Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 26 - Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions
GST [Goods and Services Tax] Exercise Chp. 1
Solution 1
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true
It is a case of inter-state transaction. That means if GST is 18%, then CGST is Nil.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true
GST is never calculated on the GST already paid.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Banking (Recurring Deposit Accounts) Exercise Chp. 2
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Total sum deposited in 6 months = 5000 ⨉ 6 = Rs. 30,000
Maturity value = Rs. 33,000
Thus,
Interest received = 33,000 – 30,000 = 3,000
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
n = 6 ⨉ 12 = 72
P = 80
r = 6
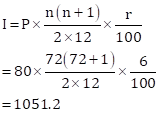
∴ Maturity value = P ⨉ n + I
=Rs. 6811.20
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is incorrect, as the correct one is ![]()
Hence, the Reason is false.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 3
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Face value = Rs.100
Dividend on one share = 10% of 100 = Rs.10
Total number of shares = 60,000 ÷ 100 = 600
Thus total dividend = 10 ⨉ 600 = Rs.6000
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Case 1: 16% Rs.100 shares at Rs.80
Face value = Rs.100
Dividend on one share = 16% of 100 = Rs.16
Market value = Rs.80
Therefore,
![]()
Case 2: 20% Rs.100 shares at Rs.120
Face value = Rs.100
Dividend on one share = 20% of 100 = Rs.20
Market value = Rs.120
Therefore,
![]()
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 4
Solution 1
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
(x-4)2 > 4
x – 4 > 4 or x – 4 < -4
x > 8 or x < 0
8 < x < 0
Hence, the Assertion is false.
Now,
x2 > 4
x > 2 or x < -2
2 < x < -2
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
-6x < -40
6x > 40
x > 6.666
as x ∈ W
x = {7, 8, 9, ….}
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 5
Solution 1
Correct option: (d) Both A and R are false.
For quadratic equation 2x2 + 6x + 3 = 0,
Discriminant = 36 – 24 = 12, which is greater than zero.
Thus roots are real and distinct.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
Now,
If for a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c ∈R and a ≠ 0, then if discriminant > 0 and perfect square, implies roots of the quadratic equation are real, distinct and rational.
The statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
We have,
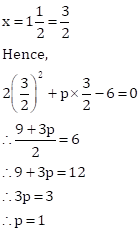
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 7
Solution 1
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
![]()
Hence, the Assertion is true.
Mean proportion of x and y = ![]()
The statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (d) Both A and R are false.
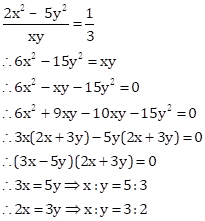
Hence, the Assertion is false.
If four quantities a, b, c and d form a proportion, then Componendo and Dividendo property states that
(a + c):(a - c)=(b + d)(b - d)
The statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 21
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
![]()
Also, A = 90o – B
⇒ tan A = cot B
⇒ tan A ⨉ tan B = 1
Hence,
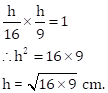
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
(sec θ - tan θ)⨉ (sec θ + tan θ) = sec2 θ - tan2 θ = 1.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 8
Solution 1
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
By remainder theorem,
If p(x) = x 51 - 51, then p(1) will be the remainder, when divided with x -1.
Now, p(1) = -50
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
If f(x) = ax3 + 9x2 + 4x - 10
By remainder theorem,
f(-3) = 5
∴ a(-3)3 + 9(-3)2 + 4(-3) – 10 = 5
∴ -27a+81-12-10=5
∴ a = 2
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 9
Solution 1
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
If A and B are two 2 ⨉ 2 matrices then A ⨉ B can be zero matrix.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is incorrect, as A ⨉ B can be zero, even if neither of the matrices A or B is zero.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
If A, B and C are three square matrices of order 2 ⨉ 2 such that AB = AC, it does not imply that B = C.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 10
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
AP is 8, 12, 16, ... 200, 204, 208, …
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
5, 8, 11, 14,... are in A.P., since d = 3
5/2, 4, 11/2, 7,... are also in A.P., since d = 3/2.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 11
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
5th term from beginning: -48
5th term from end: 24
Product: -1152
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
a = 2/9
r = -3/2
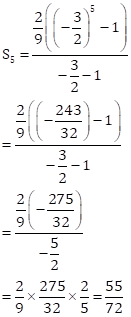
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 12
Solution 1
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
Reflection of (-5, 1) and (4, 1) with respect to a given line L is not same as (-5, 1) and (4, 1) respectively.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
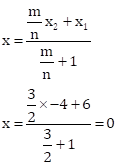
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 3
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
We have
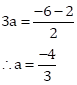
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 4
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Product of slopes of perpendicular lines is -1
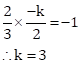
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 15
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
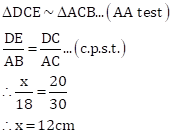
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
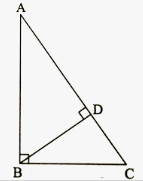
In △ABC
△ADB ~△ABC
△ABC ~△BDC
△ADB ~△BDC
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 16
Solution 1
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
We know that, there is a unique point which is at equal distance from the three non-collinear points, not locus of points.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
We know that, the locus of the mid-points of all equal chords in a circle is the circumference of the circle concentric with the given circle and having radius equal to the distance of equal chords from the centre.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 17
Solution 1
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
x = ½ ⨉ 160 = 80o
Also,
x + y = 180o
∴ y = 180 – 80 = 100o
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
PT2 = PD ⨉ PC
PT2 = 5 ⨉ 12.8 = 64
PT = 8cm
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 20
Solution 1
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Curved surface area = 2prh = 22/7 ⨉ 21 ⨉ 2 ⨉ 2 = 264 cm2.
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
Circumference of semi-circular sheet = Circumference of base of cone
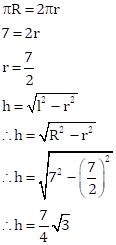
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 23
Solution 1
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
Arranging in ascending order
7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19.
As n is odd
lower quartile ![]() term = 2nd term = 9
term = 2nd term = 9
Hence, the Assertion is true.
Now,
For finding quartiles, the given data are arranged in ascending order of their magnitudes, then lower quartile ![]() term or
term or ![]() term, depending whether n is even or odd.
term, depending whether n is even or odd.
Thus, the statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (b) A is false, R is true.
Mean age = 28 years
Sum of ages = 28 ⨉ 9
Mean after addition of 10th boy = 29 years
Sum of ages after addition of 10th boy = 29 ⨉ 10
Thus, the age of new boy is 29 ⨉ 10 – 28 ⨉ 9 years.
Hence, the Assertion is false.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.
Assertion-Reasoning Type Questions Exercise Chp. 25
Solution 1
Correct option: (a) A is true, R is false.
Sample space for total number of possible outcomes
(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),
(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(2,6),
(3,1),(3,2),(3,3),(3,4),(3,5),(3,6),
(4,1),(4,2),(4,3),(4,4),(4,5),(4,6),
(5,1),(5,2),(5,3),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6),
(6,1),(6,2),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6)
Total number of outcomes =36
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is incorrect.
Hence, the Reason is false.
Solution 2
Correct option: (c) Both A and R are true.
No. of red face cards = 26
Total number of cards = 52
Thus, the probability of getting a red face-card = 26/52 = 3/26
Hence, the Assertion is true.
The statement given in Reason is correct.
Hence, the Reason is true.

