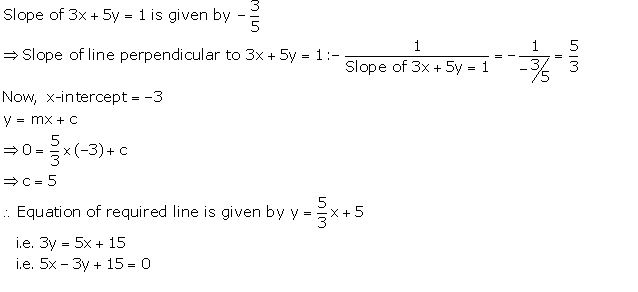Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 14 - Equation of a Line
Equation of a Line Exercise TEST YOURSELF
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (iii) 6
The line passes through the point (3, 3).
Substituting x = 3 and y = 3 in the equation, we have
5(3) – k(3) + 3 = 0
⇒ k = 6
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (i) 30°
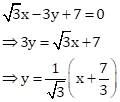
Therefore, Slope = ![]()
⇒ tan θ = tan 30°
⇒ Inclination = θ = 30°
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (ii) A is true, R is true
Since, we have two straight lines.
To check whether these two lines are parallel or not, we need to find their slopes.
And, if the slopes are equal, the lines will be parallel to each other.
Hence, assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is also true.
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (ii) A is true, R is true
The lines are:
y = x + 4 …. (I)
![]() … (II)
… (II)
Slope of line 1 = m1 = 1 = tan θ1
⇒θ1 = 45°
Slope of line 2 = m2 = ![]() = tan θ2
= tan θ2
⇒θ2 = 60°
Here, θ1 ≠ θ2
So, the lines are not parallel and thus intersecting.
Hence, A is true and R is also true.
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (ii) –4
4x + 3y = 84 … (I)
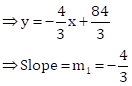
3x + ky + 7 = 0 … (II)
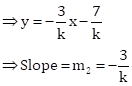
As the lines are perpendicular to each other.
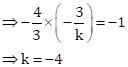
Solution 1(f)
Correct option: (i) (0, 5)
As the line 5x + 3y = 15 meets y-axis at point P.
So, x-coordinate of point P is 0.
As x = 0, we have
5(0) + 3y = 15
⇒ y = 5
Hence, P = (0, 5).
Solution 1(g)
Correct option: (iv) –1
Slope of diagonal AC ![]()
Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other.
⇒ Slope of AC × Slope of BD = –1
![]()
Solution 1(h)
Correct option: (i) 1
Line AB is perpendicular to x-axis.
As OP bisects angle O.
⇒∠X’OP = 45°
Inclination of line OP is (180° + 45°)
Slope of line OP = tan (180° + 45°) = tan 45° = 1
Solution 1(i)
Correct option: (i) A= (6, 0) and B = (0, –4)
As the line 2x – 3y = 12 meets x-axis at point A, its y-coordinate is 0.
At y = 0, we have
2x – 3(0) = 12
⇒ x = 6
⇒ A = (6, 0)
As the line 2x – 3y = 12 meets y-axis at point B, its x-coordinate is 0.
At x = 0, we have
2(0) – 3y = 12
⇒ y = –4
⇒ B = (0, –4)
Solution 2
Using section formula, the co-ordinates of the point P are

3x + 5y = 7
![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
As the required line is parallel to the line 3x + 5y = 7,
Slope of the required line = Slope of the given line =![]()
Thus, the equation of the required line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 3 = ![]() (x - 11)
(x - 11)
5y + 15 = -3x + 33
3x + 5y = 18
Solution 3
Using section formula, the co-ordinates of the point P are

The equation of the given line is
5x - 3y = 4
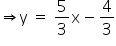
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since, the required line is perpendicular to the given line,
Slope of the required line = 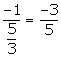
Thus, the equation of the required line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
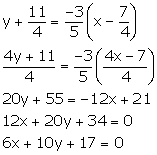
Solution 4
Point P lies on y-axis, so putting x = 0 in the equation 5x + 3y + 15 = 0, we get, y = -5
Thus, the co-ordinates of the point P are (0, -5).
x - 3y + 4 = 0 ![]()
Slope of this line =![]()
The required equation is perpendicular to given equation x - 3y + 4 = 0.
![]() Slope of the required line =
Slope of the required line = 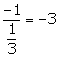
(x1, y1) = (0, -5)
Thus, the required equation of the line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 5 = -3(x - 0)
3x + y + 5 = 0
Solution 5
(i) Slope of PQ = ![]()
Equation of the line PQ is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 4 = -1(x + 1)
y - 4 = -x - 1
x + y = 3
(ii) For point A (on x-axis), y = 0.
Putting y = 0 in the equation of PQ, we get,
x = 3
Thus, the co-ordinates of point A are (3, 0).
For point B (on y-axis), x = 0.
Putting x = 0 in the equation of PQ, we get,
y = 3
Thus, the co-ordinates of point B are (0, 3).
(iii) M is the mid-point of AB.
So, the co-ordinates of point M are
![]()
Solution 6

Solution 7
The given line is
x = 3y + 2 ...(1)
3y = x - 2
![]()
Slope of this line is ![]() .
.
The required line intersects the given line at right angle.
![]() Slope of the required line =
Slope of the required line =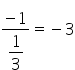
The required line passes through (0, 0) = (x1, y1)
The equation of the required line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = -3(x - 0)
3x + y = 0 ...(2)
Point X is the intersection of the lines (1) and (2).
Using (1) in (2), we get,
9y + 6 + y = 0
![]()
![]()
Thus, the co-ordinates of the point X are ![]() .
.
Solution 8
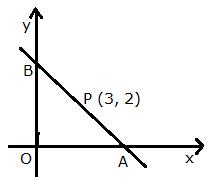
Let the line intersect the x-axis at point A (x, 0) and y-axis at point B (0, y).
Since, P is the mid-point of AB, we have:

