Class 10 SELINA Solutions Biology Chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals Exercise Ex. 1
Solution A.1
a) 3 : 1
Solution A.2
(a) all tall
Solution A.3
(c) independent assortment
Solution A.4
(c) Gs and gs
Solution A.5
(a) Recessive X-linked disease
Solution A.6
(c) Phenotype
Solution A.7
(c) Law of segregation
Solution A.8
(d) 9:3:3:1
Solution A.9
(c) X or Y chromosome
Solution A.10
(c) Carrier
Solution B.1
|
Column I (Term) |
Column II (Answers) (Explanation) |
|
|
a |
Genetics |
(iii) Study of laws of inheritance of characters |
|
b |
Autosomes |
(v) Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes |
|
c |
Recessive gene |
(iv) A gene that can express when only in a similar pair |
|
d |
Allele |
(ii) The alternative forms of a gene |
|
e |
Homologous chromosomes |
(i) Chromosomes similar in size and shape |
Solution B.2
Colour-blindness, Thalassaemia, Sickle cell anaemia and Haemophilia (Any two)
Solution B.3
Homozygous dominant - RR
Homozygous recessive - rr
Solution C.1
(a) Duplicated chromosomes remain attached at a point termed as centromere.
(b) The full complement of DNA of an organism is termed as genome.
(c) The inheritable feature of an organism is termed as character.
(d) Axial flower position is a dominant trait of pea flower.
(e) Alternative forms of a gene are called alleles.
Solution C.2
The characteristics of a species such as physical appearance, body functions and behavior are not only the outcome of chromosome number, but these depend on the genotype of every organism. That means the set of genes present in the organisms may very and therefore lion, tiger and domestic cat have the same number of 38 chromosomes, their characteristics (like different appearances) are the result of the genes located on the chromosomes.
Solution C.3
Features of garden pea with their dominant and recessive traits: (Any 3)
|
Character |
Dominant trait |
Recessive trait |
|
Flower Colour |
Purple |
White |
|
Seed Colour |
Yellow |
Green |
|
Seed Shape |
Round |
Wrinkled |
|
Pod Shape |
Inflated |
Constricted |
|
Flower Position |
Axial |
Terminal |
|
Pod colour |
Green |
Yellow |
|
Plant height |
Tall |
Dwarf |
Solution C.4
Colour-blindness is caused due to recessive genes which occur on the X chromosome.
Males have only one X chromosome. If there is recessive gene present on X chromosome, then the male will suffer from colour-blindness.
Females have two X chromosomes. It is highly impossible that both the X chromosomes carry abnormal gene. Hence, if one gene is abnormal and since it is recessive, its expression will be masked by the normal gene present on the other X chromosome. Females are unlikely to suffer from colour-blindness.
Solution D.1
(a) Pedigree chart: A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next. In the pedigree chart, males are shown by squares and females by circles.
(b) Variations: The small differences among the individuals of the same species are called variations.
(c) Mutation: Mutation is a sudden change in one or more genes, or in the number or in the structure of chromosomes.
Solution D.2
Mendel's laws of inheritance are:
(i) Law of Dominance: Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one is able to express itself while the other remains suppressed. The one that expresses is the dominant character and the one that is unexpressed is the recessive one.
(ii) Law of Segregation: The two members of a pair of factors separate during the formation of gametes. The gametes combine together by random fusion at the time of zygote formation. This law is also known as 'law of purity of gametes'.
(iii) Law of Independent Assortment: When there are two pairs of contrasting characters, the distribution of the members of one pair into the gametes is independent of the distribution of the other pair.
Solution D.3
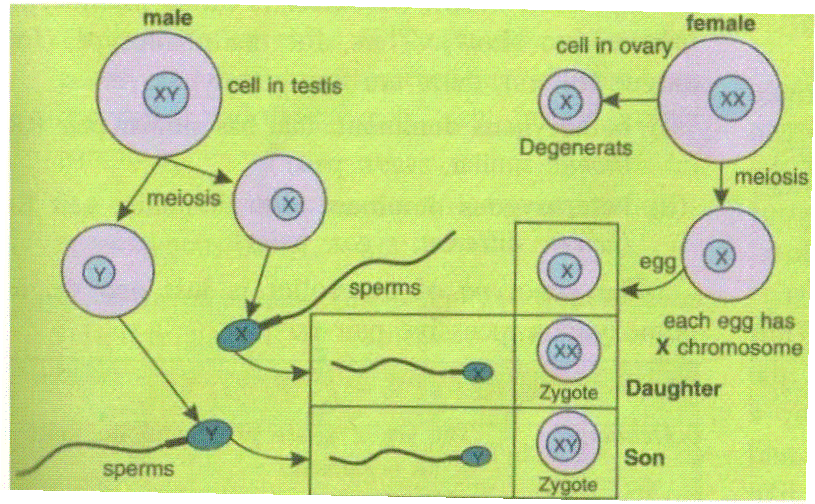
The sex of the child depends on the father. The egg contains only one X chromosome, but half of the sperms contain X-chromosome whereas the other half contains Y-chromosome. It is simply a matter of chance as to which category of sperm fuses with the ovum and this determines whether the child will be male or female.
