JEE Class main Answered
Please explain with ray diagram

Asked by himanshuneb | 25 Jan, 2019, 11:11: AM
Magnification = v/u , where v is the lens to image distance.
Here image of object at infinite distance is formed at focal length , we have v = f.
u is the lens to object distance. For the sake of studying the focal length and aperture effect, let us consider this distance u is constant.
Hence if u is constant, magnification is proportional to focal length for the object kept at infinite distance.
Hence spot radius r of sun's image is proportional to focal length f. Hence πr2 is proportional to f2.
except " (B) πr2 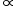 f2 ", other options are false.
f2 ", other options are false.
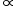 f2 ", other options are false.
f2 ", other options are false.If the lower portion of lens is covered by black paper, still the top portion will view the full size of sun due to infinite distance.
Only the light intensity collected by the lens is halved. Hence we get full image of sun but reduced intensity.
By increasing the focal length, magnification increases, hence area of image increases.
If the collecting area of light of the lens is kept constant, intensity decreases by increasing focal length .
This is due to same collecting light intensity by lens, but image is formed in more area.
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 25 Jan, 2019, 13:04: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
JEE main - Physics
Asked by jwjwwj | 16 Jan, 2025, 13:26: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by mishradarshan03 | 22 Dec, 2024, 11:45: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by sumalathamadarapu9 | 23 Oct, 2024, 22:06: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by py309649 | 13 Oct, 2024, 13:39: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by coolskrish | 13 Oct, 2024, 12:50: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by midnightmoon3355 | 09 Oct, 2024, 09:09: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by rambabunaidu4455 | 03 Oct, 2024, 16:03: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by ratchanavalli07 | 17 Sep, 2024, 07:46: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by yayashvadutta45 | 15 Sep, 2024, 19:47: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by adithireddy999 | 03 Sep, 2024, 09:35: AM