JEE Class main Answered
Solve

Asked by sarveshvibrantacademy | 14 May, 2019, 10:20: AM
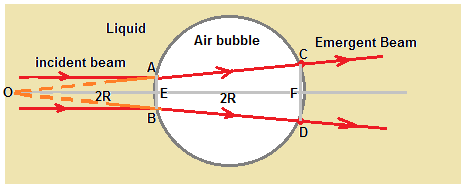
Figure shows incident parallel beam is getting diverged after refraction in air bubble,
because refractive index of air is less than refractive index of liquid.
It is given that area of beam at emergence is 4 times of area of beam at incidence.
Since area is proportional to square of diameter, diameter of beam at emergence is twice
of diameter of beam at incidence. Hence in figure CD = 2AB.
Due to diverging action, if we consider this parallel beam is from an object placed at infinite distance,
its virtual image is formed in front of spherical bubble at a point O as shown in figure.
If we consider ΔOAB and ΔOCD are similar triangle and CF = 2AE,
then we have, OF = 2OE.
Then if we consider EF = 2R, where R is radius of bubble, then we get OE = 2R.
Now if we apply the formula for refraction at sperical surface , (1/v)-(μ/u) = (1-μ)/R ...............(1)
where μ is refractive index of liquid, v is image distance, u is the object distance and R is radius of curvature.
we have u = ∞, v = -2R , by substituting these values in eqn.(1), we get, [ 1/(-2R) ] = (1-μ) / R .................(2)
from eqn.(2), we get μ = 3/2
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 14 May, 2019, 23:31: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
JEE main - Physics
Asked by sumalathamadarapu9 | 23 Oct, 2024, 22:06: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by py309649 | 13 Oct, 2024, 13:39: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by coolskrish | 13 Oct, 2024, 12:50: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by midnightmoon3355 | 09 Oct, 2024, 09:09: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by rambabunaidu4455 | 03 Oct, 2024, 16:03: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by ratchanavalli07 | 17 Sep, 2024, 07:46: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by yayashvadutta45 | 15 Sep, 2024, 19:47: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by adithireddy999 | 03 Sep, 2024, 09:35: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by vaishalinirmal739 | 29 Aug, 2024, 18:07: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by vradhysyam | 26 Aug, 2024, 17:17: PM