Class 11-science H C VERMA Solutions Physics Chapter 8 - Work and Energy
Work and Energy Exercise 132
Solution 1
![]()
Change in K.E. = ![]() m[v2-
u2 ]
m[v2-
u2 ]
= ![]() × 90 × [ 122 - 62 ]
× 90 × [ 122 - 62 ]
= 375J
Solution 2
Final speed v = u + at
= 10 + 3 × 5
v = 25m/s
Now,
![]()
= ![]() × 2 × 252
× 2 × 252
K.E. = 625J
Solution 3
Resisting force
FR = F. d
FR = F d cosƟ = 100 × 4
FR = 400 J
Solution 4
Work done,
W = mgh
= 5 × 9.8 × (sin30![]() × 10)
× 10)
W = 245 J
Solution 5
W = F.d
W = Fd cosƟ
W = 2.5 × 2.5 × cosƟ
W = 6.25J
Now,
![]()
![]()
v = 28.8 m/s
And F = ma
a = ![]() = 2.5/ 0.015 = 166.66 m/s2
= 2.5/ 0.015 = 166.66 m/s2
So, v = u+at
t = ![]() = 28.8/166.66 = 0.1728 sec
= 28.8/166.66 = 0.1728 sec
And average power, Pw = ![]() = 6.25/0.1728 = 36.1 W
= 6.25/0.1728 = 36.1 W
Solution 6
r = r2 - r1
= (3![]() + 2
+ 2![]() ) - (2
) - (2![]() + 3
+ 3![]() )
)
r = ![]() -
- ![]()
Work done W = F × r
W = (5![]() + 5
+ 5![]() ) × (
) × (![]() -
- ![]() )
)
W = 0
Solution 7
F = ma
W = F.d
W = 1×40
W =40 J
Work and Energy Exercise 133
Solution 8
Work done, W = 0∫d
F dx ( F = a+bx)
W = (a + ![]() bd)d
bd)d
Solution 9
Force = μR and F = mg sin Ɵ
mg sin Ɵ = μR
Work done W = μR cos Ɵ
W = mg sin Ɵ × cos 0 × S
W = 0.25 × 9.8 × 0.60 × 1 × 1
W = 1.5 J
Solution 10
(a) 𝜇k =![]() =
=![]()
μk=![]() (m + M)g
(m + M)g
(b) Fs = μkR = ![]() (m+M)g × mg
(m+M)g × mg
Fs = ![]() (m
+ M)
(m
+ M)
(c) W = Fs d
W = ![]() (m
+ M)
(m
+ M)
Solution 11
(a) R + P sin Ɵ = 2000 ……. 1
P cos Ɵ - 0.2 R = 0……..(2)
Solving 1 and 2 equations we get,
P =![]()
and work done W = PS cos Ɵ
W = ![]()
(b) For minimum force,
![]() [cosƟ + 0.2sinƟ]= 0 (from equation 1)
[cosƟ + 0.2sinƟ]= 0 (from equation 1)
Also, W = 40000/5 +tan Ɵ = 40000/5+0.2
W = 7690 J
Solution 12
Force F = mg sinƟ
F = 100 × sin370 = 60N
(a) Work done W = Fd cosƟ
W = 60 × 2 × cos 0 = 120 J
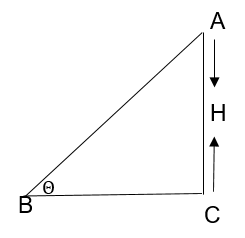
(b) In triangle ABC, AB = 2m, Ɵ = 37o
AC =h = 1.3
work done W = mgh
W = 100 × 1.2
W = 120 J
Solution 13
v2 - u2 = -2as
a = ![]()
a = ![]() × 25 = 8m/s2
× 25 = 8m/s2
frictional force F = ma = 500 × 8
F =4000 N
Solution 14
v2- u2 = 2as
a = ![]()
a = ![]() × 25
× 25
a = 8 m/s2
Force, F = ma = 500 × 8
F = 4000N
Solution 15
v = a ![]()
v1 = 0 and v2 = a
![]()
v22 - v21 = 2a'd
a' =![]() =
= ![]()
Force F = ma| = (ma2)/2
Work done W = Fd cosƟ
W = ![]() × d
× d
W = ![]()
Solution 16
(a) For a free body,
Force F = mg sinƟ + ma
a= ![]()
a= ![]()
a= 4m/s2
s = ut +![]() at2
at2
s = 0 × 1 + ![]() × 4 × 12
× 4 × 12
s = 2m
W = Fs = 20 × 2
W = 40 J
(b) W =Fs
s = ![]() =
= ![]()
s = 2
W = -mgh = -mg [s sin370]
W = -20 × 1.2
W = -24J
(c) v = u + at = 4 × 10
v = 40 m/s
![]()
![]()
K.E. = 16 J
Solution 17
(a) S = ut + ![]() at2
at2
S = 0 + ![]() at2
at2
S =5 m
Work done W = Fs cosƟ = 20 × 5 × 1
W = 100 J
(b) h = S sin Ɵ = S sin370 = 3m