Thus, A = (6, 0) and B = (0, 4)
Slope of line AB = ![]()
Let (x1, y1) = (6, 0)
The required equation of the line AB is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x - 6)
(x - 6)
3y = -2x + 12
2x + 3y = 12
Solution 9
7x + 6y = 71 ![]() 28x + 24y = 284 ...(1)
28x + 24y = 284 ...(1)
5x - 8y = -23 ![]() 15x - 24y = -69 ...(2)
15x - 24y = -69 ...(2)
Adding (1) and (2), we get,
43x = 215
x = 5
From equation 5x - 8y = -23,
8y = 5x + 23
8y = 25 + 23
8y = 48
![]() y = 6
y = 6
Thus, the required line passes through the point (5, 6).
4x - 2y = 1
2y = 4x - 1
y = 2x -![]()
Slope of this line = 2
Slope of the required line = ![]()
The required equation of the line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 6 = ![]() (x - 5)
(x - 5)
2y - 12 = -x + 5
x + 2y = 17
Solution 10
Let A = (-2, 3) and B = (4, 1)
Slope of AB = m1 = ![]()
Slope of the given line 3x = y + 1 is 3 = m2.
![]()
Hence, the line through points A and B is perpendicular to the given line.
Equation of line AB is
y - y1 = m1(x - x1)
y - 3 = ![]() (x + 2)
(x + 2)
3y - 9 = -x - 2
x + 3y = 7 ...(1)
Given line is 3x = y +1 ...(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get,
x = 1 and y = 2
So, the two lines intersect at point P = (1, 2).
The co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB are
![]()
Hence, the line 3x = y + 1 bisects the line segment joining the points A and B.
Solution 11
x cos ![]() + y sin
+ y sin ![]() = 2
= 2
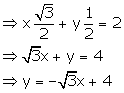
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of a line which is parallel to this given line = ![]()
Let (4, 3) = (x1, y1)
Thus, the equation of the required line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 3 = ![]() (x - 4)
(x - 4)
![]()
Solution 12
(k - 2)x + (k + 3)y - 5 = 0 ....(1)
(k + 3)y = -(k - 2)x + 5
y =![]()
Slope of this line = m1 = ![]()
(i) 2x - y + 7 = 0
y = 2x + 7
Slope of this line = m2 = 2
Line (1) is perpendicular to 2x - y + 7 = 0.

(ii) Line (1) is parallel to 2x - y + 7 = 0.
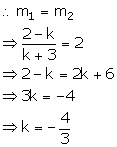
Solution 13
Slope of BC = ![]()
Equation of the line BC is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 2 = ![]() (x + 1)
(x + 1)
4y + 8 = 3x + 3
3x - 4y = 5....(1)
(i) Slope of line perpendicular to BC = 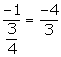
Required equation of the line through A (0, 5) and perpendicular to BC is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 5 = ![]() (x - 0)
(x - 0)
3y - 15 = -4x
4x + 3y = 15 ....(2)
(ii) The required point will be the point of intersection of lines (1) and (2).
(1) ![]() 9x - 12y = 15
9x - 12y = 15
(2) ![]() 16x + 12y = 60
16x + 12y = 60
Adding the above two equations, we get,
25x = 75
x = 3
So, 4y = 3x - 5 = 9 - 5 = 4
y = 1
Thus, the co-ordinates of the required point is (3, 1).
Solution 14
(i) A = (2, 3), B = (-1, 2), C = (3, 0)
(ii) Slope of BC = ![]()
Slope of required line which is parallel to BC = Slope of BC =![]()
(x1, y1) = (2, 3)
The required equation of the line through A and parallel to BC is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 3 = ![]() (x - 2)
(x - 2)
2y - 6 = -x + 2
x + 2y = 8
Solution 15
P is the mid-point of AB. So, the co-ordinate of point P are
![]()
Q is the mid-point of AC. So, the co-ordinate of point Q are
![]()
Slope of PQ = ![]()
Slope of BC = ![]()
Since, slope of PQ = Slope of BC,
![]() PQ || BC
PQ || BC
Also, we have:
Slope of PB = 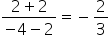
Slope of QC =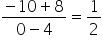
Thus, PB is not parallel to QC.
Hence, PBCQ is a trapezium.
Solution 16
(i) Let the co-ordinates of point A (lying on x-axis) be (x, 0) and the co-ordinates of point B (lying y-axis) be (0, y).
Given, P = (-4, -2) and AP: PB = 1:2
Using section formula, we have:
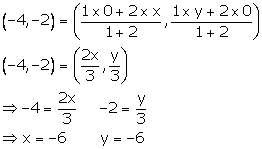
Thus, the co-ordinates of A and B are (-6, 0) and (0, -6).
(ii) Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of the required line perpendicular to AB = ![]()
(x1, y1) = (-4, -2)
Required equation of the line passing through P and perpendicular to AB is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 2 = 1(x + 4)
y + 2 = x + 4
y = x + 2
Solution 17
The required line intersects x-axis at point A (-2, 0).
Also, y-intercept = 3
So, the line also passes through B (0, 3).
Slope of line AB = ![]() = m
= m
(x1, y1) = (-2, 0)
Required equation of the line AB is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x + 2)
(x + 2)
2y = 3x + 6
Solution 18
The required line passes through A (2, 3).
Also, x-intercept = 4
So, the required line passes through B (4, 0).
Slope of AB = ![]()
(x1, y1) = (4, 0)
Required equation of the line AB is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x - 4)
(x - 4)
2y = -3x + 12
3x + 2y = 12
Solution 19
Equation of the line AB is y = x + 1
Slope of AB = 1
Inclination of line AB = ![]() (Since, tan 45o = 1)
(Since, tan 45o = 1)
![]()
Equation of line CD is y = ![]() x - 1
x - 1
Slope of CD = ![]()
Inclination of line CD = 60o (Since, tan 60o =![]() )
)
![]()
Using angle sum property in ![]() PQR,
PQR,
![]()
Solution 20
Given, P divides the line segment joining A (-2, 6) and B (3, -4) in the ratio 2: 3.
Co-ordinates of point P are

Slope of the required line = m =![]()
The required equation of the line is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 2 = ![]() (x - 0)
(x - 0)
2y - 4 = 3x
2y = 3x + 4
Solution 21
Let A = (6, 4) and B = (7, -5)
Slope of the line AB = ![]()
(x1, y1) = (6, 4)
The equation of the line AB is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 4 = -9(x - 6)
y - 4 = -9x + 54
9x + y = 58 ...(1)
Now, given that the ordinate of the required point is -23.
Putting y = -23 in (1), we get,
9x - 23 = 58
9x = 81
x = 9
Thus, the co-ordinates of the required point is (9, -23).
Solution 22
Given points are A(7, -3) and B(1, 9).
(i) Slope of AB = ![]()
(ii) Slope of perpendicular bisector of AB 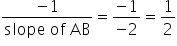
Mid-point of AB = ![]() =(4, 3)
=(4, 3)
![]() Equation of perpendicular bisector is:
Equation of perpendicular bisector is:
y - 3 = ![]() (x - 4)
(x - 4)
2y - 6 = x - 4
x - 2y + 2 = 0
(iii) Point (-2, p) lies on x - 2y + 2 = 0.
![]() -2 - 2p + 2 = 0
-2 - 2p + 2 = 0
![]() 2p = 0
2p = 0
![]() p = 0
p = 0
Solution 23
(i) Let the co-ordinates be A(x, 0) and B(0, y).
Mid-point of A and B is given by ![]()

