Class 11-commerce TR JAIN AND VK OHRI Solutions Statistics for Economics Chapter 4 - Organisation of Data
Organisation of Data Exercise 75
Solution SAQ 1
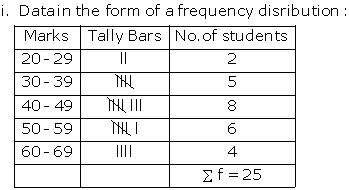
ii. Data with cumulative frequencies:
|
Marks |
No. of Students |
Marks |
No. of Students |
|
Less than 29 |
0 +2 =2 |
More than 20 |
25 |
|
Less than 39 |
2 + 5 =7 |
More than 30 |
25 - 2 =23 |
|
Less than 49 |
7 + 8 =15 |
More than 40 |
23 - 5 =18 |
|
Less than 59 |
15 + 6 =21 |
More than 50 |
18 - 8 =10 |
|
Less than 69 |
21 + 4 =25 |
More than 60 |
10 - 6 =4 |
Solution SAQ 2
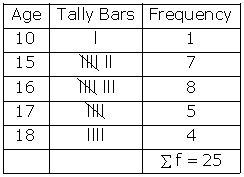
Data in the form of frequency distribution:
Solution SAQ 3
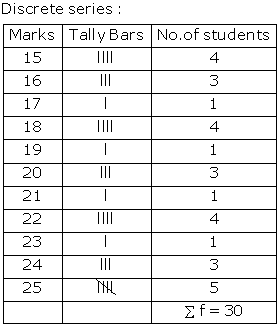
Individual series:
|
15 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
20 |
|
20 |
21 |
22 |
22 |
22 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
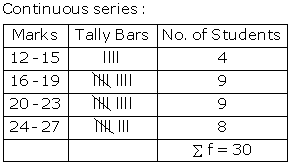
Cumulative frequency series:
|
Marks |
No. of Students |
Marks |
No. of Students |
|
Less than 15 |
0 |
More than 12 |
30 |
|
Less than 19 |
9 + 4 =13 |
More than 16 |
30 - 4 =26 |
|
Less than 23 |
13 + 9 =22 |
More than 20 |
26 - 9 =17 |
|
Less than 27 |
22 + 8 = 30 |
More than 24 |
17 - 9 =8 |
Solution SAQ 4
Exclusive frequency distribution:
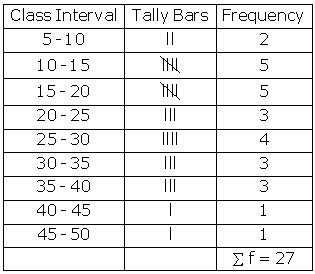
Organisation of Data Exercise 76
Solution SAQ 5
Frequency distribution:
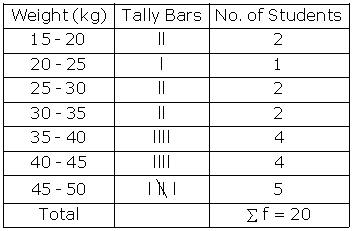
Solution SAQ 6
Given data can be written as:
|
Marks |
Cumulative Frequency (c.f) |
|
Less than 3 |
5 |
|
Less than 6 |
12 |
|
Less than 9 |
25 |
|
Less than 12 |
33 |
Simple frequency distribution:
|
Marks |
Frequency (f) |
|
0 - 3 |
5 |
|
3 - 6 |
7 (= 12 - 5) |
|
6 - 9 |
13(= 25 - 12) |
|
9 - 12 |
8(= 33 - 25) |
|
|
∑f =33 |
Solution SAQ 7
Discrete series:
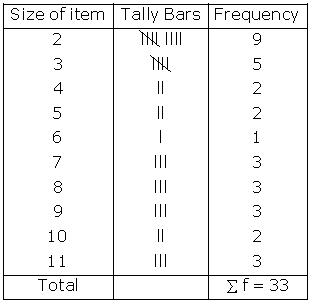
Solution SAQ 8
i. Frequency distribution:
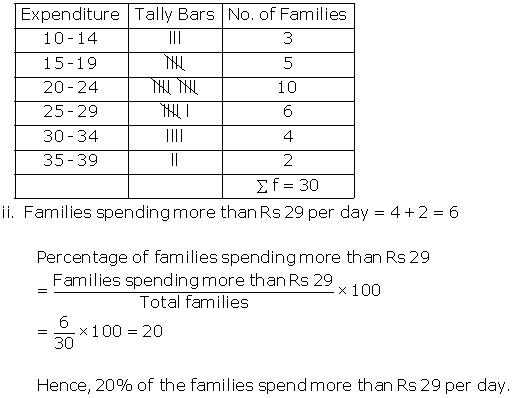
Solution SAQ 9
Frequency distribution on exclusive basis:
|
Weight (in kg) |
No. of students (f) |
|
40 - 50 |
7 |
|
50 - 60 |
7 |
|
60 - 70 |
5 |
|
70 - 80 |
3 |
|
80 - 90 |
2 |
|
90 - 100 |
1 |
|
|
∑f = 25 |
Frequency distribution on inclusive basis:
|
Weight (in kg) |
No. of students (f) |
|
40 - 50 |
9 |
|
51 - 61 |
6 |
|
62 - 72 |
6 |
|
73 - 83 |
2 |
|
84 - 94 |
2 |
|
95 - 105 |
0 |
|
|
∑f = 25 |
Organisation of Data Exercise 77
Solution SAQ 10
Lower limits and upper limits of class intervals are calculated using the following formula.
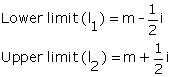
where m is mid value and i is the difference between mid-values.
|
Mid-value |
Class-interval |
Frequency (f) |
|
5 |
0 - 10 |
2 |
|
15 |
10 - 20 |
8 |
|
25 |
20 - 30 |
15 |
|
35 |
30 - 40 |
12 |
|
45 |
40 - 50 |
7 |
|
55 |
50 - 60 |
6 |
|
|
|
∑f = 50 |
Solution SAQ 11
Lower limits and upper limits of class intervals are calculated using the following formula.
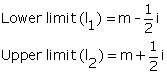
where m is mid value and i is the difference between mid-values.
|
Mid-value |
Class-interval |
Frequency (f) |
|
12 |
9.5 - 14.5 |
1 |
|
17 |
14.5 - 19.5 |
5 |
|
22 |
19.5- 24.5 |
4 |
|
27 |
24.5 - 29.5 |
4 |
|
32 |
29.5 - 34.5 |
8 |
|
37 |
34.5 - 39.5 |
6 |
|
42 |
39.5 - 44.5 |
11 |
|
47 |
44.5 - 49.5 |
4 |
|
52 |
49.5 - 54.5 |
5 |
|
|
|
∑f = 48 |