work done, W = mgh = 2 × 10 × 3
W =60 J
(c) Frictional force Ff = mg sinƟ
and work done W = Ff s cosƟ
W = mg sinƟ s sinƟ
W = 20 × 0.60 × 5
W = 60 J
Solution 18
We know,
ma = μR
a = ![]() = μg
= μg
a = 0.1 × 9.8 = 0.98 m/s2
and
v2 - u2 = 2as
s = ![]() = (0 - 0.42)/ 2 × 0.98
= (0 - 0.42)/ 2 × 0.98
s = 0.082 m
Work done
W = -μR sinƟ = - 0.1 × 2.5 × 0.082 × 1
W = - 0.02 J
Solution 19
Potential Energy
P.E. = mgh = 1.8 × 105× 9.8 × 50
P.E. = 882 x 105 J/hr
Electrical energy = ![]() P.E. = 441 × 105 J/hr
P.E. = 441 × 105 J/hr
Power P = (441 × 105)/3600
P = 12.25 × 103 W
No. of 100W lamps that can be lit = (12.25 × 103)/100
Number of lamps = 122.5 ≈ 123
Solution 20
Initial P.E. at height h,
P.Ei = mgh = 6 × 9.8 × 2 = 117.6 J
Final P.E. at the floor,
P.Ef = mgh = 0
P.E. = 117.6 - 0
P.E. = 117.6 J
Solution 21
By law of conservation of energy
mgh + ![]() m vi2 =
m vi2 = ![]() mvf
mvf
10 × 40 +![]() × 502 =
× 502 = ![]() × vf2
× vf2
v =vf = 57.4 m/s
v ≈ 58 m/s
Solution 22
Power, P = ![]() W/t
W/t
W = P × t = 460 × 117.56 …..(1)
Also
W = F × d = F × 200 …..(2)
From 1 and 2
F = (460 × 117.56)/200 = 270.3
F = 270 N
Solution 23
(a) v = ![]() = 100/10.54 m/s
= 100/10.54 m/s
K.E. = ![]() mv2 =
mv2 = ![]() × 50 × 9.4872
× 50 × 9.4872
K.E. = 2250 J
(b) Weight =mg = 50 × 9.8 = -490 J
and work done
W = -R d =![]() × d =
× d = ![]()
W = -4900 J
(c) Power P = ![]() =
=![]()
P = 465 W
Solution 24
![]() = 30 kg/min = 0.5kg/s
= 30 kg/min = 0.5kg/s
and
Power =![]() × g × h = 0.5 × 9.81 × 10
× g × h = 0.5 × 9.81 × 10
P = 49 W
Horse power =![]() = 6.6 × 10-2 hp
= 6.6 × 10-2 hp
Solution 25
Work done W = mgh
+![]() mv2
mv2
W = 0.2 × 9.8 × 1.5 +(![]() × 0.2 × 32)
× 0.2 × 32)
W = 3.84J
Solution 26
W = Fd cosƟ
W = mg cosƟ = 2000 ×10 × 12 × 1
W =24 × 104 J
P =![]() = (24 ×104 )/60 = 4000W
= (24 ×104 )/60 = 4000W
Horse power = P/746 = 4000/746 = 5.3 hp
Solution 27
Max. acceleration,
a = ![]()
a = (50/3 - 0)/5 = 3.33m/s2
Force
F = ma = 95 × 3.33
F = 316.6 N
Velocity
v = ![]() = (3.5 × 746)/316.6
= (3.5 × 746)/316.6
v=8.2 m/s
Solution 28
v2 - u2 = 2as
a = (0.42 - 0)/2 × 2
a = 0.04 m/s2
Force
F = ma - mg
and
Work done
W = Fs cosƟ = m(a-g) s cosƟ
W = 30 (0.04 - 9.8) × 2 × 1
W = -585.5 J ≈ -586 J
Work and Energy Exercise 134
Solution 29
Net force is
T - 2mg + 2ma = 0 ….. 1
T - mg - ma = 0….. 2
from equation 1 and 2
a =![]() =
= ![]()
a = ![]() m/s2
m/s2
Now,
s = ut + ![]() at2
at2
s = 0 + ![]() ×
×![]() × 12
× 12
s = ![]()
Decrease in P.E. = mgh
P.E. = (2m - m) × 9.8 × (2/m)
P.E. = 19.6 J
Solution 30
T - 3g + 3a = 0 1
T - 2g - 2a = 0 2
Solving equation 1 and 2
a = ![]() m/s2
m/s2
Now,
S =![]() (2m - 1)
(2m - 1)
S = ![]() [2 × 4 -1]
[2 × 4 -1]
h = S = 6.86 m
Mass
m = m1 - m2
m = 3 - 2 = 1kg
Decrease in P.E. = mgh
P.E. = 1 × 9.8 × 6.86
P.E. = 67 J
Solution 31
Work done = change in K.E.