(ii) Slope of line AB, m = ![]()
(iii) Equation of line AB, using A(4, 0)
![]()
2y = 3x - 12
Solution 24
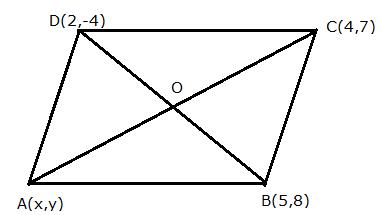
In parallelogram ABCD, A(x, y), B(5, 8), C(4, 7) and D(2, -4).
The diagonals of the parallelogram bisect each other.
O is the point of intersection of AC and BD.
Since O is the midpoint of BD, its coordinates will be
![]()
(i)
Since O is the midpoint of AC also,
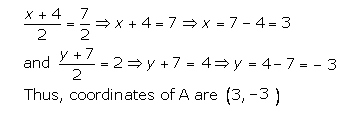
(ii)
Slope of BD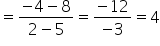
Therefore, the equation of BD is given by
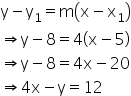
Solution 25
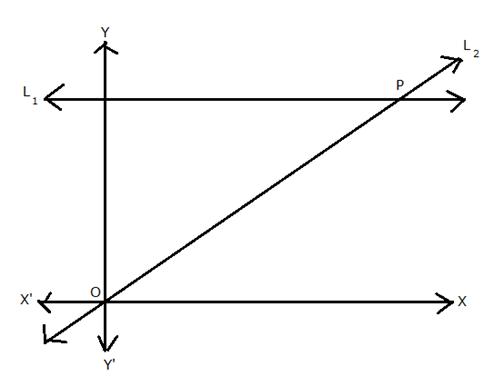
(i) 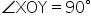
Since L2 is the bisector of angle O,
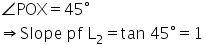
(ii) Let the co-ordinates of P be (x, y).
Since P lies on L1, its y-coordinate is 4.
Also, L2 passes through orgin,
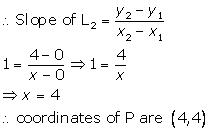
(iii)
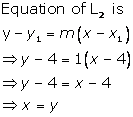
Solution 26
Solution 27

Solution 28

Solution 29
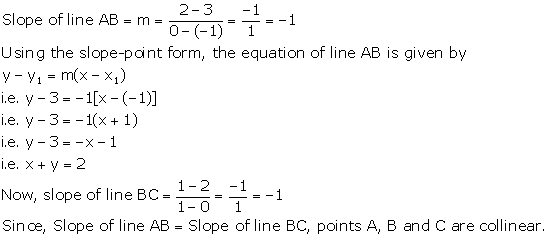
Solution 30
Solution 31
i. Since A lies on the X-axis, let the co-ordinates of A be (x, 0).
Since B lies on the Y-axis, let the co-ordinates of B be (0, y).
Let m = 1 and n = 2
Using Section formula,
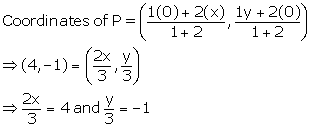
⇒ x = 6 and y = -3
So, the co-ordinates of A are (6, 0) and that of B are (0, -3).
![]()
⇒ Slope of line perpendicular to AB = m = -2
P = (4, -1)
Thus, the required equation is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
⇒ y - (-1) = -2(x - 4)
⇒ y + 1 = -2x + 8
⇒ 2x + y = 7
Equation of a Line Exercise Ex. 14(A)
Solution 2
The given line is x - 2y + 5 = 0.
(i) Substituting x = 1 and y = 3 in the given equation, we have:
L.H.S. = 1 - 2 ![]() 3 + 5 = 1 - 6 + 5 = 6 - 6 = 0 = R.H.S.
3 + 5 = 1 - 6 + 5 = 6 - 6 = 0 = R.H.S.
Thus, the point (1, 3) lies on the given line.
(ii) (0, 5)
Substituting x = 0 and y = 5 in x – 2y + 5 = 0,
LHS = 0 – 2(5) + 5 = 0 – 10 + 5 = –5 ≠ RHS
Hence, (0, 5) does not lie on the given line.
(iii) (–5, 0)
Substituting x = –5 and y = 0 in x – 2y + 5 = 0,
LHS = –5 – 2(0) + 5 = –5 – 0 + 5 = 0 = RHS
Hence, (–5, 0) lies on the given line.
(iv) Substituting x = 5 and y = 5 in the given equation, we have:
L.H.S. = 5 - 2 ![]() 5 + 5 = 5 - 10 + 5 = 10 - 10 = 0 = R.H.S.
5 + 5 = 5 - 10 + 5 = 10 - 10 = 0 = R.H.S.
Thus, the point (5, 5) lies on the given line.
Solution 3
(i) The given line is ![]()
Substituting x = 2 and y = 3 in the given equation,
![]()
Thus, the given statement is false.
(ii) The point (2, a) lies on the line 2x - y = 3.
![]() 2(2) - a = 3
2(2) - a = 3
4 - a = 3
a = 4 - 3 = 1
Thus, the given statement is false.
Solution 4
The given equation of the line is 9x + 4y = 3.
Put x = 3 and y = -k, we have:
9(3) + 4(-k) = 3
27 - 4k = 3
4k = 27 - 3 = 24
k = 6
Solution 5
The equation of the given line is ![]()
Putting x = m, y = 2m - 1, we have:
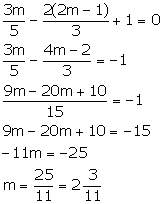
Solution 6
The given line will bisect the join of A (5, -2) and B (-1, 2), if the co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB satisfy the equation of the line.
The co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB are
![]()
Substituting x = 2 and y = 0 in the given equation, we have:
L.H.S. = 3x - 5y = 3(2) - 5(0) = 6 - 0 = 6 = R.H.S.
Hence, the line 3x - 5y = 6 bisects the join of (5, -2) and (-1, 2).
Solution 7
(i) The given line bisects the join of A (a, 3) and B (2, -5), so the co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB will satisfy the equation of the line.
The co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB are
![]()
Substituting x = ![]() and y = -1 in the
given equation, we have:
and y = -1 in the
given equation, we have:
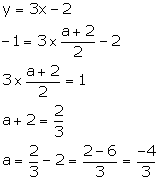
(ii) The given line bisects the join of A (8, -1) and B (0, k), so the co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB will satisfy the equation of the line.
The co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB are
![]()
Substituting x = 4
and y = ![]() in the given
equation, we have:
in the given
equation, we have:
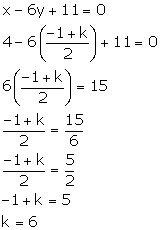
Solution 8
(i) Given, the point (-3, 2) lies on the line ax + 3y + 6 = 0.
Substituting x = -3 and y = 2 in the given equation, we have:
a(-3) + 3(2) + 6 = 0
-3a + 12 = 0
3a = 12
a = 4
(ii) Given, the line y = mx + 8 contains the point (-4, 4).
Substituting x = -4 and y = 4 in the given equation, we have:
4 = -4m + 8
4m = 4
m = 1
Solution 9
Given, the point P divides the join of (2, 1) and (-3, 6) in the ratio 2: 3.
Co-ordinates of the point P are
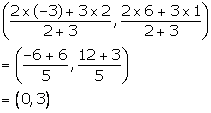
Substituting x = 0 and y = 3 in the given equation, we have:
L.H.S. = 0 - 5(3) + 15 = -15 + 15 = 0 = R.H.S.
Hence, the point P lies on the line x - 5y + 15 = 0.
Solution 10
Given, the line segment joining the points (5, -4) and (2, 2) is divided by the point Q in the ratio 1: 2.
Co-ordinates of the point Q are

