Class 10 SELINA Solutions Biology Chapter 10 - The Nervous System
The Nervous System Exercise Ex. 1
Solution A.1
(d) Neuron
Solution A.2
(c) Centrosome
Solution A.3
(c) 12, 31 pairs
Solution A.4
(c) Cerebellum
Solution A.5
(b) Ventricle
Solution A.6
(a) Nerve cell
Solution A.7
(c) Arachnoid
Solution A.8
(b) Stimulus
Solution A.9
(b) Cerebral cortex
Solution A.10
(c) Axons
Solution B.1
(a) Cerebrospinal fluid
(b) Synapse
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Ventricle
Solution B.2
(a) Stimulus : Receptor :: Impulse : Effector
(b) Cerebrum : Diencephalon :: Cerebellum : Medulla oblongata
(c) Receptor : Sensory nerve :: Motor nerve : Effector
(d) Axons : Nerve :: Cytons : Nerve cells
(e) Cerebrum : Corpus callosum :: Cerebellum : Pons
Solution B.3
(a) Gray matter (Rest are coverings of meninges)
(b) Spinal cord (Rest are parts of brain)
(c) Pons (Rest are parts of neuron)
(d) Hypothalamus (Rest are parts of hindbrain)
(e) Knitting without looking (Rest are examples of natural/inborn reflexes)
Solution C.1
(a) Corpus Callosum - It is located located in the forebrain. It connects two cerebral hemispheres and transfers information from one hemisphere to other.
(b) Central canal - It is located in centre of the spinal cord. It is in continuation with the cavities of the brain. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and acts as shock proof cushion. In addition, it also helps in exchange of materials with neurons.
Solution C.2
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) True
Solution C.3
|
Example |
Type of Reflex |
|
(i) Sneezing |
Simple |
|
(ii) Blushing |
Simple |
|
(iii) Contraction of eye pupil |
Simple |
|
(iv) Lifting up a book
|
Conditioned |
|
(v) Knitting without looking |
Conditioned |
|
(vi) Sudden application of brakes of the cycle on sighting an obstacle in front |
Conditioned |
Solution C.4
(a) Association neuron: It acts as a connecting neuron and interconnects the sensory and motor neurons.
(b) Myelin sheath: It acts like an insulation and prevents mixing of impulses in the adjacent axons.
(c) Medullary sheath: It provides insulation and prevents mixing of impulses in the adjacent axons.
(d) Cerebrospinal fluid: It acts like a cushion and protects the brain from shocks.
Solution C.5
(a) Stimulus --- receptor --- sensory neuron --- central nervous system --- motor neuron --- effector --- response
(b) Resting --- depolarization --- repolarization
(c) Dendrites --- Dendron --- perikaryon --- nucleus --- axon --- axon endings
(d) Cerebrum --- diencephalon --- mid-brain --- cerebellum --- pons --- medulla oblongata
Solution C.6
(a) Three types of neurons:
1. Sensory neurons
2. Motor neurons
3. Association neurons
(b) Three types of nerves:
1. Sensory nerves
2. Motor nerves
3. Mixed nerves
(c) Three main parts of the neuron:
1. Cyton
2. Dendrites
3. Axon
(d) Two major divisions of the nervous system:
1. Central nervous system
2. Peripheral nervous system
(e) Three layers of the meninges:
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid
3. Pia mater
(f) Three main parts of the brain:
1. Cerebrum
2. Cerebellum
3. Medulla oblongata
(g) Two parts of the autonomic nervous system:
1. Sympathetic nervous system
2. Parasympathetic nervous system
(h) Two types of reflexes:
1. Natural (inborn) reflex
2. Conditioned (acquired) reflex
Solution C.7
(a) CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid
(b) CNS: Central Nervous System
(c) PNS: Peripheral Nervous System
(d) ANS: Autonomic Nervous System
Solution D.1
(a) Neuron: Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system specialized to transmit information in the form of electrical impulses to different parts of the body.
(b) Nerve: Nerve is a bundle of nerve fibres (axons) of separate neurons, enclosed in a tubular sheath.
(c) Stimulus: An agent or the sudden change of the external or internal environment that results in a change in an organism or any of its body parts is called a stimulus.
(d) Synaptic cleft: The gaps between the axon terminals and the dendrites of another one or more neurons are called synaptic clefts.
(e) Reflex action: Reflex action is an automatic or quick or immediate involuntary action in the body brought about by a stimulus.
(f) Corpus callosum: Corpus callosum is a sheet of fibres connecting the two cerebral hemispheres.