-μR S + mg = [![]() m1v12
m1v12![]() m2v22] - 0
m2v22] - 0
-μ × 40 × 2 + 1 × 10 = ![]() (4 × 0.32+ 1 × 0.62 )
(4 × 0.32+ 1 × 0.62 )
μ = 0.12
Solution 32
Work done by block
= T.E at A - T.E. at B
= ![]() mv2+ mgh -0
mv2+ mgh -0
= ![]() × 0.1 × 52+ 0.1 × 10 × 0.2
× 0.1 × 52+ 0.1 × 10 × 0.2
W = 1.45 J
Work done by tube = - Work done by block
W'= -1.45 J
Solution 33
Work done,
W = K.ET - P.ET
W = (0 + ![]() mv2) - mgh
mv2) - mgh
W = [![]() × 1400 × 152] - [1400 × 9.8 × 10]
× 1400 × 152] - [1400 × 9.8 × 10]
W = 20300J
Solution 34
(a) Work done W = mgh = 0.2 × 10 × 3.2 (to lift the block)
W = 6.4 J
(b) Work done W = mg sinƟ (to slide the block)
W = 6.4J
(c) When block falls on ground work done is
W
= ![]() m v2 - 0
m v2 - 0
6.4
= ![]() × 0.2 × v2
× 0.2 × v2
v = 8m/s
(d) W = ![]() m v2 - 0
m v2 - 0
6.4 = ![]() × 0.2 × v2
× 0.2 × v2
v = 8 m/s
Solution 35
(a) Work done, W = 0 because no work is done by ladder.
(b) Work done W = μRS = fd
= - (200 ×3/10 ) × 10 = -600 J
(c) Work done, W = mg sinƟ × d = 200 × 8/10 × 10
W = 1600 J
Solution 36
By conservation of energy of point A and B
mgH = ![]() m v2+ mgh
m v2+ mgh
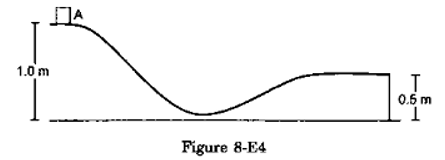
g × 1 = ![]() v2+ g × 0.5
v2+ g × 0.5
v = √9.8 = 0.3 m/s
After B, body obeys projectile motion, so
S = ut + ![]() a t2
a t2
-0.5 = u sinƟ
t + ![]() (-9.8)t2
(-9.8)t2
t = 0.31 s
and X = 4 cosƟ× t
X =1
Solution 37
Work done, W = mgh = 10 × 1
W = 10 J
Frictional force, F =μR = μmg = 0.2 × 10
F = 2N
and W = Fs
s = ![]() =
= ![]() = 5m
= 5m
Solution 38
W = (m/l) dx g(x)
Total work done is :
W = l/3∫0 (m/l) dx g(x)
W = mgl/18
Solution 39
Work done for small element is:
dW = μRx
dw = μ(M/L dx) g(x)
Total work done is :
W = 2L/3∫0 μ M/L g (×) dx
W = (2𝜇MgL)/9
Solution 40
Work done = change in P.E.
