Class 12-commerce T S GREWAL Solutions Accountancy Chapter 3: Goodwill: Nature and Valuation
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.28
Solution Ex. 1
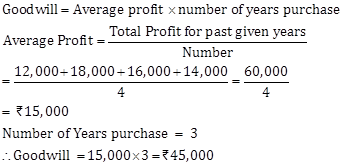
Solution Ex. 2
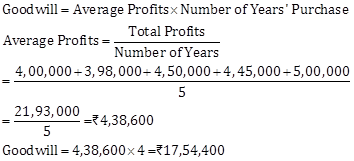
Solution Ex. 3
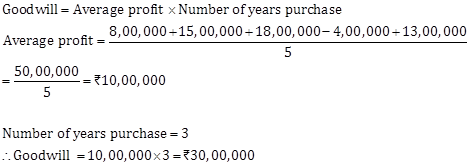
Solution Ex. 4
Goodwill = Average Profit × Number of years purchase
Goodwill = 2,00,000 × 1.5 = Rs.3,00,000
Working Notes:
1.
|
Calculation of Profits (last 3 years) |
|
|
Year |
Profit |
|
1st Year |
1,00,000 |
|
2nd year |
2,00,000 (1,00,000 × 2) |
|
3rd year |
3,00,000 (2,00,000 ×1.5) |
|
Total |
6,00,000 |
2.
Calculation Of Average profit

Solution Ex. 5
Computation of Goodwill:
![]()
Working Notes:
Calculation of Average Profit (Five Years)
|
Year |
Profit |
|
2014-15 |
14,000 |
|
2015-16 |
15,500 |
|
2016-17 |
10,000 |
|
2017-18 |
16,000 |
|
2018-19 |
15,000 |
|
Total Profit |
70,500 |
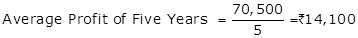
Calculation of Average Profit (Four Years)
|
Year |
Profit |
|
2015-16 |
15,500 |
|
2016-17 |
10,000 |
|
2017-18 |
16,000 |
|
2018-19 |
15,000 |
|
Total Profit |
56,500 |
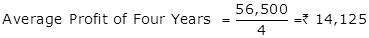
Average Profits (4 Years) > Average Profits (5 Years)
Accordingly, for Goodwill Valuation, Average profits = 14,125
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.29
Solution Ex. 6
It is given that Goodwill is to be valued at 100% of the average annual profits of the previous three or four years, whichever is higher.
i. Average Annual Profits of the previous three years ending 31st March 2017, 2018 and 2019:
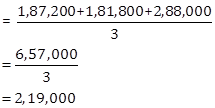
ii. Average Annual Profits of the previous four years ending 31st March 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019:
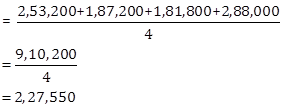
Comparing
the above, since average of the annual profits of the previous four years is
higher, value of Goodwill will be:![]()
Solution Ex. 7
Goodwill = Normal Average Profit × Number of years' of purchase
![]()
Working Note 1: Calculation of Normal Average Profit
|
Year |
Actual Profit |
+ |
Non-Recurring Expenses/ Loses |
- |
Non-Recurring Incomes/ Gains |
- |
Unrecorded Expenses |
= |
Normal Profit |
|
2016-17 |
1,00,000 |
+ |
0 |
- |
12,500 |
- |
0 |
= |
87,500 |
|
2017-18 |
1,25,000 |
+ |
25,000 |
- |
0 |
- |
0 |
= |
1,50,000 |
|
2018-19 |
1,12,500 |
+ |
|
- |
|
- |
12,500 |
= |
1,00,000 |
|
Normal Profits for last 3 years |
|
|
|
3,37,500 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
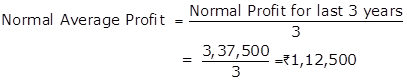
Solution Ex. 8
Goodwill = Average Profit × Number of years Purchase
Goodwill = 2,35,000 (WN 1)×4 = Rs.9,40,000
Working Note 1: Calculation of Normal Average Profit
|
|
|
|||||
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
|
Profit /(Loss) |
1,50,000 |
3,50,000 |
5,00,000 |
7,10,000 |
(5,90,000) |
|
|
Adjustments: Travelling Expenses Depreciation Interest |
- - - |
- - - |
- - - |
- - (10,000) |
1,00,000 (25,000) (10,000) |
|
|
Normal Profit |
1,50,000 |
3,50,000 |
5,00,000 |
7,00,000 |
(5,25,000) |
|
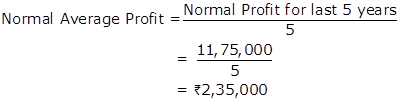
Solution Ex. 9
Goodwill = Normal Average Profit × Number of years' purchase
Normal Average Profit = 60,0000
![]()
Working Note:
|
Year |
Actual Profit |
+ |
Abnormal Loss Non-Recurring |
- |
Abnormal Gain Non-Recurring |
= |
Normal Profit |
|
2019 |
30,000 |
+ |
40,000 |
- |
Nil |
= |
70,000 |
|
2018 |
(80,000) |
+ |
1,10,00 |