Substituting x = 4 and y = -2 in the given equation, we have:
L.H.S. = x - 2y = 4
- 2(-2) = 4 + 4 = 8 ![]() R.H.S.
R.H.S.
Hence, the given line does not contain point Q.
Solution 11
Consider the given equations:
4x + 3y = 1 ....(1)
3x - y + 9 = 0 ....(2)
Multiplying (2) with 3, we have:
9x - 3y = -27 ....(3)
Adding (1) and (3), we get,
13x = -26
x = -2
From (2), y = 3x + 9 = -6 + 9 = 3
Thus, the point of intersection of the given lines (1) and (2) is (-2, 3).
The point (-2, 3) lies on the line (2k - 1)x - 2y = 4.
![]() (2k - 1)(-2) - 2(3) = 4
(2k - 1)(-2) - 2(3) = 4
-4k + 2 - 6 = 4
-4k = 8
k = -2
Solution 12
We know that two or more lines are said to be concurrent if they intersect at a single point.
We first find the point of intersection of the first two lines.
2x + 5y = 1 ....(1)
x - 3y = 6 ....(2)
Multiplying (2) by 2, we get
2x - 6y = 12 ....(3)
Subtracting (3) from (1), we get
11y = -11
y = -1
From (2), x = 6 + 3y = 6 - 3 = 3
So, the point of intersection of the first two lines is (3, -1).
If this point lie on the third line, i.e., x + 5y + 2 = 0, then the given lines will be concurrent.
Substituting x = 3 and y = -1 in x + 5y + 2 = 0, we have
L.H.S. = x + 5y + 2 = 3 + 5(-1) + 2 = 5 - 5 = 0 = R.H.S.
Thus, (3, -1) lies on the third line also.
Hence, the given lines are concurrent.
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (iv) 8
Point (m, –4) lies on the line x + y = 4.
⇒ m – 4 = 4
⇒ m = 8
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (i) 2
As the line kx – y = 9 passes through the point (6, 3).
So, (6, 3) satisfies the line kx – y = 9.
⇒ k(6) – 3 = 9
⇒ 6k = 12
⇒ k = 2
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (i) no
To check whether the line ![]() passes through the point (2, –4), we need to check whether it satisfies the given equation of a line or not.
passes through the point (2, –4), we need to check whether it satisfies the given equation of a line or not.
![]()
Thus, the statement is not true.
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iii) 2
x + y = 8 ... (I)
x – y = 0 … (II)
Solving the two equations simultaneously, we get
x = 4, y = 4
So, the point of intersection of the two lines is (4, 4).
Since, (4, 4) lies on the line mx – 2y = 0.
⇒ m(4) – 2(4) = 0
⇒ m = 2
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (ii) 4
As the line x + y = 4 bisects the line segment joining the points A(0, k) and B(4, 0).
So, the mid-point of AB satisfies the equation of the line.
Midpoint of AB ![]()
Substituting ![]() in the equation, we get
in the equation, we get
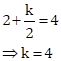
Equation of a Line Exercise Ex. 14(B)
Solution 3
Slope of the line passing through (0, 2) and (-3, -1) = ![]()
Slope of the line passing through (-1, 5) and (4, a) = ![]()
Since, the lines are parallel.
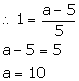
Solution 4
Slope of the line passing through (-4, -2) and (2, -3) = ![]()
Slope of the line passing through (a, 5) and (2, -1) = ![]()
Since, the lines are perpendicular.
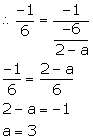
Solution 5
The given points are A (4, -2), B (-4, 4) and C (10, 6).
![]()
![]()
![]()
It can be seen that:
![]()
Hence, AB ![]() AC.
AC.
Thus, the given points are the vertices of a right-angled triangle.
Solution 6
The given points are A (4, 5), B (1, 2), C (4, 3) and D (7, 6).
![]()
![]()
Since, slope of AB = slope of CD
Therefore AB || CD
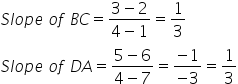
Since, slope of BC = slope of DA
Therefore, BC || DA
Hence, ABCD is a parallelogram
Solution 7
Let the given points be A (-2, 4), B (4, 8), C (10, 7) and D (11, -5).
Let P, Q, R and S be the mid-points of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively.
Co-ordinates of P are
![]()
Co-ordinates of Q are
![]()
Co-ordinates of R are
![]()
Co-ordinates of S are
![]()
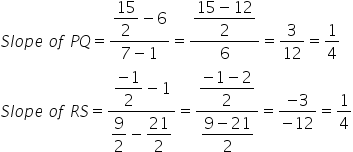
Since, slope of PQ = Slope of RS, PQ || RS.
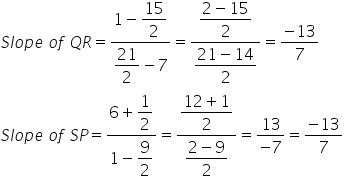
Since, slope of QR = Slope of SP, QR || SP.
Hence, PQRS is a parallelogram.
Solution 8
The points P, Q, R will be collinear if slope of PQ and QR is the same.
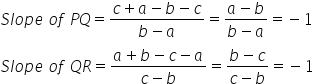
Since slope of PQ = slope of QR, the points P, Q, and R are collinear.
Solution 9
Let A = (x, 2) and B = (8, -11)
Slope of AB = ![]()
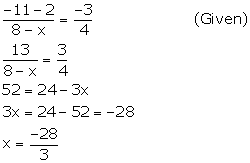
