Class 11-science H C VERMA Solutions Physics Chapter 14 - Some Mechanical Properties of Matter
Some Mechanical Properties of Matter Exercise 300
Solution 1
m=10kg ;
l=3m ;
A=4mm2;
Y=2×1011 N/m2
Solution :
a) Stress=![]()
![]()
![]()
b) Y=![]()
![]()
c) Strain=![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 2
m=100kg;
l=2m;
![]() =
=![]()
![]()
Solution:
a) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
b) Strain=![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
c) Compression
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 3
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 4
Lst=Lcu
Ast=Acu
Fst=Fcu
a) Stress=![]()
![]()
So, stress in both wire is same.
b) strain![]()
![]()
Solution 5
Lst=Lcu
Ast=Acu
Fst=Fcu=mg
Strain=![]()
![]()
Solution 6
(a) Let mass put in hanger is m
For lower wire
TL=(m1+m)g;
![]() ;
;
AL=0.003cm2=3![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
For upper wire
TU=( m2 + m1+m)g;
![]() ;
;
Au=0.006cm2=![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
So, lower wire will break first. So maximum mass put in hanger is 14kg.
(b) If m1=10kg and m2=36kg
For lower wire,
![]()
![]()
![]()
For upper wire,
![]()
![]()
![]()
So, upper wire will break first. So, maximum mass put in hanger is 2kg.
Solution 7
F=100N;
![]()
L=2m;
A=2cm2
![]()
![]()
Solution 8
Y=![]()
![]()
L=2m;
A=4cm2
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 9
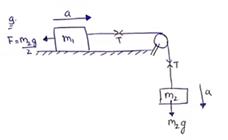
Translatory motion equations
m2g-T=m2a 1)
T-![]() = m1a
2)
= m1a
2)
Adding both equation(1) and (2)
![]() =( m1 +m2)a
=( m1 +m2)a
![]()
Put in equation (1) and (2)
![]()
![]()
Now,
Strain=![]()
Strain=![]()
Solution 10
At equilibrium T=mg
Now, when it is moved by angle θ and released, because of centrifugal force at lowest point, Tension becomes-
T'=mg+![]()
So, change in tension
![]()
By energy Conservation
0+
mgl(1-cosθ)=![]()
![]()
Now, ![]()
L=4m
m=20kg;
![]()
Y=2![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Some Mechanical Properties of Matter Exercise 301
Solution 11
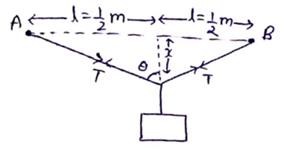
Let depression is wire be x
Now, length of wire becomes=2![]()
Change in length=2![]()
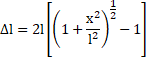
By binomial expansion
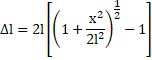
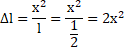
From equilibrium of forces,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now,
![]()
![]()
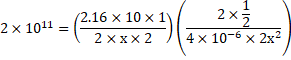
On solving,
![]()
Solution 12
A=0.01![]()
T=20N
Y=1.1×![]()
e=0.32
![]()
![]()
Now,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 13
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 14
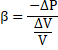
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Change in
density=![]()
=1032-1030
=2![]()
Solution 15
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 16
![]()
![]()
F![]()
![]()
Solution 17
a) ![]()
![]()
![]()
b) ![]()
![]()
![]()
c) ![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 18
a) Force by air above it
![]()
![]()
![]()
b) By mercury below it
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
c) By mercury surface in contact with it
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 19
a) ![]()
![]()
![]()
b) ![]()
![]()
c) ![]()
![]()
Solution 20
![]()
![]()
So,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 21
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Not rise in bare meter tube=76-0.5=75.5cm
Solution 22
Pressure in tube 5cm below water surface is
![]()
So, excess Pressure
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 23
Surface energy=TA
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 24
Radius of big drop![]()
Let radius of
small drop be![]()
Here,
Volume of big drop = Volume of small drop
![]()
![]()
![]()
Increase in
surface energy=![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 25
a) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
b)Initially
![]() …………………(1)
…………………(1)
Now,
![]() …………..….(2)
…………..….(2)
Dividing Both equation
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 26
a) ![]()
![]()
![]()
b) ![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 27
Force due to surface Tension = Force by gravity
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 28
After melting the Ice cube will acquire shape of sphere as it is kept in gravity free space and due to surface tension.
Volume of cube= volume of sphere
![]()
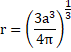
Surface
Area of spherical drop=![]()
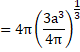
![]()
Solution 29
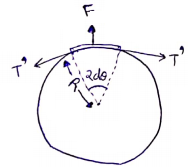
Considering a small section on thread subtending an angle of 2dθ at center.
Force due to soap solution on this section=2T(2Rdθ)
This
force is balanced by tension in thread= 2T'sin d![]() =2T'dθ
=2T'dθ
By equilibrium of force
2T(2Rdθ)= 2T'dθ
T'=2TR
T'=2T(![]() )
)
T'=![]()
![]()
T'=![]()
Solution 30
a) Viscous Force
![]() ηrv
ηrv
![]()
![]()
b)
hydrostatic force=![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
c) At the time of terminal velocity
Download force= Upward force
![]() ηrv
ηrv
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 31
![]()
![]()
![]()
Some Mechanical Properties of Matter Exercise 302
Solution 32
V=![]() m/s
m/s
R=1![]() m
m
![]()
poise=10-3poisullie
Reynold's number
![]()
![]()
![]()
Reynold number is less than 1200. Therefore, it is a steady Flow.

