Class 10 SELINA Solutions Chemistry Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry
Analytical Chemistry Exercise Intext 1
Solution 1
(i) Analysis: The determination of chemical components in a given sample is called analysis.
(ii) Qualitative analysis: The analysis which involves the identification of the unknown substances in a given sample is called qualitative analysis.
(iii) Reagent:A reagent is a substance that reacts with another substance.
(iv) Precipitation: It is the process of formation of an insoluble solid when solutions are mixed. The solid thus formed is called precipitate.
Solution 2
(i) Yellow
(ii) Colourless
(iii) PaleGreen
(iv) Colourless
Solution 3
a. Pb2+
b. Cu2+
Solution 4
|
Name of solution |
Soluble metal hydroxides |
Insoluble metal hydroxides |
|
Caustic soda solution |
Zn(OH)2 Pb(OH)2 |
Fe(OH)3 |
|
Ammonium hydroxide solution |
Zn(OH)2 Cu(OH)2 |
Fe(OH)3 Fe(OH)2 |
Solution 5
When ammonium salt is heated with caustic soda solution, ammonia gas is evolved.
The word equation is:
Ammonium chloride + Sodium hydroxide ![]() Sodium chloride + water + ammonia
Sodium chloride + water + ammonia
Ammonium sulphate + Sodium hydroxide ![]() Sodium sulphate + water + ammonia
Sodium sulphate + water + ammonia
The balance equation is:
NH4Cl+NaOH![]() NaCl+H2O+NH3↑
NaCl+H2O+NH3↑
(NH4)2SO4 + 2NaOH ![]() Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2NH3↑
Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2NH3↑
Solution 6
NH4OH and NaOH can be distinguished by using calcium salts.
For example on adding NaOH to Ca(NO3)2, Ca(OH)2 is obtained as white precipitate which is sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
Ca(NO3)2+2NaOH![]() Ca(OH)2+2NaNO3
Ca(OH)2+2NaNO3
On addition of NH4OH to calcium salts, no precipitation of Ca(OH)2 occurs even with the addition of excess of NH4OH.This is because the concentration of OH- ions from the ionization of NH4OH is so low that it cannot precipitate the hydroxide of calcium.
Solution 7
If an alkali is added too quickly, then it is easy to miss a precipitate which redissolves in excess alkali.
Solution 8
(a) 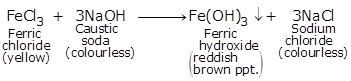
(b) 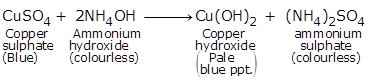
Analytical Chemistry Exercise Ex. 4
Solution A
1. (iii)
Aqueous solution of copper sulphate is blue.
2. (iii)
FeSO4 + 2NaOH → Fe(OH)2 + Na2SO4
(Dirty green, (Colourless)
gelatinous ppt.)
3. (iii)
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
Sodium zincate
(Colourless)
Zz Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
4. Option (i)
The salt solution which does not react with ammonium hydroxide is calcium nitrate.
Solution B 1
(a) Cu(OH)2
(b) ZnO
(c) NaOH
(d) NH4OH
(e) Na+, Ca2+
(f) Fe2+, Mn2+
(g) Aluminium
(h) Zn(OH)2 and Al(OH)3
(i) PbO
(j) Ammonium ion
(k) PbO
(l) ZnO
(m) K2ZnO2
Solution B 2
(a) Ferrous salts: Light green
(b) Ammoniumsalts: Colourless
(c) Cupric salts: Blue
(d) Calcium salts: Colourless
(e) Aluminium salts: Colourless
Solution C 1
Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.

Solution C 2
(i)
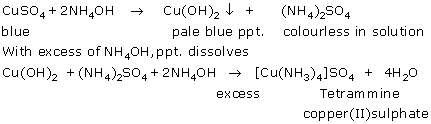
(ii)
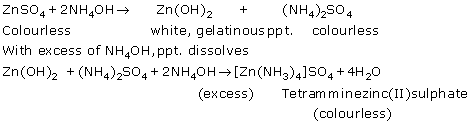
(iii)
![]()
Solution C 3

Solution C 4
When freshly precipitated aluminum hydroxide reacts with caustic soda solution, whitesalt of sodium meta aluminate is obtained.
![]()
Solution C 5
(a) Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
(b) 2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2Na2AlO2 + 3H2
Solution C 6
(a) Sodium hydroxide on reaction with calcium salt gives a milky white precipitate, while that of with lead it gives chalky white precipitate.
(b) Sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide on reaction with lead salt gives brown coloured precipitate, while that of with zinc it forms white gelatin like precipitate.
(c) Sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide on reaction with Copper salt gives pale blue coloured precipitate, while that of with ferrous salt solution it forms dirty green coloured precipitate.
(d)Sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide on reaction with Fe(II) salt gives dirty green coloured precipitate, while that of with Fe(III) salt solution it forms reddish brown insoluble precipitate.
(e) Ammonium hydroxide on reaction with lead nitrate gives a chalky white insoluble precipitate, while that of with ferrous nitrate will not give any precipitation.
Solution C 7
Add sodium hydroxide solution to each of the solutions. The solution in which a white precipitate soluble in excess of sodium hydroxide is Zinc nitrate and the one which forms a white precipitate insoluble in excess of sodium hydroxide is Calcium nitrate.
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Ca(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
Ca(OH)2 is sparingly soluble salt.
Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Zn(OH)2 + 2NaOH
Zn(OH)2 is gelatinous white soluble
(with excess of NaOH ppt of Zn(OH)2 dissolves.)
Zn(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + 2H2O
(excess) Sodium zincate (colouless)
(Disclaimer: the qus. no. in TBS is 5 instead of 7)
Solution D 1
Reagent bottles A and B can identified by using calcium salts such as Ca(NO3)2.
On adding NaOH to Ca (NO3)2, Ca (OH) 2 is precipitated as white precipitate which is sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
Ca(NO3)2+2NaOH![]() Ca(OH)2+2NaNO3
Ca(OH)2+2NaNO3
Whereas, on addition of NH4OH to calcium salts, no precipitation of Ca(OH)2 occurs even with addition of excess of NH4OH because the concentration of OH-ions from the ionization of NH4OH is so low that it cannot precipitate the hydroxide of calcium.
So the reagent bottle which gives white precipitate is NaOH and the other is NH4OH.
Solution D 2
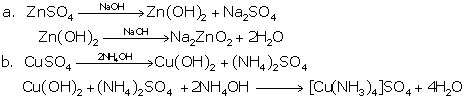
Solution D 3
(a) Amphoteric oxides are compounds which react with both acids and alkalis to form salt and water.
(b) ZnO + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
(c) Sodium zincate
Aluminium zincate
Solution D 4
(a) ZnCl2
(b) Zn(OH)2
(c) Dilute ammonia means ammonium hydroxide. Therefore, the balanced chemical equation involved in the above reaction is as follows:
ZnCl2 + 2NH4OH → Zn(OH)2 + 2NH4Cl