Solution D.2
(a) Differences between cerebrum and cerebellum (function):
|
Cerebrum |
Cerebellum |
|
The cerebrum controls all voluntary actions. It enables us to think, reason, plan and memorize. |
The cerebellum on the other hand maintains balance of the body and coordinates muscular activity. |
(b) Differences between sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system (location and role):
|
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|
Sympathetic nervous system is located between the neck and the waist region. |
Parasympathetic nervous system is located in the head and neck region and in sacral region. |
|
It prepares the body for violent action against the abnormal condition. |
It is concerned with re-establishing normal conditions after the violent act is over. |
(c) Differences between sensory nerve and motor nerve (direction of impulse carried):
|
Sensory Nerve |
Motor Nerve |
|
Sensory nerve brings impulses from the receptors i.e. sense organs to the brain or spinal cord. |
Motor nerve carries impulse from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs such as muscles or glands. |
(d) Differences between cerebrum and spinal cord (arrangement of cytons and axons of neurons):
|
Cerebrum |
Spinal Cord |
|
The grey matter containing cytons lies in the cortex (outer region) while the white matter containing axons lies in the medullary region (inner region). |
The grey matter containing cytons lies in the medullary region i.e. inner side while the white matter containing axons lies in the cortex i.e. the outer region. |
(e) Differences between cranial nerves and spinal nerves (number in pairs):
|
Cranial Nerves |
Spinal Nerves |
|
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves. |
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. |
(f) Differences between nerve impulse and flow of electricity (transmission and speed):
|
Nerve impulse |
Flow of electricity |
|
Here, neither any substance nor any electrons or ions move along the nerve fibre. |
Here, electrons actually move along the wire. |
|
Nerve impulses travel at a speed of about 100 metres per second. |
Electricity is conducted at a speed of about 150,000 km per second. |
(g) Differences between medulla oblongata and cerebellum (function):
|
Medulla Oblongata |
Cerebellum |
|
Medulla oblongata controls the activities of internal organs and many other involuntary actions |
The cerebellum maintains balance of the body and coordinates muscular activity. |
Solution D.3
|
Organ |
Sympathetic System |
Parasympathetic System |
|
e.g. Lungs |
Dilates bronchi and bronchioles |
Constricts bronchi and bronchioles |
|
1. Heart |
Accelerates heartbeat |
Retards heartbeat |
|
2. Pupil of the eye |
Dilates |
Constricts |
|
3. Salivary gland |
Inhibits the secretion of saliva causing the drying of the mouth |
Stimulates the release of saliva |
Solution D.4
(a) The brain and the spinal cord lie in the skull and the vertebral column respectively. They have an important role to play because all bodily activities are controlled by them. A stimulus from any part of the body is always carried to the brain or spinal cord for the correct response. A response to a stimulus is also generated in the central nervous system. Therefore, the brain and the spinal cord are called the central nervous system.
(b) Neurotransmitters are broken down by an enzyme just after passing an impulse from one neuron to the other to make the synapse ready for the next transmission of impulse.
Solution D.5
Myelinated neuron
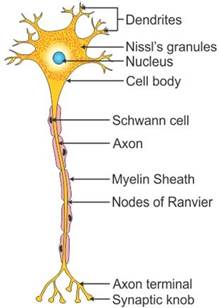
Solution D.6
The advantages of having a nervous system are as follows:
(a) Keeps us informed about the outside world through sense organs.
(b) Enables us to remember, think and reason out.
(c) Controls and harmonizes all voluntary muscular activities such as running, holding, writing
(d) Regulates involuntary activities such as breathing, beating of the heart without our thinking about them.
Solution D.7
Differences between reflex action and voluntary action:
|
Reflex action |
Voluntary action |
|
1. Reflex actions are involuntary actions which occur unknowingly. |
1. Voluntary actions are performed consciously. |
|
2. Commands originate mostly in the spinal cord and autonomic nervous system and a few in the brain as well. |
2. Commands originate in the brain. |
|
3. Involves muscles and glands |
3. Involves only muscles |
|
4. Mainly self-protective due to the environment. |
4. Mainly for fulfilment of a desired goal. |
|
5. Initiated by some stimulus. |
5. Initiated by a willing thought |
Solution E.1
Salivation is an example of conditioned reflex that develops due to experience or learning. Saliva starts pouring when you chew or eat food. Therefore, this reflex will occur not just on the sight or smell of food. The brain actually needs to remember the taste of food. Boy B started salivating because he must have tasted that food prior unlike boy A.
Solution E.2
(a) 1 - Cerebrum, 2 - Cerebellum, 3 - Pons, 4 - Medulla oblongata.
(b) Meninges. The three layers of meninges are dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater.
(c) Neuron/nerve cell.
(d) Cerebellum (part 2) coordinates muscular activity and balance of the body.
Solution E.3
(a) The phenomenon shown in the figure is spinal reflex action. It is an automatic, quick, immediate, involuntary action in the body brought about by a stimulus.
(b) 1 - Sensory neuron, 2 - Motor neuron.
Sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting sensory impulses from sensory organs (receptors) to the central nervous system.
Motor neurons are in charge of transmitting motor commands from the central nervous system to the effector organs (muscle/gland) in order to initiate responses.
(c) Vertebrae is the bony protective covering and meninges is the membranous protective covering of spinal cord.
(d) 3 - Gray matter, 4 - White matter
(e) Gray matter is made up of cell bodies of neurons, while white matter primarily consists of axons of neurons.
(f) The point of contact between two nerve cells is called a synapse.
(g) The fluid filled inside the central canal of spinal cord is called cerebrospinal fluid.
(h) The small gap between two neurons is called synaptic cleft.
(i) Acetylcholine is an example of a neurotransmitter.
(j) Nerve cell
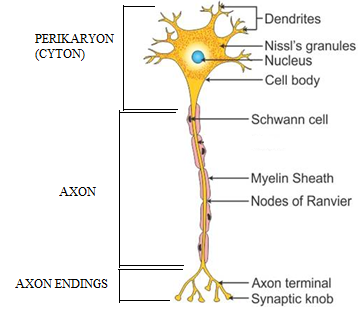
Solution E.4
(a) The given diagram is of a 'nerve cell' or 'neuron'.
(b) Nerve cells are found in the brain and spinal cord of our nervous system.
(c) Neurons or nerve cells have the ability to detect, receive, and transmit a wide range of stimuli. They are capable of responding to both physical and chemical stimuli. They are required for every movement performed by our body and brain.
(d) Centrosome is absent in the nerve cells. Centrosomes are the organelles which play an important role in cell division. There is absence of centrioles in the nerve cells and because of this they are unable to perform mitosis and meiosis and hence these cells do not divide.
(e) Nerve cell

Solution E.5
1 - Central Nervous System
2 - Autonomic
3 - 12
4 - spinal
5 - 31
6 - neck
7 - waist
8 - dilates
9 - constricts
10 - liver
11 - neck
12 - sacrum

