Class 9 FRANK Solutions Physics Chapter 5: Heat - Transmission of Heat
Prepare for achieving an impressive exam score with TopperLearning’s Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 5 Heat - Transmission of Heat. Learn the models of heat transfer. Read our textbook solutions to revise the difference between good and bad conductors of heat. Other topics that are covered in Chapter 5 include greenhouse gases, conduction, radiation and convection.
Our experts have carefully created the ICSE Class 9 Physics resources such as textbook solutions, videos, revision notes, etc. You may use these to quickly revisit important syllabus concepts during your exam.
226
227
Heat - Transmission of Heat Exercise 226
Solution 1
Conduction, convection and radiation are three modes of transfer of heat.
Solution 2
The process of conduction involves the transmission of heat from the hot end to the cold end from particle to particle of the medium.
Solution 3
No, conduction is not possible in vacuum.
Solution 4
Thermal insulation means restriction of transfer of heat by any means.
Solution 5
Good conductor allow heat to pass through them easily while bad conductor of heat does not allow heat to pass them.
Solution 6
No, liquids are poor conductors of heat.
Solution 7
(i) Metals are the best conductor of heat.
(ii) Gases are the worst conductor of heat.
(ii) Gases are the worst conductor of heat.
Solution 8
Among all the metals, Silver is most conducting.
Solution 9
Air is most non-conducting.
Solution 10
No, air is not a good conductor of heat.
Solution 11
Yes, this is a correct statement. Ebonite and asbestos are worst conductor of heat.
Solution 12
Cooking utensils are made up of metals because metals are good conductors of heat and they easily allow the heat to pass through them.
Solution 13
Brick is bad conductor of heat, hence bricks greatly reduce the conduction of heat from outside to the room. In order to ensure better insulation, bricks are made hollow so that air filled between these gaps provides insulation to heat.
Solution 14
Mercury is good conductor of heat.
Solution 15
In cold countries, windows have two glass panes and a thin layer of air in between these two glass panes because air is a poor conductor of heat; it obstructs the conduction of heat from the room to the outside.
Solution 16
Order of increasing heat conductivity:
Air < water< mercury < copper.
Air < water< mercury < copper.
Solution 17
(i) Water is heated from below because water is heated by process of convection and in process of convection heat always flows in upward direction from downward direction.
(ii) In process of convection heat is transferred from one point to another by actual movement of particles of medium and as particles of solid cannot move so process of convection is not possible in case of solids.
(iii) Conduction is not possible in Vacuum because process of conduction require a material medium for transfer of heat.
(iv) Inside the refrigerator, cooling takes place by convection. The freezing chamber at the top produces cool and heavy air which descends and hot air from below goes up setting convection current. Thus, cooling in a refrigerator is kept near the top.
(v) As earth surface gets heated by sun rays and due to process of convection the air near earth surface open to sunlight get heated while in shade sun rays does not fall on earth surface so air near that surface would not heat up.
(ii) In process of convection heat is transferred from one point to another by actual movement of particles of medium and as particles of solid cannot move so process of convection is not possible in case of solids.
(iii) Conduction is not possible in Vacuum because process of conduction require a material medium for transfer of heat.
(iv) Inside the refrigerator, cooling takes place by convection. The freezing chamber at the top produces cool and heavy air which descends and hot air from below goes up setting convection current. Thus, cooling in a refrigerator is kept near the top.
(v) As earth surface gets heated by sun rays and due to process of convection the air near earth surface open to sunlight get heated while in shade sun rays does not fall on earth surface so air near that surface would not heat up.
Solution 18
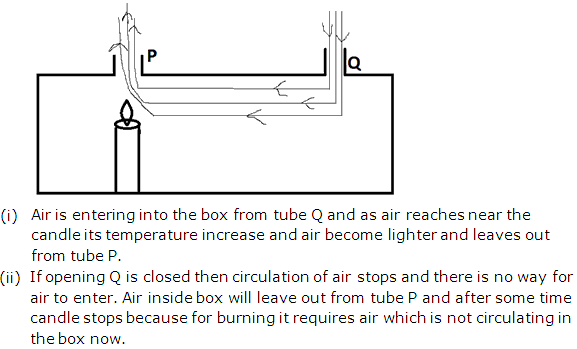
Solution 19
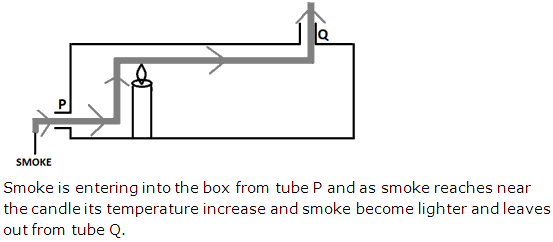
Heat - Transmission of Heat Exercise 227
Solution 20
We receive heat from sun by process of Radiation.
Solution 21
Radiating power of a surface can be increased by blackening it.
