Class 9 SELINA Solutions Biology Chapter 8: Five Kingdom Classification
Five Kingdom Classification Exercise Ex. 1
Solution A.1(a)
(iv) vertebrates and invertebrates
Solution A.1(b)
In this question, all options are correct because:
(i) Mushroom, Yeast, Fern - Fungi (Fern belongs to Pteridophytes)
(ii) Paramecium, Euglena, Sponge - Protista (Sponge belongs to Porifera)
(iii) Starfish, Roaches, Dogfish - Pisces (Starfish belongs to Echinodermata)
(iv) Bat, Parrot, Oyster - Vertebrates (Oyster belongs to Mollusca)
Solution A.1(c)
(iii) Rana tigrina
Solution A.1(d)
(iv) Mule is neither a donkey nor a horse
Solution A.1(e)
(iv) Genus
Solution A.1(f)
(iii) Monera
Solution A.1(g)
(ii) Euglena
Solution A.1(h)
(i) Gymnosperms
Solution A.1(i)
(iv) Phyllids
Solution A.1(j)
(ii) Dogfish
Solution B.1
Carolus Linnaeus had introduced the binomial system of naming living beings.
Solution B.2
The two characters common to dog, humans, squirrel, bat, camel and monkey are:
(c ) external ears
(d) give birth to young ones
Solution B.3
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1.Pine |
(iv) Gymnosperm (v) Plantae |
|
2. Earthworm |
(vi) Animalia |
|
3. Bread mould |
(i) Fungi |
|
4. Amoeba |
(vii) Protista |
|
5. Moss |
(v) Plantae (viii) Bryophyta |
|
6.Bacteria |
(ii) Monera (iii) Prokaryote |
Solution B.4
(a) Vertebrates
(b) Mammals
(c) Insects
(d) Aves
Solution B.5
The following animals are invertebrates:
• Housefly
• Silverfish
• Jellyfish
• Sponge
Solution B.6
The following animals (belonging to different classes) breathe by means of lungs but have no external ears (pinnae):
1. Snake (Class - Reptilia)
2. Frog (Class - Amphibia)
3. Peacock (Class - Aves)
Solution B.7
(i) Amoeba - Nucleus, tentacle, food vacuole
(ii) Hydra - Invertebrata, Cnidaria, Crustacea
(iii) Fish - Gills, paired fins, ear drum
(iv) Earthworm - Invertebrata, Annelida, Insecta
(v) Grasshopper - Wings, trachea, proboscis (No term can be underlined because grasshoppers have a tracheal system, two pairs of wings and tubular mouth part called proboscis for feeding and sucking)
(vi) Butterfly - Insecta, Invertebrata, Mollusca
(vii) Whale - Gills, mammary glands, fat under the skin
(viii) Pigeon - Feathers, wings, hair
(ix) Monkey - External ear, sweat glands, lateral line
(x) Bat - Aves, Mammalia, Chordata
Solution C.1
(a) Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia
(b) Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
(c) Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca and Echinodermata
(d) Pisces, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia
(e) Bony fishes and Cartilaginous fishes
Solution C.2
(a) Species: A species is defined as a group of organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of interbreeding among themselves to produce fertile young ones.
(b) Clitellum: Clitellum is a short, cylindrical band of thickened glandular tissue in the body wall of certain annelids, such as earthworms and leeches.
(c) Moulting: The casting off and the regrowing of the exoskeleton is called moulting.
(d) Diaphragm: The thin muscle below the lungs and the heart that separates the thorax and the abdomen internally is called the diaphragm.
(e) Nocturnal animals: Animals that are active during the night are called nocturnal animals.
Solution C.3
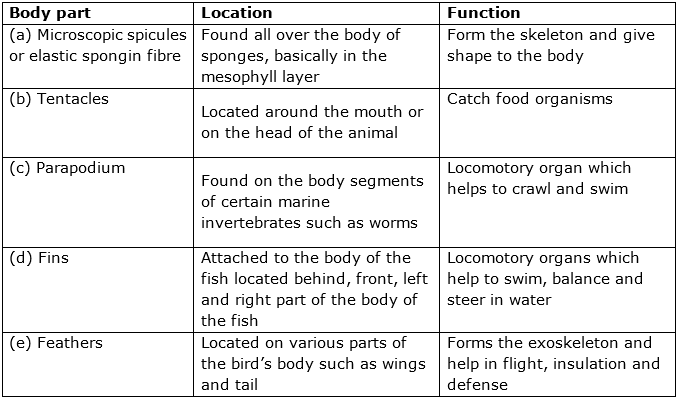
Solution C.4
Phylum ![]() Class
Class ![]() Order
Order ![]() Family
Family ![]() Genus
Genus ![]() Species
Species
Solution C.5
Ficus religiosa (Peepal)
Zea mays (Maize)
Bombyx mori (Silkmoth)
Solution C.6
|
Column I (Group) |
Column II (Animal) |
|
Annelida |
Earthworm |
|
Porifera |
Sponge |
|
Mollusca |
Octopus |
|
Reptilia |
Snake |
|
Pisces |
Trout |
|
Mammal |
Rabbit |
Amphibia from Column I and Pigeon from column II are left out. They do not match as Pigeon comes under Class Aves and not Class Amphibia.
Solution C.7
|
Man |
Domestic cat |
Peepal tree |
|
Homo sapiens |
Felis domesticus |
Ficus religiosa
|
Solution C.8
In science, people from different countries with different languages have to read about each others research. So, it was necessary to eliminate any possible confusion created by local names. Scientific names are based on certain rules which are universal. They are unique and can be used to identify an organism anywhere around the world. That is why, scientific names of living beings are considered better than their common names.
