Class 9 SELINA Solutions Biology Chapter 4: The Flower
The Flower Exercise Ex. 1
Solution A.1(a)
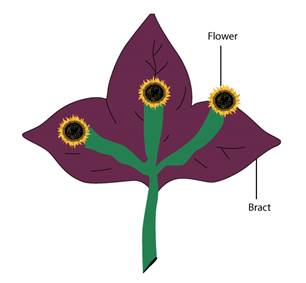
(iv) Large colourful bracts
Solution A.1(b)
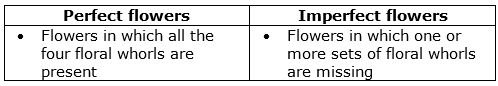
(iv) It has all the four whorls
Solution A.1(c)
(iii) Ovary
Solution A.1(d)
(iii) Ovule
Solution A.1(e)
(iv) Androecium and gynoecium
Solution A.1(f)
(iii) Pedicel
Solution A.1(g)
(iii) Stigma
Solution A.1(h)
(ii) Tepals
Solution A.1(i)
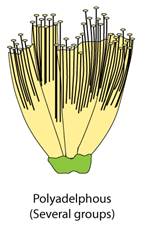
(iii) Polyandrous
Solution A.1(j)
(iv) Hermaphrodite
Solution B.1
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Polyadelphous |
(iv) Bombax |
|
(b) Pollen grains |
(v) Pollen sac |
|
(c) Free petals |
(i) Polypetalous |
|
(d) Non-essential |
(ii) Calyx, corolla |
|
(e) Sweet fragrant fluid |
(iii) Nectar |
Solution B.2
(a) Sepals, Petals, Stamen and Pistil
(b) Staminate (male) flowers and Pistillate (female) flowers
(c) Anther and Filament
(d) Stigma, Style and Ovary
(e) Monadelphous, Diadelphous and Polyadelphous
Solution B.3
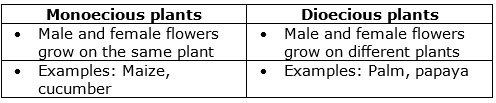
(a) Monoecious plants: Maize and cucumber
(b) Dioecious plants: Palm and papaya
(c) Imperfect flowers: Papaya and palm
(d) Bisexual flowers: Lily and rose
Solution B.4
(a) The floral parts are borne on the thalamus in four whorls.
(b) The collective name of the petal is corolla.
(c) Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls of the flower.
(d) Placenta attaches the ovules to the wall of the ovary.
(e) The sweet fragrant liquid of flowers is termed as nectar.
Solution B.5
(a) Sepals : Calyx :: Petals : Corolla
(b) Stamens : Androecium :: Pistil : Gynoecium
(c) Petals : Polypetalous :: Stamens : Polyandrous
(d) Green petals : Sepaloid :: Coloured sepals : Petaloid
(e) Pollen grains : Anther :: Ovules : Ovary
Solution B.6
|
Flowers |
Type of androecium |
|
(a) China rose |
Monadelphous |
|
(b) Bombax |
Polyadelphous |
|
(c) Pea |
Diadelphous |
Solution C.1
(a) Incomplete flower - If one or more sets of floral structures are missing, the flower is called incomplete flower. E.g. American elm.
(b) Staminate flower - A unisexual flower which contains only the stamens, i.e., male parts of a flower is called male or staminate flower. E.g. Eastern cottonwood.
(c) Pistillate flower - A flower which contains only the carpels, i.e., female parts of a flower is called female or pistillate flower. E.g. Date palm.
(d) Bisexual flower - A flower which contains both stamens and carpels is called bisexual or hermaphrodite flower. E.g. Hibiscus.
Solution C.2
(a) Flower and Inflorescence
|
Flower |
Inflorescence |
|
Flower is a specialized shoot in which the leaves are modified into floral structures. |
Inflorescence is the mode of arrangement of flowers on the axis of the plant. |
(b) Petals and Petaloid tepals
|
Petals |
Petaloid tepals |
|
Petals are non-essential parts of a flower which help in protection of reproductive parts and make the flower attractive for pollination. |
Undifferentiated petals and sepals together form the perianth. When perianth is non-green and brightly coloured, it is called a petaloid. |
Solution C.3
(a) Flower: Flower is a specialized shoot in which the leaves are modified into floral structures.
(b) Inflorescence: Inflorescence is the arrangement of a cluster of flowers on the floral axis.
(c) Placentation: The manner in which the ovules are arranged or attached to the wall of the ovary is called placentation.
