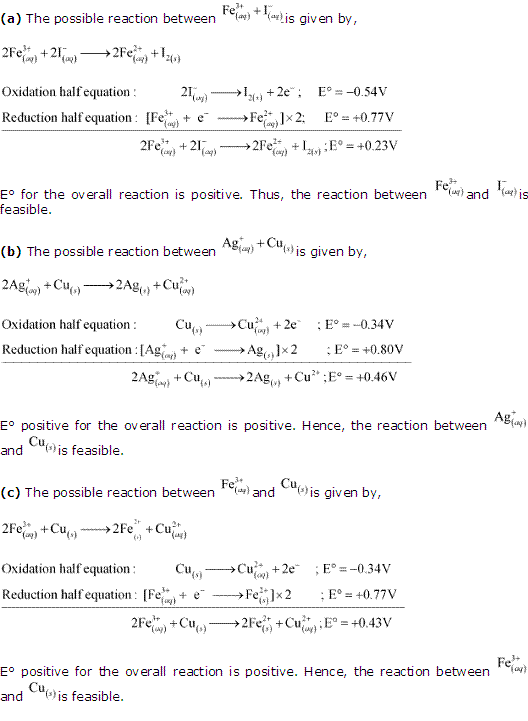
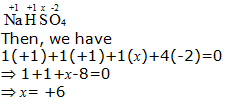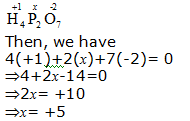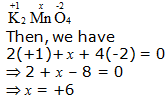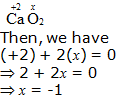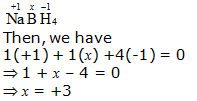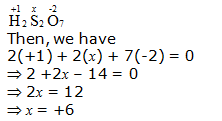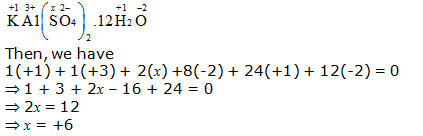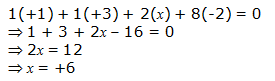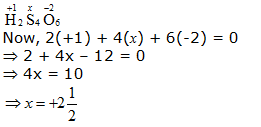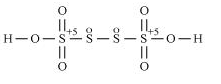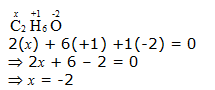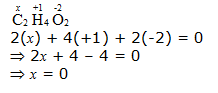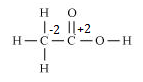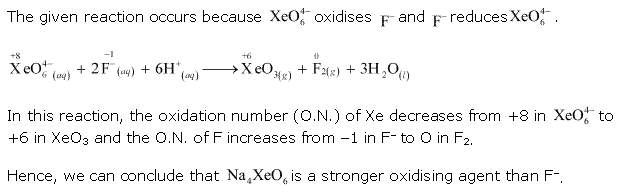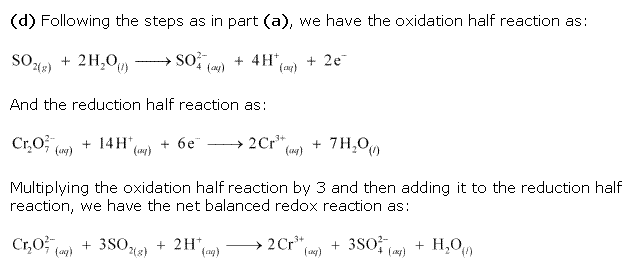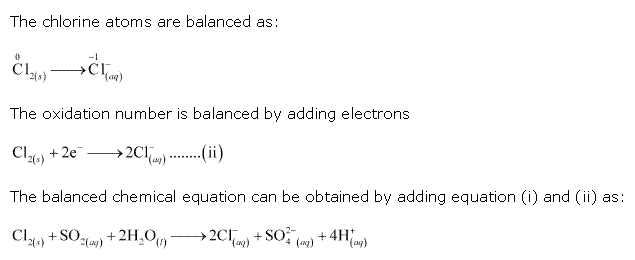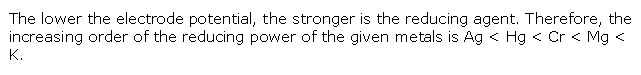Class 11-science NCERT Solutions Chemistry Chapter 7 - Redox Reactions
Redox Reactions Exercise 252
Solution 1
a. NaH2PO4
Let the oxidation number of P be x.
We know that,
Oxidation number of Na = +1
Oxidation number of H = +1
Oxidation number of O = –2
![]()
Then, we have
1(+1) +2(+1)+1(x)+4(-2) =0
![]() 1+2+x-8 = 0
1+2+x-8 = 0
![]() x = +5
x = +5
Hence, the oxidation number of P is +5.
b. NaHSO4
Hence, the oxidation number of S is + 6.
c. H4P2O7
Hence, the oxidation number of P is + 5.
d. K2MnO4
Hence, the oxidation number of Mn is + 6.
e. CaO2
Hence, the oxidation number of O is – 1.
f. NaBH4
Hence, the oxidation number of B is + 3.
g. H2S2O7
Hence, the oxidation number of S is + 6.
h. KAl(SO4)2.12H2O
Or,
We can ignore the water molecule as it is a neutral molecule. Then, the sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms of the water molecule may be taken as zero. Therefore, after ignoring the water molecule, we have
Hence, the oxidation number of S is + 6.
Solution 2
a. KI3
b. H2S4O6
However, O.N. cannot be fractional. Hence, S must be present in different oxidation states in the molecule.
The O.N. of two of the four S atoms is +5 and the O.N. of the other two S atoms is 0.
c. Fe3O4
On taking the O.N. of O as –2, the O.N. of Fe is found to be ![]() . However, O.N. cannot be fractional.
. However, O.N. cannot be fractional.
Here, one of the three Fe atoms exhibits the O.N. of +2 and the other two Fe atoms exhibit the O.N. of +3.
d. CH3CH2OH
Hence, the O.N. of C is –2.
e. CH3COOH
However, 0 is average O.N. of C. The two carbon atoms present in this molecule are present in different environments. Hence, they cannot have the same oxidation number. Thus, C exhibits the oxidation states of +2 and –2 in CH3COOH.