Solution C.9
According to the 'Two-Kingdom Classification', proposed by Carolus Linnaeus in 1758, living organisms were classified into two broad kingdoms, Plants and Animals.
The drawbacks in classifying organisms under the old two kingdom classification are:
1. Bacteria were kept in Kingdom Plantae. These organisms have no chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Bacteria do not have a definite nucleus nor a nuclear membrane nor chromosomes.
2. Fungi were kept in Kingdom Plantae. Bread mould is a multicellular fungi. However, it does not possess roots, stem and leaves, lacks chlorophyll and does bear any flowers, fruits and seeds like plants.
Solution C.10
Species means an organism of a particular kind whose members can interbreed among themselves to produce fertile young ones.
All humans on the earth today may differ widely in their facial features, colour, height, etc. Yet, they belong to a single species Homo sapiens because they can interbreed among themselves and produce a normal offpsring.
Solution C.11
(a) Insecta and Arachnida
|
Insecta |
Arachnida |
|
Have three pairs of legs |
Have four pairs of legs |
(b) Flatworm and Roundworm
|
Flatworm |
Roundworm |
|
Dorso-ventrally flattened |
Cylindrical in shape and are tapered at both ends
|
Solution C.12
(a) Insects and Birds
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Have wings |
Insects |
Birds |
|
Invertebrates |
Vertebrates |
|
(b) Whales and Fishes
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Aquatic |
Whales |
Fishes |
|
Have lungs for breathing |
Have gills for breathing
|
|
(c) Snakes and Earthworms
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Do not have any limbs |
Snakes |
Earthworm |
|
Vertebrates
|
Invertebrates
|
|
(d) Bat and Pigeon
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Breathe through lungs |
Bat |
Pigeon |
|
Have external ears |
Have internal ears |
|
(e) Cuttlefish and Dogfish
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Marine animals |
Cuttlefish |
Dogfish |
|
Invertebrates
|
Vertebrates
|
|
(f) Wall lizard and Frog
|
Similarity |
Difference |
|
|
Cold-blooded animals |
Wall lizard |
Frog |
|
Completely adapted to life on land
|
Live partly on land and partly in water |
|
Solution D.1
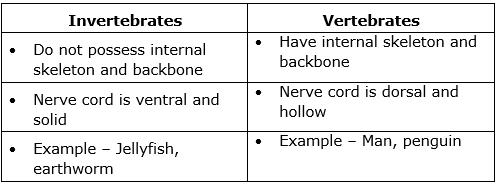
(a) Differences between invertebrates and vertebrates:
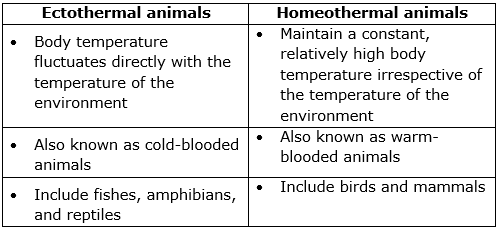
(b) Differences between ectothermal and homeothermal animals:
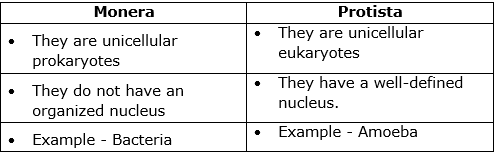
(c) Differences between Monera and Protista:
(d) Differences between bryophytes and pteridophytes:
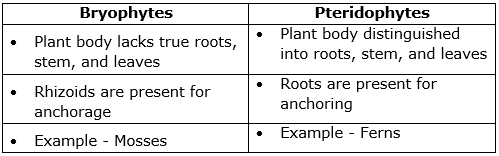
(e) Differences between roundworms and ringed worms:
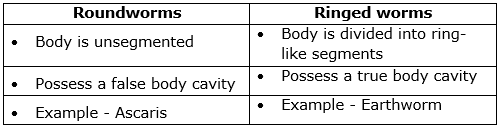
Solution D.2
|
Cold-blooded animals |
Warm-blooded animals |
|
These animals cannot maintain their body temperature. Their body temperature is regulated by the external environment. |
Animals whose body temperature is kept relatively constant by internal mechanisms. |
|
E.g. Insects, Amphibians |
E.g. Birds, Mammals |
Solution E.1
(a) Toadstool (mushroom).
(b) Kingdom Fungi.
(c) Characteristics of fungi that differentiate it from plants:
1. Fungi lack chlorophyll while plants possess chlorophyll.
2. Fungi are multinucleate while plants are uninucleate.
3. Fungi have a cell wall made of chitin while plants have a cell wall made of cellulose.
Solution E.2
The organism shown in a peacock.
(a) Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata (Vertebrata)
Class: Aves
(b) Significant characteristics of organisms belonging to class Aves:
1. They have exoskeleton made of feathers.
2. Their body is streamlined and the skeleton is light to facilitate flying.
3. They have scaly legs and four-chambered heart.
(c) Key features phylum Chordata (Vertebrata):
1. They have a well-developed vertebral column.
2. They have a head, trunk and two pairs of appendages.
Vertebrates are divided into five classes:
1. Pisces
2. Amphibia
3. Reptilia
4. Aves
5. Mammalia
Solution E.3
(a) Phylum Cnidaria/Coelenterata
(b) The cnidarians are found in water, mostly in seas while few forms are found in fresh water.
(c) A - Sea anemone, B - Hydra, C - Jelly fish, D - Coral
(d) The cavity enclosed by the two-layered body wall is coelenteron.
(e) Locomotory structure shown in the figure is tentacle.
