Class 9 SELINA Solutions Biology Chapter 16: Diseases: Cause And Control
Diseases: Cause And Control Exercise Ex. 1
Solution A.1(a)
(iii) pandemic
Solution A.1(b)
(iv) AIDS
Solution A.1(c)
(iii) Anopheles mosquito
Solution A.1(d)
(iv) Entamoeba
Solution A.1(e)
(iv) Tuberculosis
Solution A.1(f)
(ii) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Solution A.1(g)
(iii) Thalassemia
Solution A.1(h)
(ii) Protozoan
Solution A.1(i)
(ii) Tsetse fly
Solution A.1(j)
(iii) Liver
Solution B.1
(a) Pandemic diseases are widely distributed worldwide.
(b) Plague is an epidemic disease. (Yellow fever is an endemic disease.)
(c) Chicken pox is caused by a virus. (Tuberculosis is caused by a bacterium.)
(d) Asthma/Hay fever is a kind of an allergy.
(e) Ascariasis is caused by a roundworm. (Taeniasis is caused by a tapeworm.)
Solution B.2
(a) HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
(b) AIDS: Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
(c) BCG: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
(d) COVID-19: Coronavirus disease-19
(e) RNA: Ribonucleic acid
Solution B.3
(a) F (False). Filariasis is transmitted by the Culex mosquito.
(b) T (True)
(c) F (False). BCG vaccine is used for tuberculosis.
(d) F (False). Louis Pasteur discovered a cure for rabies.
(e) F (False). AIDS is caused by a virus.
(f) T (True)
(g) T (True)
(h) F (False). Chicken pox and hepatitis are viral diseases.
(i) T (True)
(j) F (False). AIDS is caused by HIV virus.
(k) T (True)
(l) F (False). Smallpox has been eradicated from India.
(m) F (False). The disease filariasis is caused by the filarial worm Wuchereria bancrofti.
Solution B.4
(a) BCG
(b) Lungs
(C) AIDS
(d) Virus
(e) Elephantiasis
Solution B.5
(a) Endemic diseases, Epidemic diseases, Pandemic diseases and Sporadic diseases
(b) Communicable or Infectious diseases and Non-communicable or Non-infectious diseases
(c) Arthritis and Cataract
(d) Malaria, Sleeping sickness and Amoebic dysentery
(e) Ascariasis, Taeniasis and Filariasis
Solution B.6
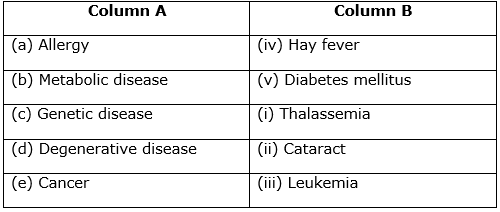
Solution B.7
(a) April 7 : World Health Day :: December 1: World AIDS Day
(b) Malaria : Plasmodium :: Filariasis : Wuchereria bancrofti
(c) Hepatitis : Liver :: Tuberculosis : Lungs
(d) Mumps : Viral disease :: Typhoid : Bacterial disease
(e) Covid-19 : Pandemic :: Yellow fever : Endemic
Solution B.8
(a) Malaria (Rest are diseases caused by bacteria)
(b) Ascariasis (Rest are diseases caused by viruses)
(c) Hepatitis (Rest are diseases caused by parasitic worms)
(d) Depression (Rest are nutritional deficiency diseases)
(e) Cataract (Rest are diseases caused by protozoa)
Solution C.1
(a) Infection is the transmission of disease-causing pathogens from one person to another.
(b) Pathogen is defined as an organism that has the potential to cause infectious diseases in its host.
(c) Incubation period is the period between the entry of germs and the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease.
(d) Disease is a departure from normal health through structural or functional disorder of the body.
(e) A vaccine is a biological preparation of a weakened or killed pathogen which stimulates the formation of antibodies and develops immunity against a particular disease.
Solution C.2
(a) Cholera: Vibrio cholerae
(b) Typhoid: Salmonella typhi
(c) Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
(d) Taeniasis: Taenia solium
(e) Filariasis: Wuchereria bancrofti
Solution C.3
Causative germ of AIDS:
HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus)
Transmission of AIDS:
(a) Sexual intercourse
(b) Mother to child transmission
(c) Contaminated blood transfusions
Solution D.1
(a) BCG: It is a vaccine which is effective against the bacterial disease tuberculosis (TB). It develops immunity to TB. BCG stands for Bacillus Calmette Guerin.
(b) Incubation period: It is the period between the entry of germs and the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. Example: Incubation period of pneumonia is 1-3 days.
