Class 10 SELINA Solutions Chemistry Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds A. Hydrogen Chloride
Exercise Ex. 8
Solution A 1
(a) conc. H2SO4
Solution A 2
Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is dried by conc. sulphuric acid.
Solution A 3
Option C
HCl is highly soluble in water.
HCl is highly soluble in water. Its high solubility may be demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
Solution B 1
(a) Quicklime is not used to dry HCl gas because CaO is alkaline.
(b) When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid below 200oC one of the product formed is sodium hydrogen sulphate.
Solution B 2
(a) Manganese dioxide
(b) Hydrogen chloride and ammonia
(c) Hydrogen and oxygen
(d) AgCl(Silver chloride)
(e) Aqua regia
(f) Fountain experiment
(g) Hydrogen chloride gas
(h) Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
(i) Hydrogen chloride
(j) Hydrogen reacts with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride.
Solution B 3
(a) When potassium sulphite is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, sulphur dioxide gas is evolved.
![]()
(b) When concentrated hydrochloric acid is made to react with manganese dioxide, chlorine gas is evolved.
![]()
Solution B 4
A is Silver nitrate
B is Hydrochloric acid
C is Silver chloride
Solution B 5
Aqua regia contains one part by volume of conc. nitric acid and three parts by volume of conc. hydrochloric acid.
Solution C 1
|
S.No. |
Substances added |
Gas evolved |
Odour |
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium ribbon
Manganese(IV) oxide with heating
Sodium sulphide |
Carbon dioxide
Hydrogen
Cl2
Hydrogen sulphide |
Odourless
Odourless
Strong Pungent odour
Rotten egg |
Solution C 2
(a) NH4OH + HCl ![]() NH4Cl + H2O
NH4Cl + H2O
(b) NaHSO3 + HCl![]() NaCl + H2O + SO2
NaCl + H2O + SO2
(c) Pb(NO3)2 +2HCl ![]() PbCl2 +2HNO3
PbCl2 +2HNO3
(d) Pb3O4 + 8HCl ![]() 3PbCl2 +4H2O +Cl2
3PbCl2 +4H2O +Cl2
Solution C 3
A mixture having three parts of conc. Hydrochloric acid and one part of conc. Nitric acid is called aqua-regia.
Nitric acid acts as oxidizing agent.
Solution C 4
(a) Sodium carbonate on treating with dil.HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of carbon dioxide gas.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
Sodium sulphite on treating with dil.HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of sulphur dioxide gas.
Na2SO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 ↑
(b) Sodium thiosulphate reacts with dil. HCl to produce sulphur dioxide gas and precipitates yellow sulphur.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 + S↓
Sulphur is not precipitated when sulphites are treated with dil.HCl.
Solution C 5
MnO2, PbO2 and red lead react with conc. HCl acid to liberate Cl2. This shows that hydrochloric acid is oxidized to chlorine by oxidizing agents.
Solution C 6
Equations for the reactions of hydrochloric acid on
(a) silver nitrate solution
![]()
(b) magnesium foil
![]()
(c) caustic soda solution
![]()
(d) zinc carbonate
![]()
(e) manganese (IV) oxide
![]()
(f) copper oxide
![]()
Solution C 7
(a) Fe +2HCl ![]() FeCl2 +H2
FeCl2 +H2
(b) NaHCO3 + HCl ![]() NaCl + H2O + CO2
NaCl + H2O + CO2
(c) FeS + 2HCl ![]() FeCl2 + H2S
FeCl2 + H2S
(d) ![]()
Solution C 8(a)
Add AgNO3 to both dilute HCl and dilute HNO3 solutions. If white ppt of AgCl is formed then HCl and no ppt indicates HNO3.
HCl + AgNO3 → AgCl ↓ + HNO3
Solution C 8(b)
Two gases which can be used in the study of the fountain experiment are hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas.
The common property demonstrated by fountain experiment:
Highly soluble nature of hydrogen chloride and ammonia gas in water.
The acidic and alkaline property of gases when litmus solution is added to the reaction mixture and shows the colour change by the gas dissolved in water.
Solution C 9(a)
Hydrogen sulphide gas is evolved which has the smell of rotten eggs.
Solution C 9(b)
A white precipitate of silver chloride is formed which is soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
Solution C 9(c)
When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to lead nitrate solution a white coloured ppt of lead chloride appears.
Pb(NO3)2 + HCl ⟶ PbCl2 + 2HNO3
Solution C 9(d)
When small piece of zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas observed.
Solution C 9(e)
Dilute HCl is added to sodium carbonate crystals:
Sodium carbonate crystals on reaction with dilute HCl form sodium chloride, water and carbon dioxide gas, which is evolved with brisk effervescence. This is a neutralisation reaction because sodium carbonate is a basic salt, while hydrochloric acid is an acid. The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
![]()
Solution C 9(f)
(i) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to lead nitrate solution and the mixture is heated:
Dil. HCl does not normally react with nitrates. However, lead nitrate and mercury (I) nitrate react with hydrochloric acid to give white precipitate of lead chloride and mercury (I) chloride.
Pb(NO3)2 + 2HCl → PbCl2↓ + 2HNO3
Precipitate of lead chloride dissolves on heating.
(ii) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium thiosulphate:
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with thiosulphates to produce sulphur dioxide gas and yellow sulphur is precipitated.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 + S↓
Reaction distinguishes thiosulphates and sulphites as sulphur is not precipitated when sulphites are treated with dilute HCl.
