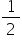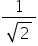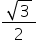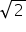CBSE Class 10 Answered
- Trigonometric ratios of acute angle A in right triangle ABC:
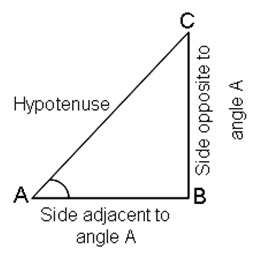

Each trigonometric ratio is a real number. It has no unit.
All the trigonometric symbols, cosine, sine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant, have no literal meaning.
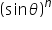 is generally written as
is generally written as 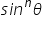 , n being a positive integer. Similarly, other trigonometric ratios can also be written.
, n being a positive integer. Similarly, other trigonometric ratios can also be written.
The values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the length of the sides of the triangle, if the angles remain the same.
Pythagoras theorem: In a right triangle, square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
When any two sides of a right triangle are given, its third side can be obtained by using Pythagoras theorem.
Relation between trigonometric ratios:
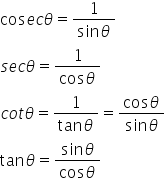
- Values of Trigonometric ratios of some specific angles:
|
ÐA |
0° |
30° |
45° |
60° |
90° |
|
sin A |
0 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
cos A |
1 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
tan A |
0 |
|
1 |
|
Not defined |
|
cosec A |
Not defined |
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
sec A |
1 |
|
|
2 |
Not defined |
|
cot A |
Not defined |
|
1 |
|
0 |
The value of sin A or cos A never exceeds 1, whereas the value of sec A or cosec A is always greater than 1 or equal to 1.
The value of sin increases from 0 to 1 when
increases from 0 to 1 when  increases from 00 to 900.
increases from 00 to 900.
The value of cos decreases from 1 to 0 when
decreases from 1 to 0 when  increases from 00 to 900.
increases from 00 to 900.
Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles:
- sin (90o – A) = cos A
- cos (90o – A) = sin A
- tan (90o – A) = cot A
- cot (90o – A) = tan A
- sec (90o – A) = cosec A
- cosec (90o – A) = sec A
An equation involving trigonometric ratios of an angle, say, is termed as a trigonometric identity if it is satisfied by all values of  .
.
Basic trigonometric identities:

Practice makes perfect!!!
STudy the table and write the values for specific number of times.
This is the conveentional method to memorize the lessons.
Use the values in practice problems!!!!!