Solution 10
Given, A (5, 4), B (-3, -2) and C (1, -8) are the vertices of a triangle ABC.
(i) Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of the altitude of AB = 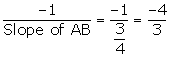
(ii) Since, D is the mid-point of BC.
Co-ordinates of point D are
![]()
Slope of AD = ![]()
(iii) Slope of AC = ![]()
Slope of line parallel to AC = Slope of AC = 3
Solution 11
(i) Since, BC is perpendicular to AB,
Slope of AB = 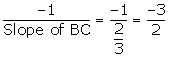
(ii) Since, AD is parallel to BC,
Slope of AD = Slope of BC = ![]()
Solution 2
(i) A = (-3, -2) and B = (1, 2)
Slope of AB = ![]()
Inclination of line AB = ![]() = 45o
= 45o
(ii) A = (0, ![]() ) and B = (3, 0)
) and B = (3, 0)
Slope of AB = ![]()
Inclination of line AB = ![]() = 30o
= 30o
(iii) A = (-1, 2![]() ) and B = (-2,
) and B = (-2, ![]() )
)
Slope of AB = ![]()
Inclination of line AB = ![]() = 60o
= 60o
Solution 12
Given, points A (K, 3), B (2, -4) and C (-K + 1, -2) are collinear.
![]() Slope of AB = Slope of BC
Slope of AB = Slope of BC
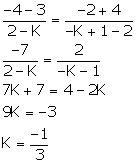
Solution 13
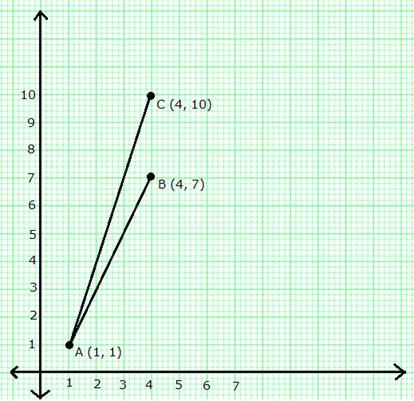
From the graph, clearly, AC has steeper slope.
Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of AC = ![]()
The line with greater slope is steeper. Hence, AC has steeper slope.
Solution 14
Since, PQ || RS,
Slope of PQ = Slope of RS
(i) Slope of PQ = ![]()
Slope of RS = ![]()
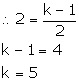
(ii) Slope of PQ = ![]()
Slope of RS = ![]()
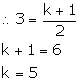
(iii) Slope of PQ = ![]()
Slope of RS = ![]()
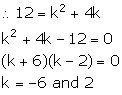
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (iii) 60°
Slope = ![]()
![]()
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (iv) ![]()
Slope of a line = 5
Slope of a line perpendicular to the given line ![]()
∴ Slope of a line perpendicular to the given line ![]()
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (ii) ![]()
Origin is (0, 0).
Slope of a line passing through origin and the point (–3, 4) is
![]()
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (iii) 45°
Slope of a line passing through the points (4, 3) and (5, 4) is
![]()
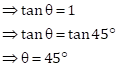
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (ii) 1
Slope of a line passing through the points (8, –5) and (–4, 7) is
![]()
Slope of the line perpendicular to the above line = 1
Equation of a Line Exercise Ex. 14(C)
Solution 2
Given, y-intercept = c = -1 and inclination = 45o.
Slope = m = tan 45o = 1
Substituting the values of c and m in the equation y = mx + c, we get,
y = x - 1, which is the required equation.
Solution 3
Given, slope = ![]()
The line passes through (-3, 4) = (x1, y1)
Substituting the values in y - y1 = m(x - x1), we get,
y - 4 = ![]() (x + 3)
(x + 3)
3y - 12 = -4x - 12
4x + 3y = 0, which is the required equation.
Solution 4
Slope of the line =
tan 60o = ![]()
The line passes through the point (5, 4) = (x1, y1)
Substituting the values in y - y1 = m(x - x1), we get,
y - 4 = ![]() (x - 5)
(x - 5)
y - 4 = ![]() x - 5
x - 5![]()
y =![]() x + 4 - 5
x + 4 - 5![]() , which is the
required equation.
, which is the
required equation.
Solution 5
(i) Let (0, 1) = (x1, y1) and (1, 2) = (x2, y2)
![]()
The required equation of the line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 1 = 1(x - 0)
y - 1 = x
y = x + 1
(ii) Let (-1, -4) = (x1, y1) and (3, 0) = (x2, y2)
![]()
The required equation of the line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 4 = 1(x + 1)
y + 4 = x + 1
y = x - 3
Solution 6
Given, co-ordinates of two points P and Q are (2, 6) and (-3, 5) respectively.
(i) Gradient of PQ
= ![]()
(ii) The equation of the line PQ is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 6 = ![]() (x - 2)
(x - 2)
5y - 30 = x - 2
5y = x + 28
(iii) Let the line PQ intersects the x-axis at point A (x, 0).
Putting y = 0 in the equation of the line PQ, we get,
0 = x + 28
x = -28
Thus, the co-ordinates of the point where PQ intersects the x-axis are A (-28, 0).
Solution 7
(i) Given, co-ordinates of two points A and B are (−3, 4) and (2, −1).
Slope =![]()
The equation of the line AB is given by:
y − y1 = m(x − x1)
y − 4 = −1(x + 3)
y − 4 = −x − 3
x + y = 1
(ii) Let the line AB intersects the y-axis at point (0, y).
