()
(iv)
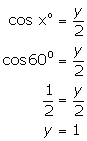
Solution 11

Adding (1) and (2)