W = mgh - mgH
W = 1 × 10 × (0.8 - 1)
W = -2 J
Work and Energy Exercise 135
Solution 41
k = (mg)/x = 50/0.1 = 500N/m
Total energy T.E. =![]() m v 2+
m v 2+ ![]() k x2 ……. (1)
k x2 ……. (1)
and
T.E. (at height h) = ![]() k (h - ×)2 + mgh …. (2)
k (h - ×)2 + mgh …. (2)
Equating 1 and 2
![]() m v 2+
m v 2+ ![]() k ×2 = ½ k
(h - x)2+ mgh
k ×2 = ½ k
(h - x)2+ mgh
![]() × 5 × 22+
× 5 × 22+ ![]() × 500 × 0.12 =
× 500 × 0.12 = ![]() × 500 (h - 0.12) + 5 × 10 × h
× 500 (h - 0.12) + 5 × 10 × h
h = 0.2 m
h = 20cm
Solution 42
By law of conservation of energy:
![]() k x2 = mgh
k x2 = mgh
![]() ×100 × 0.1 = mgh =
0.25 × 10 × h
×100 × 0.1 = mgh =
0.25 × 10 × h
h = 0.2m
h = 20 cm
Solution 43
By work energy principle
(i) for downward motion,
0-0 = (-mg sinƟ
× s) - μRs - ![]() kx2
kx2
80μ + 0.02R = 60 …… (1)
(ii) for upward motion
0 - 0 = (-mg sinƟ
× s) - μRs + ![]() kx2
kx2
-16 μ + 0.02 k = 12 …… (2)
Solving 1 and 2 we get,
μ = 0.5
and
k = 1000 N/m
Solution 44
Energy at A = Energy at B
![]() m v 2a =
m v 2a =![]() m vb2+ k x2
m vb2+ k x2
mv2 = ![]() + k x2
+ k x2
k =![]()
Solution 45
From figure
mgx = ![]() k x2
k x2
x = ![]()
Solution 46
By law of conservation of energy
![]() m v2 =
m v2 = ![]() k1x2+
k1x2+ ![]() k2x2
k2x2
So, v = ×√(k1 + k2)/m
Solution 47
(a) By law of conservation of energy:
![]() m v2 =
m v2 = ![]() k x2
k x2
Max × = v√m/k
(b) Velocity of the block will not be the same when it comes back to the original position, it will be of smaller magnitude and opposite direction.
Solution 48
By law of conservation of energy:
![]() mv2 =
mv2 = ![]() k x2
k x2
v = 1.58 m/s2
Now, projectile motion
y = (u sinƟ
)t - ![]() g t2
g t2
Ɵ = 00 , y = -2
t = 0.63 sec
and
x = (u cosƟ)t = 1.58 × 0.63
x = 1m
Solution 49
Minimum velocity at A = v
Minimum velocity at B = 0
By law of conservation of energy
![]() m v2 = mg (2l)
m v2 = mg (2l)
v = 2√gl
Solution 50
from figure
kx cosƟ = mg
40 x X x (0.4/[0.4 + x]) = 0.32 × 10
x = 0.1m
and
S = √(h + x)-h2 = √[(0.4+0.1)2 - 0.42]
S = 0.3m
Change in K.E. = Work done
![]() mv2 = -
mv2 = -![]() kx2+ mgs
kx2+ mgs
![]() ×0.32 × v2 = -
×0.32 × v2 = -![]() x 40 × 0.12+0.32 × 10 × 0.3
x 40 × 0.12+0.32 × 10 × 0.3
v =1.5 m/s
Work and Energy Exercise 136
Solution 51
cosƟ = cos37° = BC/AC =4/5