(d) Bract: When a flower arises in the axil of a leaf-like structure, the structure is called as bract.
(e) Epicalyx: A series of small sepal-like bracts forming an outer calyx beneath the calyx is called epicalyx.
Solution C.4
(a) Placenta:
Location: Cushion or swollen region in the ovary
Function: Gives origin to ovules
(b) Thalamus:
Location: Tip of the flower stalk
Function: Bears all the parts of the flower
(c) Anther:
Location: Part of the stamen
Function: Produces male gametes or pollen grains
(d) Stigma:
Location: Terminal knob-like part
Function: Serves as the landing place for pollen grains during pollination
Solution D.1
(a) Differences between Monoecious and Dioecious plants:
(b) Differences between Perfect and Imperfect flowers:
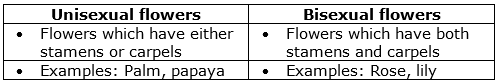
(c) Differences between Unisexual and Bisexual flowers:
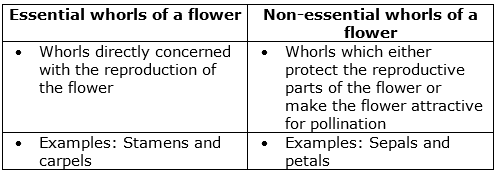
(d) Differences between Essential and Non-essential whorls of a flower:
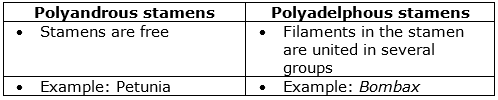
(e) Differences between Polyandrous and Polyadelphous stamens:
Solution D.2
(a) The androecium of pea flower is diadelphous because it has 10 stamens, which are arranged in two separate groups or bundles. The shorter bundle contains 9 stamens that are fused together at their filaments and form a staminal tube. The longer bundle contains a single free stamen.
(b) Ray florets of sunflower are neuters because they do not possess both male and female reproductive structures.
(c) The sepals of Salvia are brightly coloured and showy, attracting insects for pollination. The petals are reduced or absent, making the sepals the most prominent flower of the flower.
Solution D. 3
When a flower arises in the axil of a leaf-like structure, this structure is known as bract. Because bracts are large and brightly coloured structures, they are often mistaken for petals. This helps to attract insects for pollination.
Solution D.4
|
Type of Androecium |
Explanation |
Diagram |
Example of a flower |
|
Monadelphous |
Stamens are united in one group by their filaments but anthers are free |
|
China rose |
|
Diadelphous |
Filaments are united in two bundles |
|
Pea |
|
Polyadelphous |
Filaments are united in several groups |
|
Bombax |
Solution E.1
1 - Anther
2 - Filament
3 - Placenta
4 - Ovule
5 - Stigma
6 - Style
7 - Ovary
8 - Petal
9 - Sepal
10 - Receptacle / Thalamus
Solution E.2
(a) Figure A represents stamen. Stamens collectively form Androecium.
(b) Contents of the pollen sacs in B are male gametes.
(c) The contents of the pollen sacs would come out through agents like air, wind, insects leading to pollination in flowers.
Solution E.3
|
|
Kind of androecium |
Example of a flower |
|
A |
Polyandrous |
Petunia |
|
B |
Monadelphous |
China rose |
|
C |
Diadelphous |
Pea |
|
D |
Polyadelphous |
Bombax |
Solution E.4
(a) Anther and filament are two important parts of the male reproductive organ (stamen).
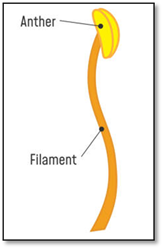
(b) Stigma, style, ovary and ovule are four important parts of the female reproductive organ (pistil).
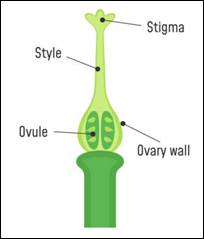
(c) Stamens are collectively named as androecium while pistils (carpels) are collectively referred to as the gynoecium.
(d) Pollen grains are produced in the anthers (stamen) and ovules are formed in the ovary (pistil).
(e) Ovary transforms into a fruit while the ovules turn into seeds respectively.
Solution E.5
(a) Polysepalous calyx

(b) Gamosepalous calyx

(c) Polypetalous corolla
(d) Gamopetalous corolla

(e) Bracteate flower