If the egg fuses with X-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XX and the resulting child is female.
If the egg fuses with Y-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XY and the resulting child is male.
Solution D.4
(a) Differences between karyotype and karyokinesis:
|
Karyotype |
Karyokinesis |
|
The complete set of chromosomes in the cells of an organism is its karyotype. |
The division of the nucleus during mitosis is called karyokinesis. |
(b) Differences between autosomes and sex chromosomes:
|
Autosomes |
Sex chromosomes |
|
1. They determine the somatic traits. |
1. They determine the sex of an organism. |
|
2. They are numbered as 1 to 22. |
2. They are recognized by the letters XO, XY, ZO, ZW. |
|
3. They show Mendelian inheritance. |
3. They do not show Mendelian inheritance. |
|
4. Human show 22 pairs of autosomes. |
4. Humans show only 1 pair of sex chromosome. |
(c) Differences between homozygous and heterozygous chromosomes:
|
Homozygous chromosomes |
Heterozygous chromosomes |
|
It has two same copies of the same allele coding for a particular trait. |
It contains two different copies of alleles coding for a particular trait. |
Solution E.1
|
B |
b |
|
|
B |
BB |
Bb |
|
b |
Bb |
bb |
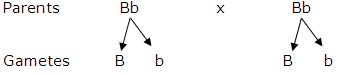
Genotype - 1 BB (Homozygous Black) : 2 Bb (Heterozygous Black) :1 bb (Homozygous Brown)
Phenotype - 3 (Black Fur) : 1 (Brown Fur)
Solution E.2
(a) Black
(b) No
Solution E.3
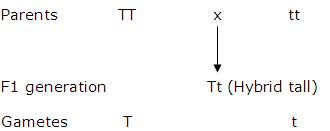
(a) Cross between a pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant
F2 generation -
|
Gametes |
T |
t |
|
T |
TT |
Tt |
|
t |
Tt |
tt |
Genotype - 1 TT (Homozygous tall) : 2 Tt (Heterozygous tall) :1 tt (Homozygous dwarf)
Phenotype - 3 (Tall) : 1(Dwarf)
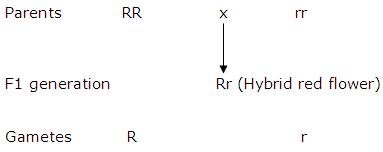
(b) Cross between a red flower variety of pea (RR) with a white flower variety of pea (rr)
F2 generation -
|
Gametes |
R |
r |
|
R |
RR |
Rr |
|
r |
Rr |
rr |
Genotype - 1 RR (Homozygous red) : 2 Rr (Heterozygous red) :1 rr (Homozygous white)
Phenotype - 3 (Red) : 1(White)
Solution E.4
(a) Seed shape is studied in the experiment.
(b) Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
(c) The F1 offspring are round seeds (phenotype) with a genotype as Rr.
(d) The above cross involves law of dominance.
Law of Dominance - Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one is able to express itself while the other remains suppressed. The one that expresses is the dominant character and the one unexpressed is the recessive. The recessive character can express only when the pair consists of both recessives (homozygous recessive).
(e) Rr × Rr
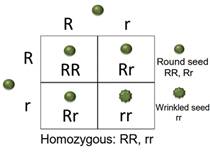
(f) Phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny is 3:1.
(g) Genotypic ratio of F2 offspring is 1:2:1.
(h) Yellow and green are two traits of seed colour. Yellow colour is dominant and green colour is recessive.
(i) The scientific name of garden pea is Pisum sativum.
(j) Mendel selected pea plant for his hybridisation studies because of the following features:
1. Many varieties were available in alternative forms of a character.
2. The life span of a pea plant is short, and many generations can be obtained and studied in less time.
Solution E.5
The cross can be depicted as follows:
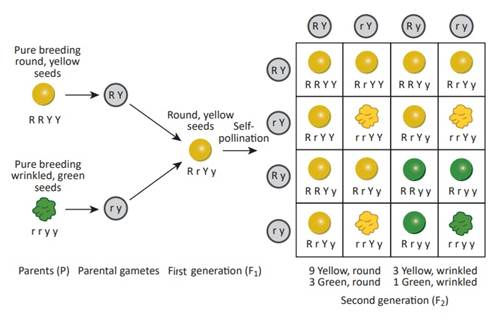
(a) The genotype of the F1 generation is RrYy.
(b) The phenotype of the F1 offspring is round and yellow seeds.
(c) The possible combinations of gametes that can be obtained from F1 hybrids are RY (Round yellow), rY (Wrinkled yellow), Ry (Round green) and ry (Wrinkled green).
(d) When two plants of F1 generation are crossed, F2 generation of plants is obtained in the phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 where the phenotypes of the offspring are round and yellow, round and green, wrinkled and yellow and wrinkled and green respectively.
(e) The law of independent assortment explains the dihybrid phenotypic ratio.
Law of independent assortment: When there are two pairs of characters, the distribution of the alleles of one character into the gametes is independent of the distribution of the alleles of the other character.