Putting x = 0 in the equation of the line, we get,
0 + y = 1
y = 1
Thus, the co-ordinates of the point where the line AB intersects the y-axis are (0, 1).
Solution 8
Slope of line AB = tan 45o = 1
The line AB passes through P (3, 4). So, the equation of the line AB is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 4 = 1(x - 3)
y - 4 = x - 3
y = x + 1
Slope of line CD =
tan 60o = ![]()
The line CD passes through P (3, 4). So, the equation of the line CD is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 4 = ![]() (x - 3)
(x - 3)
y - 4 = ![]() x - 3
x - 3 ![]()
y = ![]() x + 4 - 3
x + 4 - 3 ![]()
Solution 9
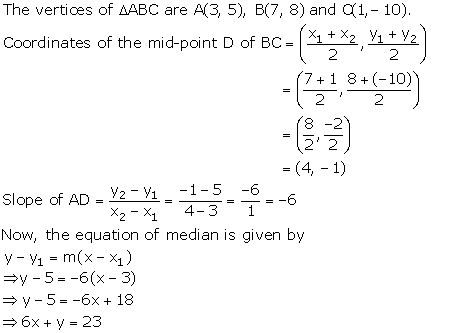
Solution 10
Since, ABCD is a parallelogram,
![]()
![]() B = 180o
- 60o = 120o
B = 180o
- 60o = 120o
Slope
of BC = tan 120o = tan (90o + 30o) = cot30o
= ![]()
Equation of the line BC is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 5
= ![]() (x - 7)
(x - 7)
y - 5
= ![]() x - 7
x - 7![]()
y = ![]() x + 5 - 7
x + 5 - 7![]()
Since, CD || AB and AB || x-axis, slope of CD = Slope of AB = 0
Equation of the line CD is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 5 = 0(x - 7)
y = 5
Solution 11
The given equations are:
x + 2y = 7 ....(1)
x - y = 4 ....(2)
Subtracting (2) from (1), we get,
3y = 3
y = 1
From (2), x = 4 + y = 4 + 1 = 5
The required line passes through (0, 0) and (5, 1).
![]()
Required equation of the line is given by:
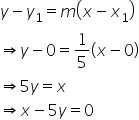
Solution 12
Given, the co-ordinates of vertices A, B and C of a triangle ABC are (4, 7), (-2, 3) and (0, 1) respectively.
Let AD be the median through vertex A.
Co-ordinates of the point D are
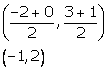
![]() Slope of AD =
Slope of AD = ![]()
The equation of the median AD is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 7 = 1(x - 4)
y - 7 = x - 4
x - y + 3 = 0
The slope of the line which is parallel to line AC will be equal to the slope of AC.
Slope of AC = ![]()
The equation of the line which is parallel to AC and passes through B is given by:
y - 3 = ![]() (x + 2)
(x + 2)
2y - 6 = 3x + 6
2y = 3x + 12
3x - 2y + 12 = 0
Solution 13
Let A = (1, 4), B = (2, 3), and C = (-1, 2).
Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of line perpendicular to AB = ![]()
The equation of the perpendicular drawn through C onto AB is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 2 = 1(x + 1)
y - 2 = x + 1
y = x + 3
Solution 14
(i) When x-intercept = 5, corresponding point on x-axis is (5, 0)
When y-intercept = 3, corresponding point on y-axis is (0, 3).
Let (x1, y1) = (5, 0) and (x2, y2) = (0, 3)
Slope = ![]()
The required equation is:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x - 5)
(x - 5)
5y = -3x + 15
3x + 5y = 15
(ii) When x-intercept = -4, corresponding point on x-axis is (-4, 0)
When y-intercept = 6, corresponding point on y-axis is (0, 6).
Let (x1, y1) = (-4, 0) and (x2, y2) = (0, 6)
Slope = ![]()
The required equation is:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x + 4)
(x + 4)
2y = 3x + 12
Solution 15
Since, x-intercept is 6, so the corresponding point on x-axis is (6, 0).
Slope = m = ![]()
Required equation of the line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x - 6)
(x - 6)
6y = -5x + 30
5x + 6y = 30
Solution 16
Since, x-intercept is 5, so the corresponding point on x-axis is (5, 0).
The line also passes through (-3, 2).
![]() Slope of the line =
Slope of the line = ![]()
Required equation of the line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x - 5)
(x - 5)
4y = -x + 5
x + 4y = 5
Solution 17
Since, y-intercept = 5, so the corresponding point on y-axis is (0, 5).
The line passes through (1, 3).
![]() Slope of the line =
Slope of the line = ![]()
Required equation of the line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 5 = -2(x - 0)
y - 5 = -2x
2x + y = 5
Solution 18
Let AB and CD be two equally inclined lines as shown in the figure.
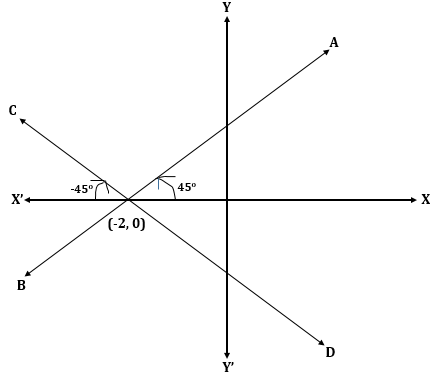
For line AB:
Slope = m = tan 45o = 1
(x1, y1) = (-2, 0)
Equation of the line AB is:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = 1(x + 2)
y = x + 2
For line CD:
Slope = m = tan (-45o) = -1
(x1, y1) = (-2, 0)
Equation of the line CD is:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = -1(x + 2)
y = -x - 2
x + y + 2 = 0
Solution 19
(i)
(ii)