AC = (h + x) = ![]()
and x =AC - h = ![]() - h =
- h = ![]()
By work energy principle,
![]() k x2 =
k x2 = ![]() m v2
m v2
v =![]()
Solution 52
vmin = √2gl
Total energy at A = Total energy at B
mgh = ![]() m v2 [v = √2gl]
m v2 [v = √2gl]
h = l
Solution 53
(a) By law of conservation of energy,
![]() mv12 =
mv12 = ![]() m v22+ mgl
m v22+ mgl
![]() × m × (√gl )2 =
× m × (√gl )2 = ![]() m v22+ mgl
m v22+ mgl
v2 =(√8gl)
and
TB = (mv22)/R = [m × (√8gl)2]/l
TB = 8mg
(b) By law of conservation at A and C
![]() mv12 =
mv12 = ![]() m v32+ mgh
m v32+ mgh
![]() × (√logl)2 =
× (√logl)2 = ![]() × v32+ g × 2l
× v32+ g × 2l
v3 = (√6gl)
and
Tension
Tc =[ (mv32)/l ] - mg
Tc = 5mg
(c) By law of conservation of energy at A and D
![]() mv12 =
mv12 = ![]() m v42+ mgh
m v42+ mgh
![]() (√logl)2 =
(√logl)2 = ![]() m v42+ gl (1 + cos600)
m v42+ gl (1 + cos600)
v4 = √7gl
and
Tension
TD = (mv2)/l - mg cos600
by putting v = 7gl we get,
TD = 6.5mg
Solution 54
from figure,
cosƟ =![]()
and
AC = AB cosƟ
AC = 0.4
and
CD = AD -AC
CD = 0.1 m
Energy is same at B and D
![]() m v2 = mgh
m v2 = mgh
![]() v2 = 10 × 0.1
v2 = 10 × 0.1
v = ![]() m/s
m/s
Tension T = (mv2)/r +mg
T= (0.1 ×2)/0.5 + 0.1 × 10
T = 1.4 N
Solution 55
According to figure,
(mv2)/R = mg
v = ![]()
Energy is same at A and P
![]() kx2 =
kx2 = ![]()
x =![]()
Solution 56
Change in K.E. is given as
![]() m v2 -
m v2 - ![]() mu2 =-mgh
mu2 =-mgh
v2 = 3gl - 2gl (1 +cosƟ) …….. 1
and
(mv2)/l = mg cosƟ
v2 =gl cosƟ ……… 2
from equation 1 and 2
3gl - 2gl - 2gl cosƟ = gl cosƟ
θ = cos-1(![]() )
)
Thus,
Angle = 1800 - cos-1
(![]() )
)
Angle = cos-1 (-1/3)
Solution 57
(a) mg cosƟ = (mv2)/l
v = (√gl cosƟ) ….. 1
Change in K.E. is given as :
![]() mv2 -
mv2 -![]() mu2 =mgh
mu2 =mgh
![]() v2 -
v2 - ![]() (√57)2 = g (1.5[ 1 +cosƟ])
(√57)2 = g (1.5[ 1 +cosƟ])
v = (√57 - 3g(1 + cosƟ) ……. 2
from equation 1 and 2
1.5 × g cosƟ = 57 - 3g (1+cosƟ)
Ɵ = 530
(b) v = √57 - 3g (1+cosƟ) Ɵ =53
v = 3m/s
(c) After, point B projectile motion will take place
H = OE + DC
H = 1.5 cosƟ + (u2sin2Ɵ)/2×g
H = 1.5 × ![]() + (9 ×0.82)/2×10
+ (9 ×0.82)/2×10
H = 1.2m
Solution 58
Total energy at A and B are same
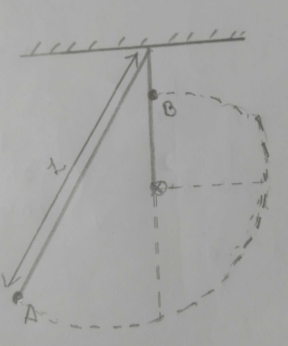
K.EA+ P.EA = K.EB+ P.EB
we get,
P.EA = P.EB
Thus maximum height is same as initial height.
