Class 9 FRANK Solutions Physics Chapter 8: Electricity and Magnetism - Current Electricity
Prepare for your exam with Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 8 Electricity and Magnetism – Current Electricity. Revise concepts including the electric cell, electric current, resistance, rheostat and more, with TopperLearning’s model answers. Learn to write the symbols of battery, ammeter, cell and other components of an electric circuit.
Understand and revise the factors that influence the resistance of a wire by exploring our learning portal’s ICSE Class 9 Physics Frank textbook solutions. For any doubts related to concepts based on electricity, check out our ‘UnDoubt’ platform and get answers from our academic experts.
312
313
Electricity and Magnetism - Current Electricity Exercise 312
Solution 1
The flow of electrons in a particular direction in a conductor is called an electric current.
Solution 2
An electric cell is the source of electric current in which chemical energy changes to electrical energy.
Solution 3
The charge on an electron is -1.6 x 10-19C.
Solution 4
The constituents of cell are two electrodes in the form of conducting rods immersed in the solution called electrolyte.
Solution 5
(i) S. I unit of electric current is Ampere
(ii) S.I unit of potential difference is volt.
(iii) S.I unit of resistance is ohm.
(ii) S.I unit of potential difference is volt.
(iii) S.I unit of resistance is ohm.
Solution 6
I = 1A
T = 1s.
I = Q/t = ne/t
So, n = I . t / e = 1 . (1 / 1.6 x 10-19) = 6.25 x 1018 electrons.
T = 1s.
I = Q/t = ne/t
So, n = I . t / e = 1 . (1 / 1.6 x 10-19) = 6.25 x 1018 electrons.
Solution 7
I = Q/t = 0.7 / 7 = 0.1 Ampere.
Solution 8
Rheostat is used to control the current in the circuit.
Electricity and Magnetism - Current Electricity Exercise 313
Solution 9
Rheostat is the variable name of electrical resistance.
Solution 10
Switch is used to put the current on and off in the circuit.
Solution 11
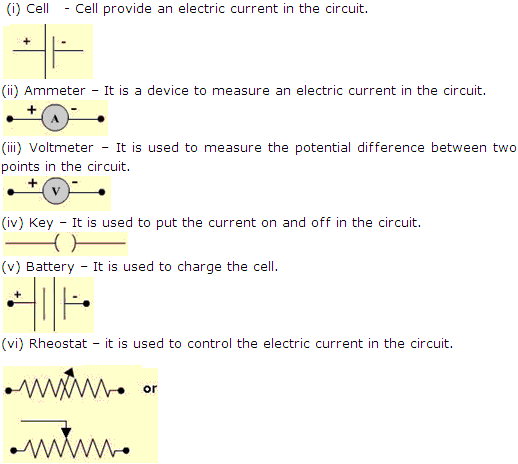
Solution 12
I = Q/ t So, Q = I .t = 1.2 x 3.0 = 3.6 C.
Solution 13
A - is a voltmeter to measure the potential difference, B is an electric resistance to control the current in the circuit , C is the ammeter to measure the magnitude of an electric current, D is cell to provide electric current in circuit, E is an electric key to on and off the circuit, F is the rheostat to control the current in circuit.
Solution 14
The slope of the graph represents that with current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference applied the resistance of conductor is constant.
Solution 15
Potential difference between two conductors is defined as the amount of work done in moving the unit positive charge from one conductor to another through the wire.
Solution 16
Yes, electric current is a scalar quantity.
Solution 17
The electric resistance of the wire depends on the following factors :
(i)The length of the wire.
(ii)The area of cross-section of the wire.
(iii)The temperature of the wire.
(iv)The material of the wire.
(i)The length of the wire.
(ii)The area of cross-section of the wire.
(iii)The temperature of the wire.
(iv)The material of the wire.
Solution 18
The S.I unit of resistance is ohm.
Solution 19
If another bulb is connected in series then the resistance of the wire will increase.
If another bulb is connected in parallel then resistance will decrease.
If another bulb is connected in parallel then resistance will decrease.
Solution 20
V = I R.
Solution 21
The resistance of the wire is 2 ohms if a current of 1 ampere flows through it when the potential difference across it is 2 volt.
Solution 22
The current I = V/R = 14/28 = 0.5 Ampere.
Solution 23
The factors on which resistance of the wire depends are :
(i) The length of the wire , resistance is directly proportional to the length of wire.
(ii) The cross-section of the wire , resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-section of the wire.
(iii) The temperature of the wire , resistance of wire is directly proportional to the temperature of the wire.
(iv) The material of the wire (good conductors possess less resistance.)
(i) The length of the wire , resistance is directly proportional to the length of wire.
(ii) The cross-section of the wire , resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-section of the wire.
(iii) The temperature of the wire , resistance of wire is directly proportional to the temperature of the wire.
(iv) The material of the wire (good conductors possess less resistance.)
Solution 24
W = V.Q = 6. 3 = 18Joule.
Solution 25
The resistance of the conductor is the property due to which it opposes the flow of current in it.
Solution 26
The potential difference between two points is 1 volt if the work done in transferring 1 coulomb of charge from one point to another point is 1 joule.