Solution C 10
(a) Sodium thiosulphate is reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid:
![]()
(b) Calcium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid:
![]()
(c) Conc. hydrochloric acid and potassium permanganate solution:
![]()
(d) Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium sulphide:
![]()
(e) Action of hydrochloric acid on sodium bicarbonate.
NaHCO3(s) + HCl(l)→ NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Solution C 11
Balanced equations with conditions for the following conversions:
(a) Sodium chloride → Hydrogen chloride
![]()
(b) Hydrogen chloride → Iron (II) chloride
![]()
(c) Hydrogen chloride → Ammonium chloride
![]()
(d) Hydrogen chloride → Lead chloride
![]()
Solution C 12
(a) Anhydrous HCl is poor conductor due to the absence of ions in it whereas aqueous HCl is excellent conductor since it contains ions.
(b) When the stopper is opened HCl gas comes in contact with water vapors of air and gives white fumes due to the formation of hydrochloric acid.
(c) A solution of HCl in water gives hydronium ions and conducts electricity, but HCl is also soluble in dry toluene, but in that case it neither (i) turns blue litmus red (ii) nor does conducts electricity. This indicates the absence of H+ ions in toluene showing thereby that hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound.
(d) When ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of HCl, dense white fumes are formed due to the formation of ammonium chloride.
HCl + NH4OH ![]() NH4Cl + H2O
NH4Cl + H2O
(e) Dry hydrogen chloride is not acidic whereas moist Hydrogen chloride is acidic. In presence of a drop of water HCl gas dissolves in water and forms hydrochloric acid which turns blue litmus paper red.
(f) Hydrogen chloride is not collected over water as it is highly soluble in water.
(g) b. Dilute hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated by boiling beyond 22.2% because molecules of HCl(g) get mixed with water vapour.
Solution C 13
Because HCl undergoes a chemical reaction with quick lime.
2HCl + CaO → CaCl2 + H2O
Solution D 1
(a) Concentrated H2SO4
(b) The balanced equation for the reaction: ![]()
(c) The drying agent used in drying hydrogen chloride gas is conc. sulphuric acid.
(d) Phosphorous pentoxide and calcium oxide are good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas because they react with hydrogen chloride.
![]()
(e) Hydrogen chloride gas is highly soluble in water. Therefore, it is not collected over water.
(f) The funnel arrangement is done to dissolve HCl gas in water.
Solution D 2
(a) Hydrochloric acid is prepared by this method.
(b) The reactants are sodium chloride and Sulphuric acid.
(c) The empty flask acts as Anti-Suction device. In case the back suction occurs the water will collect in it and will not reach the generating flask.
(d) The drying agent is Conc. Sulphuric acid. Sulphuric acid is chosen as drying agent because it does not react with HCl.
(e) The Inverted funnel :
Prevents or minimizes back suction of water.
Provides a large surface area for absorption of HCl gas.
Solution D 3
We can prove that hydrochloric acid contains both hydrogen and chlorine by the following experiment.
Take a voltameter used for electrolysis of water, fitted with platinum cathode and graphite anode.
Into the voltameter pour 4 molar HCl and pass direct current.
It is seen that a colourless gas is evolved at cathode and a greenish gas is evolved at anode.
When a burning splinter is brought near a colourless gas, it bursts into flame thereby proving that it is hydrogen gas.
When moist starch iodide paper is held in the greenish yellow gas, it turns blue black, thereby proving that the gas is chlorine.
2HCl ? H2 + Cl2
This experiment proves that hydrochloric acid contains both hydrogen and chlorine.
Solution D 4
Three tests are:
HCl gas gives thick white fumes of ammonium chloride when glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near the vapours of the acid.
NH3 + HCl ![]() NH4Cl
NH4Cl
With silver nitrate HCl gives white precipitate of silver chloride. The precipitate is insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
AgNO3 + HCl ![]() AgCl + HNO3
AgCl + HNO3
A greenish yellow gas is liberated when concentrated hydrochloric acid is heated with oxidizing agent like manganese dioxide.
MnO2 + 4HCl ![]() MnCl2 +2H2O + Cl2
MnCl2 +2H2O + Cl2
Solution D 5
Conversion of metallic nitrates to insoluble metallic chlorides using dil. HCl:
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
Solution D 6
NaCl + H2SO4![]() NaHSO4 + HCl
NaHSO4 + HCl
Fe + 2HCl ![]() FeCl2 + H2
FeCl2 + H2
HCl + NH3 ![]() NH4Cl
NH4Cl
PbO2 + 4HCl ![]() PbCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
PbCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Solution D 7
(a) Diagram to show the arrangement used for the absorption of HCl gas in water:
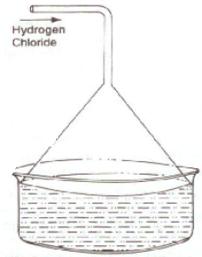
(b) Such an arrangement is necessary to prevent back suction of water into the apparatus and it provides a large surface area for dissolution of hydrogen chloride gas.
(c) Balanced chemical equations for the laboratory preparation of HCl gas:
![]()
![]()
Solution D 8
(a) The gas is HCl (hydrogen chloride) gas.
(b) The extreme solubility of hydrogen chloride gas is demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
(c) Another gas which has the same property and can be demonstrated through this experiment is ammonia gas.
Solution D 9
(a) ![]()
(b) For purification of HCl, it is dried by passing through conc. Sulphuric acid. It is preferred over the other drying agent because it does not react with HCl
(c) i. Temperature should be maintained at nearly 200oC.
ii. Delivery tube should be dipped in drying agent i.e., conc. H2SO4.
iii. The lower end of the thistle funnel must be dipped in conc. Sulphuric acid.
Solution D 10
NA