(b)
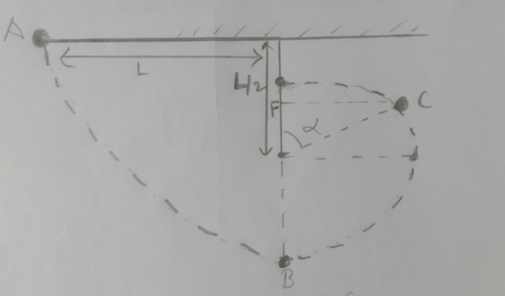
At C, ½ mvc2 - 0 = mg (L/2)(1 - cos∝)
Vc = (√gL (1-cos∝)) ….. 1
Again,
Vc = (√gL cos∝) ….. 2
equating 1 and 2
cos∝ = ⅔ …… 3
Now, BF = ![]() +
+![]() cos∝
cos∝
BF = (5L/6)
(c)
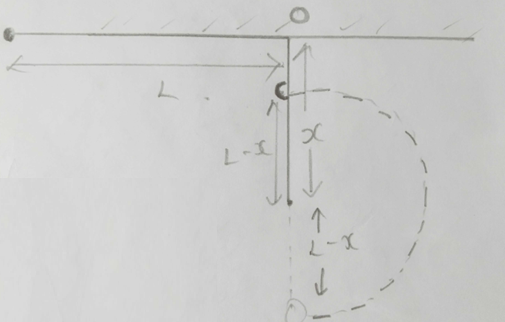
(mvc2)/L-x = mg
vc = (√g (L-x)) …. 1
Also,
½ mvc2 - 0 = mg (OC)
vc = (√2g (2x-L)) ….. 2
Equating 1 and 2
g (L-x) = 2g (2x - L)
x/L = 0.6
Solution 59
From figure,
(mv2)/R = mg cosƟ
v = (√gRcosƟ) …….. 1
and
Change in K.E. = Work done
![]() m v2 - 0 = mg (R - R cosƟ)
m v2 - 0 = mg (R - R cosƟ)
v = (√2gR [1-cosƟ]) ….. 2
from 1 and 2
gR cosƟ = 2gR (1-cosƟ)
Ɵ = cos-1(![]() )
)
Solution 60
(a) Net force = mg cosƟ = √3/2 mg
(b) N = 0
and
![]() = mg cosƟ
= mg cosƟ
v = (√gR cosƟ) …..1
and
![]() mv2 = mgR
(cos30° - cosƟ)
mv2 = mgR
(cos30° - cosƟ)
v = (√2gR√3/2 - cosƟ]) …. 2
from equation 1 and 2 we get,
Ɵ = cos-1(![]() )
)
and distance , l =R [Ɵ - π/6]
l = 0.43R
Solution 61
(a) from free body diagram
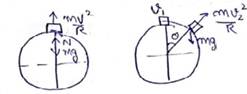
N = mg - (mv2)/R
(b) When particle moves with maximum velocity then,
mg = (mv2)/R
v = √gR
(c ) From figure,
v1 = (√gR)/2 ……. 1
and
(mv22)/R = mg cosƟ
v2 = (√gR cosƟ) …… 2
Also, change in K.E. = Work done
![]() m v22 -
m v22 - ![]() m v1= mgR (1 - cosƟ) …… 3
m v1= mgR (1 - cosƟ) …… 3
from equation 2 and 3
gR cosƟ = v12+ 2gR (1 - cosƟ)
Ɵ = cos-1(![]() )
)
Work and Energy Exercise 137
Solution 62
(a) FAB = mg sinƟ
WB = FABS
WB = mg sinƟ × l ….. 1
and
WC = mgR(1-cosƟ) ….. 2
Total work done
W = WB+ WC
and
change in K.E. = Work done
v0 = [√2g(R (1-cosƟ) + l sinƟ]
(b) By work energy equation
change in K.E. = Work done
vc = [√6g (l sinƟ)+R (1-cosƟ) ]
and
Force,
F = (m vc2)/R
F = 6mg (l/R sinƟ+1-cosƟ)
(c) (mv2)/R = mg cosƟ
v = √gR cosƟ ….. 1
Also,
v = [√2gR (1-cosƟ)]….. 2
equating 1 and 2 we get,
Ɵ = cos-1 (![]() )
)
Solution 63
(a) G.P.E = dm g R cosƟ
= (mgR cosƟ dƟ)/l [dm = m/l R dƟ]
Total G.P.E = 0∫l/r(mgR2)/l cosƟ dƟ [Ɵ = l/R]
G.P.E =(mgR2)/l sin(l/R)
(b) K.E. = change in P.E
K.E. = (mgR2)/l [sin (l/R) + sinƟ - sin (Ɵ +l/R)]
(c) From above equation
K.E. = (mgR2)/l [sin (l/R) + sinƟ - sin (Ɵ +l/R)]
as Ɵ = 0
![]() = (gR/l)[1 - cos(l/R)]
= (gR/l)[1 - cos(l/R)]
Solution 64
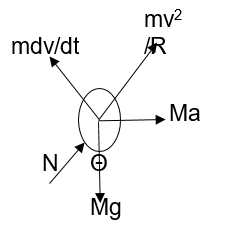
According to figure,
m![]() = ma cosƟ
+ mg sinƟ
= ma cosƟ
+ mg sinƟ
Vdv = a R cosƟ dƟ + gR sin Ɵ dƟ [v = R dƟ/dt]
Integ
V = [2R (a sin Ɵ + g - g cosƟ)]½