(iii)

Solution 20
Given, P divides the line segment joining A (4, -8) and B (12, 0) in the ratio 3: 1.
Co-ordinates of point P are

Slope = m =![]() (Given)
(Given)
Thus, the required equation of the line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 2 = ![]() (x - 10)
(x - 10)
5y + 10 = -2x + 20
2x + 5y = 10
Solution 21
(i) Co-ordinates of the centroid of triangle ABC are
(ii) Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of the line parallel to AB = Slope of AB = -1
Thus, the required equation of the line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
Solution 22
Given, AP: CP = 2: 3
![]() Co-ordinates of P are
Co-ordinates of P are

Slope of BP = ![]()
Required equation of the line passing through points B and P is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 1 = 0(x - 3)
y = 1
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (i) x-axis
Slope of the line passing through the points (–7, 4) and (5, 4) is
![]()
Equation of this line is:
y – 4 = 0(x + 7)
⇒ y = 4
It is parallel to x-axis.
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (ii) y – x = 2
Slope of the line = tan 45° = 1
Equation of the line is:
y – 2 = 1(x – 0)
⇒ y – 2 = x
⇒ y – x = 2
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (iv) (0, 4)
The line intersects y-axis at point A.
So, x-coordinate of A will be 0.
Putting x = 0 in the equation, we have
5(0) – 2y + 8 = 0
⇒ y = 4
Hence, A = (0, 4).
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (i) x – y = 7
Equation of a line with x-intercept 7 and y-intercept –7 is:
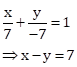
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (iii) slope = 1 and x-intercept ![]()
Equation of a line is given as 5x – 5y = 12
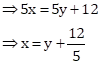
This is in the form x = mx + c.
Thus, slope = 1 and x-intercept ![]()
Equation of a Line Exercise Ex. 14(D)
Solution 2
(i) y = 4
Comparing this equation with y = mx + c, we have:
Slope = m = 0
y-intercept = c = 4
(ii) ax - by = 0 ![]() by = ax
by = ax ![]() y =
y = ![]()
Comparing this equation with y = mx + c, we have:
Slope = m = ![]()
y-intercept = c = 0
(iii) 3x - 4y = 5 ![]()
Comparing this equation with y = mx + c, we have:
Slope = m = ![]()
y-intercept = c = ![]()
Solution 3
Given equation of a line is x - y = 4.
![]() y = x - 4
y = x - 4
Comparing this equation with y = mx + c, we have
Slope = m = 1
y-intercept = c = -4
Let the inclination be ![]() .
.
Slope = 1 = tan ![]() = tan 45o
= tan 45o
![]()
Solution 4
(i) 3x + 4y + 7 = 0
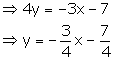
Slope of this line =![]()
28x - 21y + 50 = 0
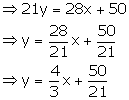
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since, product of slopes of the two lines = -1, the lines are perpendicular to each other.
(ii) x - 3y = 4
3y = x - 4
y =![]()
Slope of this line =![]()
3x - y = 7
y = 3x - 7
Slope of this line = 3
Product of slopes of the two lines = 1 ![]() -1
-1
So, the lines are not perpendicular to each other.
(iii) 3x + 2y = 5
2y = -3x + 5
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
x + 2y = 1
2y = -x + 1
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since the slopes of two lines are not equal, the lines are not parallel to each other.
(iv) Given, the slope of the line through (1, 4) and (x, 2) is 2.
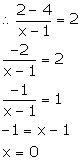
Solution 5
(i) x + 2y + 3 = 0
2y = -x - 3
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of the line which is parallel to the given line = Slope of the given line = ![]()
(ii) ![]()
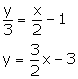
Slope of this line =![]()
Slope of the line which is parallel to the given line = Slope of the given line = ![]()
Solution 6
(i) ![]()
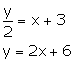
Slope of this line = 2
Slope of the line which is perpendicular to the given line = ![]()
(ii) ![]()
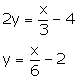
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of the line which is perpendicular to the given line = 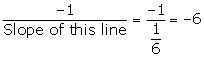
Solution 7
(i) 2x - by + 5 = 0
by = 2x + 5
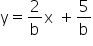
Slope of this line =![]()
ax + 3y = 2
3y = -ax + 2
y = ![]()
Slope of this line =![]()
Since, the lines are parallel, the slopes of the two lines must be equal.
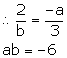
(ii) mx + 3y + 7 = 0
3y = -mx - 7
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
5x - ny - 3 = 0
ny = 5x - 3
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since, the lines are perpendicular; the product of their slopes is -1.
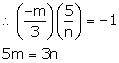
Solution 8
2x - y + 5 = 0
y = 2x + 5
Slope of this line = 2
px + 3y = 4
3y = -px + 4
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since, the lines are perpendicular to each other, the product of their slopes is -1.

Solution 9
(i) 2x - 2y + 3 = 0
2y = 2x + 3
y = x + ![]()
Slope of the line AB = 1
(ii) Required angle = ![]()
Slope = tan![]() = 1 = tan 45o
= 1 = tan 45o
![]() = 45o
= 45o
Solution 10
4x + 3y = 9
3y = -4x + 9
y = ![]() + 3
+ 3
Slope of this line = ![]()
px - 6y + 3 = 0
6y = px + 3
y = ![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Since, the lines are parallel, their slopes will be equal.
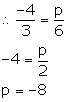
Solution 11