Solution 22
Heat radiation travels with speed of light and always follows straight path.
Solution 23
The flask consists of a double walled glass container with vacuum between the walls A and B. The inner side of A and the outer side of B are silvered. It has a narrow mouth which is closed by a non-conducting rubber stopper.
If a hot liquid is placed inside the flask, it cannot lose heat by conduction or convection, as there is no air between the walls. The small amount of heat lost from the liquid by radiation is reflected back into the liquid by silvering of the inner wall A and any radiation striking the outer wall B, is reflected back and prevented from reaching the liquid.
If a hot liquid is placed inside the flask, it cannot lose heat by conduction or convection, as there is no air between the walls. The small amount of heat lost from the liquid by radiation is reflected back into the liquid by silvering of the inner wall A and any radiation striking the outer wall B, is reflected back and prevented from reaching the liquid.
Solution 24
Green house is a glass house constructed to keep delicate and rare plants that require warmth and protection from weather. It is constructed by panels of glass. The temperature in a green house rises because heat enters the house through the glass but cannot escape out, because the glass reflects the heat back to the inside of the house. This makes glass house warmer than the outside environment.
Solution 25
Take two sheets of tin plates, one blackened and the other is polished brightly. Fix some drawing pins on the outer side of both sheets using wax. Fix these plates vertically at a very short distance apart. Place a Bunsen burner midway between them. When you light the burner you will observe that the pins from the black painted sheet start dropping while the pins on the polished surface remain in the same position for much longer time.
Thus, we can conclude that black surface is better absorber of heat than the polished one.
Thus, we can conclude that black surface is better absorber of heat than the polished one.
Solution 26
(i) As convection require medium for transfer of heat so heat loss due to convection can be minimized if the substance is kept away from any material medium.
(ii) Similarly for conduction, as conduction also require medium for transfer of heat so heat loss due to conduction can be minimized if the substance is kept away from any material medium.
(iii) Heat loss due to radiation can be minimized by polishing the surface as polished surfaces radiate less heat.
(ii) Similarly for conduction, as conduction also require medium for transfer of heat so heat loss due to conduction can be minimized if the substance is kept away from any material medium.
(iii) Heat loss due to radiation can be minimized by polishing the surface as polished surfaces radiate less heat.
Solution 27
(i) As no material medium surrounds the ball so there is no possibility of losing heat by conduction or convection. The ball will lose heat by Radiation.
(ii) Ball will lose minimum amount of heat if it is polished.
(iii) As loss of heat take place by Radiation and process of radiation does not require any material medium, so there is no role of air in loss of heat.
(ii) Ball will lose minimum amount of heat if it is polished.
(iii) As loss of heat take place by Radiation and process of radiation does not require any material medium, so there is no role of air in loss of heat.
Solution 28
(i) CFC means Chlorofluorocarbons which are produced mainly by refrigeration industries, aerosol cans, coolants, propellants and plastic foams. They cause global warming.
(ii) UV means ultraviolet range of radiations. These are the radiations which are emitted by sun and they enter our atmosphere.
(iii) WHO is World Health Organization which put a check on diseases and global warming etc.
(ii) UV means ultraviolet range of radiations. These are the radiations which are emitted by sun and they enter our atmosphere.
(iii) WHO is World Health Organization which put a check on diseases and global warming etc.
Solution 29
Green house is a glass house constructed to keep delicate and rare plants that require warmth and protection from weather. It is constructed by panels of glass. The temperature in a green house rises because heat enters the house through the glass but cannot escape out, because the glass reflects the heat back to the inside of the house. This makes glass house warmer than the outside environment. This phenomenon is called green house effect.
Solution 30
Carbon dioxide, Carbon monoxide, methane are green house gases.
Solution 31
As fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy they are not available again and again if are fully exhausted, so they should not be used extensively.
Solution 32
Global warming occurs due to the presence of carbon di- oxide, CFCs, methane in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide acts as a transparent gas to incoming shortwave radiations which the earth re-radiates into space. It therefore traps the outgoing longwave radiations thus warming lower atmosphere of the earth thereby causing global warming.
Solution 33
Harmful effects of global warming are:
(a). The atmospheric temperature of earth would increase thereby making it difficult for a living being to survive.
(b). It would melt down the polar caps thus increasing the size of the ocean and leading to floods, tsunami, etc.
(c). The increase in temperature would affect climate and rainfall thus affecting flora and fauna.
(d). Human beings would be vulnerable to diseases as microbes would get warmth to grow.
(a). The atmospheric temperature of earth would increase thereby making it difficult for a living being to survive.
(b). It would melt down the polar caps thus increasing the size of the ocean and leading to floods, tsunami, etc.
(c). The increase in temperature would affect climate and rainfall thus affecting flora and fauna.
(d). Human beings would be vulnerable to diseases as microbes would get warmth to grow.