(c) Chicken pox: It is a viral disease caused by the Herpes Varicella zoster virus. It spreads rapidly by close contact with an infected person. A live attenuated vaccine containing Varicella is administered to children of 12-18 months for active immunisation.
(d) Hepatitis A: It is a viral disease caused by Hepatitis A virus which results in inflammation of the liver. It has an incubation period of 14-45 days. It is mainly transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Solution D.2
|
Disease |
Causative agent |
Symptoms |
Prevention |
|
Malaria |
Protozoan, Plasmodium |
Chills, high fever, profuse sweating, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue and body pain |
Destruction of mosquitoes at all stages and avoid mosquito bites by using mosquito nets or repellents |
|
Chicken pox |
Virus, Varicella zoster |
Highly irritating rashes near the chest and back, gradually spreading to the arms, legs, face and head |
Active immunisation by administering live attenuated vaccine containing Varicella |
|
Tuberculosis |
Bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
Persistent cough, afternoon fever, bloody mucus, loss of weight, fatigue and chest pain |
BCG vaccination and isolation of the patient |
Solution D.3
The different ways in which infectious diseases can spread are as follows:
- Direct contact: Person to person, animal to person and expected mother to child
- Indirect contact: Doorknob, phone, etc.
- Droplet transmission: Sneezing, coughing, etc.
- Particle transmission: Air particles can transfer infectious diseases
- Bites and Stings: Mosquitoes, lice, ticks, etc.
- Food Contamination: Food, beverages, etc.
Solution D.4
|
NON-INFECTIOUS DISEASES |
CAUSE OF THE DISEASE |
|
Asthma |
Allergy |
|
Cataract |
Ageing |
|
Beri-Beri |
Nutritional deficiency |
|
Cancer |
Carcinogens like chemicals, tobacco smoking, pollution etc. |
Solution D.5
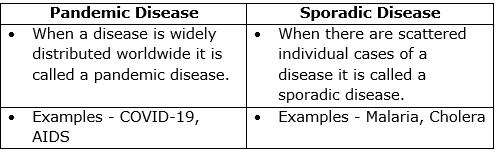
(a) Differences between pandemic and sporadic diseases:
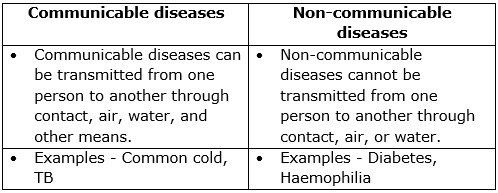
(b) Differences between communicable and non-communicable diseases:
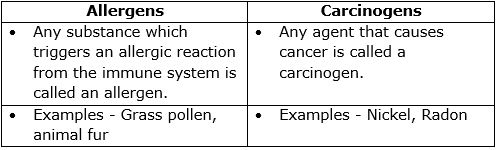
(c) Differences between allergens and carcinogens:
(d) Differences between endemic and epidemic diseases:
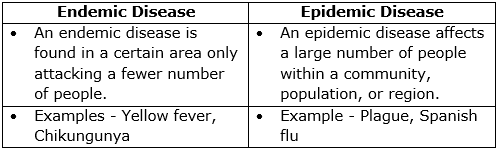
(e) Differences between pathogen and vector:
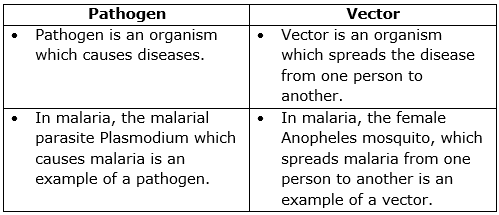
Solution D.6
Preventive measures advised by WHO to minimize the chances of COVID-19:
(1) Stay at home.
(2) Wash hands regularly with soap and water.
(3) Avoid crowded places.
(4) Wear masks in public places and maintain social distancing.
(5) Get vaccinated.
Solution E.1
(a) The microorganism is HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
(b) It belongs to the category of viruses.
(c) 1 - Viral protein, 2 - Protein covering, 3 - RNA
(d) Yes, it causes a disease called Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
(e) Transmission of AIDS:
1. Sexual intercourse between a man and a woman, when either of the two is infected.
2. Contaminated blood transfusions.
Solution E.2
(a) The animal depicted is tapeworm.
(b) It belongs to phylum Platyhelminthes.
(c) The disease caused by tapeworm is taeniasis.
(d) The scientific name of tapeworm is Taenia solium.
(e) Cow and pig are two common hosts (animals) for tapeworm.