Solution 12
(i) The slope of the line parallel to x-axis is 0.
(x1, y1) = (-5, 7)
Required equation of the line is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 7 = 0(x + 5)
y = 7
(ii) The equation of a line parallel to y-axis is x = a where 'a' is the x-intercept.
Since the line passes through (-5, 7), the equation of a line parallel to given line x = -5.
That is, x + 5 = 0
Solution 13
x - 3y = 4
![]() 3y = x - 4
3y = x - 4
![]()
![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of a line parallel to this line = ![]()
Required equation of the line passing through (5, -3) is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y + 3 = ![]() (x - 5)
(x - 5)
3y + 9 = x - 5
x - 3y - 14 = 0
Solution 14
4x + 5y = 6
5y = -4x + 6
y = ![]()
Slope of this line
= ![]()
The required line is perpendicular to the line 4x + 5y = 6.
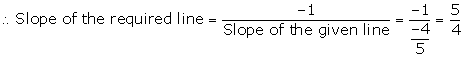
The required equation of the line is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 1 = ![]() (x + 2)
(x + 2)
4y - 4 = 5x + 10
5x - 4y + 14 = 0
Solution 15
Let A = (6, -3) and B = (0, 3).
We know the perpendicular bisector of a line is perpendicular to the line and it bisects the line.
That is, it passes through the mid-point of the line.
Co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB are
![]()
Thus, the required line passes through (3, 0).
Slope of AB = ![]()
![]() Slope of the required line =
Slope of the required line = ![]()
Thus, the equation of the required line is given by:
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = 1(x - 3)
y = x - 3
Solution 16
We know that in a rhombus, diagonals bisect each other at right angle.
Let O be the point of intersection of the diagonals AC and BD.
Co-ordinates of O are
![]()
Slope of BD = ![]()
For line BD:
Slope = m = ![]() , (x1, y1) = (-5, 6)
, (x1, y1) = (-5, 6)
Equation of the line BD is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 6 = ![]() (x + 5)
(x + 5)
3y - 18 = -x - 5
x + 3y = 13
For line AC:
Slope = m = ![]() , (x1, y1) = (-2, 5)
, (x1, y1) = (-2, 5)
Equation of the line AC is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 5 = 3(x + 2)
y - 5 = 3x + 6
y = 3x + 11
Solution 17
(i) We know the median through A will pass through the mid-point of BC. Let AD be the median through A.
Co-ordinates of the mid-point of BC, i.e., D are
![]()
Slope of AD = ![]()
Equation of the median AD is
y - 3 = -8(x - 0)
8x + y = 3
(ii) Let BE be the altitude of the triangle through B.
Slope of AC = ![]()
![]() Slope of BE =
Slope of BE = ![]()
Equation of altitude BE is
y - 2 = ![]() (x - 2)
(x - 2)
3y - 6 = x - 2
3y = x + 4
(iii) Slope of AB = ![]()
Slope of the line parallel to AB = Slope of AB = 7
So, the equation of the line passing through C and parallel to AB is
y - 4 = 7(x + 2)
y - 4 = 7x + 14
y = 7x + 18
Solution 18
(i) 2y = 3x + 5
![]()
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of the line AB = 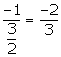
(x1, y1) = (3, 2)
The required equation of the line AB is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 2 = ![]() (x - 3)
(x - 3)
3y - 6 = -2x + 6
2x + 3y = 12
(ii) For the point A (the point on x-axis), the value of y = 0.
![]() 2x + 3y = 12
2x + 3y = 12 ![]() 2x = 12
2x = 12 ![]() x = 6
x = 6
Co-ordinates of point A are (6, 0).
For the point B (the point on y-axis), the value of x = 0.
![]() 2x + 3y = 12
2x + 3y = 12 ![]() 3y = 12
3y = 12 ![]() y = 4
y = 4
Co-ordinates of point B are (0, 4).
Area of ![]() OAB =
OAB = ![]()
![]() OA
OA ![]() OB =
OB = ![]()
![]() 6
6 ![]() 4 = 12 square units
4 = 12 square units
Solution 19
For the point A (the point on x-axis), the value of y = 0.
![]() 4x - 3y + 12 = 0
4x - 3y + 12 = 0 ![]() 4x = -12
4x = -12 ![]() x = -3
x = -3
Co-ordinates of point A are (-3, 0).
Here, (x1, y1) = (-3, 0)
The given line is 4x - 3y + 12 = 0
3y = 4x + 12
y =![]() + 4
+ 4
Slope of this line = ![]()
![]() Slope of a line perpendicular to the given line =
Slope of a line perpendicular to the given line = 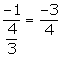
Required equation of the line passing through A is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ![]() (x + 3)
(x + 3)
4y = -3x - 9
3x + 4y + 9 = 0
Solution 20
(i) The given equation is
2x - 3y + 18 = 0
3y = 2x + 18
y = ![]() x + 6
x + 6
Slope of this line = ![]()
Slope of a line perpendicular to this line = 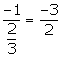
(x1, y1) = (-5, 7)
The required equation of the line AP is given by
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 7 = ![]() (x + 5)
(x + 5)
2y - 14 = -3x - 15
3x + 2y + 1 = 0
(ii) P is the foot of perpendicular from point A.
So P is the point of intersection of the lines 2x - 3y + 18 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 1 = 0.
2x - 3y + 18 = 0 ![]() 4x - 6y + 36 = 0
4x - 6y + 36 = 0
3x + 2y + 1 = 0 ![]() 9x + 6y + 3 = 0
9x + 6y + 3 = 0
Adding the two equations, we get,
13x + 39 = 0
x = -3
![]() 3y = 2x + 18 = -6 + 18 = 12
3y = 2x + 18 = -6 + 18 = 12
y = 4
Thus, the co-ordinates of the point P are (-3, 4).
Solution 21
For the line AB:
![]()
(x1, y1) = (4, 0)
Equation of the line AB is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = -1(x - 4)
y = -x + 4
x + y = 4 ....(1)
For the line BC:
![]()
(x1, y1) = (2, 2)
Equation of the line BC is
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 2 = -2(x - 2)
y - 2 = -2x + 4
2x + y = 6 ....(2)
Given that AB cuts the y-axis at P. So, the abscissa of point P is 0.
Putting x = 0 in (1), we get,
y = 4
Thus, the co-ordinates of point P are (0, 4).
Given that BC cuts the x-axis at Q. So, the ordinate of point Q is 0.
Putting y = 0 in (2), we get,
2x = 6 ![]() x = 3
x = 3
Thus, the co-ordinates of point Q are (3, 0).
Solution 22
Consider 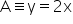
Putting x = 0 and y = 0 in the equation y = 2x, we have
LHS = 0 and RHS = 0
Thus, the line y = 2x passes through the origin.
Hence, A L3
L3
Consider 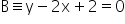
Putting x = 0 in y - 2x + 2 = 0, we get, y = -2
Putting y = 0 in y - 2x + 2 = 0, we get, x = 1
So, x-intercept = 1 and y-intercept = -2
So, x-intercept is positive and y-intercept is negative.
Hence, B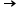 L4
L4
Consider 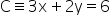
Putting x = 0 in 3x + 2y = 6, we get, y = 3
Putting y = 0 in 3x + 2y = 6, we get, x = 2
So, both x-intercept and y-intercept are positive.
Hence, C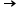 L2
L2
Consider 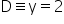
The slope of the line y = 2 is 0.
So, the line y = 2 is parallel to x-axis.
Hence, D L1
L1
Solution 1(a)
Correct option: (ii) x + y = 5
Equation of a line with x-intercept 5 and y-intercept also 5 is:
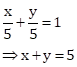
Solution 1(b)
Correct option: (iii) equal in magnitude with opposite signs
Inclination = 1
⇒ tan θ = 1
⇒ tan θ = tan 45°
⇒θ = 45°
Thus, its intercepts with both the axes are equal in magnitude with opposite signs.
Solution 1(c)
Correct option: (iii) 2x + y = 3
Equation of a line passing through (1, 1) is:
y – 1 = m(x – 1) … (I)
Also, y = mx + 3
⇒ mx + 3 – 1 = mx – m
⇒ m = –2
From (I), we have
y – 1 = –2(x – 1)
⇒ 2x + y = 3
Solution 1(d)
Correct option: (ii) x – y = 3
x – y = 3 … (I)
x + y = 0 … (II)
Solving the two equations, we get
![]()
Also, tan θ = tan 45° = 1
Equation of the required line is
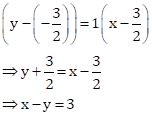
Solution 1(e)
Correct option: (iv) x + y = 12
As the line cuts equal intercepts with both the axes, slope of the line = –1.
Equation of the line is
y – 6 = –1(x – 6)
⇒ x + y = 12