- |
Nil |
= |
30,000 |
|
2017 |
1,10,000 |
+ |
Nil |
- |
30,000 |
= |
80,000 |
|
Normal Profits for last 3 years |
= |
1,80,000 |
|||||
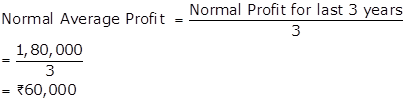
Solution Ex. 10
Goodwill = Normal Average Profit × Number of years' of purchase
![]()
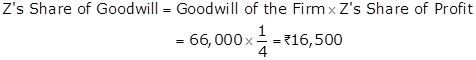
Working Notes:
|
Year |
Actual Profit |
+ |
Abnormal Loss Non-Recurring |
- |
Abnormal Gain Non-Recurring |
= |
Normal Profit |
|
2017 |
50,000 |
+ |
Nil |
- |
5,000 |
= |
45,000 |
|
2018 |
(20,000) |
+ |
30,000 |
- |
Nil |
= |
10,000 |
|
2019 |
70,000 |
+ |
Nil |
- |
18,000 + 8,000 |
= |
44,000 |
|
Normal Profits for last 3 years |
|
99,000 |
|||||
|
|
|||||||
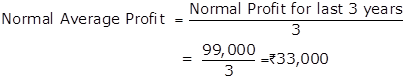
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.30
Solution Ex. 11
Goodwill = Average Profit × Number of years Purchase
Goodwill = 1,41,250 ×2 = Rs.2,82,500
Working Notes:
1.
|
Calculation Of Normal Profits (31st March Closed) |
||||
|
Years |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
Profit /Loss |
80,000 |
1,45,000 |
1,60,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
Adjustment |
20,000 |
(25,000) |
(15,000) |
|
|
Normal Profit |
1,00,000 |
1,20,000 |
1,45,000 |
2,00,000 |
Total of Normal Profit = 1,00,000 + 1,20,000 + 1,45,000 + 2,00,000
= Rs.5,65,000
2.
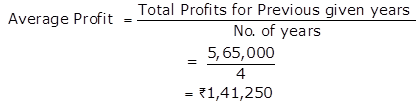
Solution Ex. 12
Goodwill = Average Profit × Number of years Purchase
Goodwill = Rs.1,00,000 ×3 = Rs.3,00,000
Working Notes:
1.
|
|
Calculation Of Normal Profits (31st March Closed) |
||||
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
Profit /Loss |
(90,000) |
1,60,000 |
1,50,000 |
65,000 |
1,77,000 |
|
Adjustment |
-- |
(50,000) |
20,000 |
85,000@ |
(17,000) |
|
Normal Profit |
(90,000) |
1,10,000 |
1,70,000 |
1,50,000 |
1,60,000 |
Total of Normal Profit = (-90,000) + 1,10,000 + 1,70,000 + 1,50,000 + 1,60,000
= Rs.5,00,000
@Adjustment Amount
|
Overhauling cost of second hand machinery (Wrongly accounted as expense instead of capital expenditure) |
Rs.1,00,000 |
|
Less: Depreciation
to be debited from Profit andLoss Account |
Rs.15,000 |
|
Adjustment Normal profit added |
Rs.85,000 |
2.
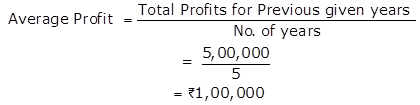
Solution Ex. 13
![]()
Working Notes:
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2015 |
20,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
20,000 |
|
2016 |
24,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
48,000 |
|
2017 |
30,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
90,000 |
|
2018 |
25,000 |
× |
4 |
= |
1,00,000 |
|
2019 |
18,000 |
× |
5 |
= |
90,000 |
|
Total |
15 |
|
3,48,000 |
||
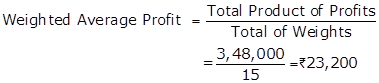
Solution Ex. 14
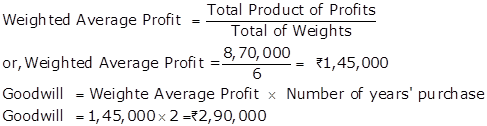
Working Notes:
|
Year |
Profit before Partners Remuneration |
- |
Partners Remuneration |
= |
Profit after Partners Remuneration |
|
2016-17 |
2,00,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
1,10,000 |
|
2017-18 |
2,30,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
1,40,000 |
|
2018-19 |
2,50,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
1,60,000 |
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2016-17 |
1,10,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
1,10,000 |
|
2017-18 |
1,40,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
2,80,000 |
|
2018-19 |
1,60,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
4,80,000 |
|
Total |
6 |
|
8,70,000 |
||
Solution Ex. 15
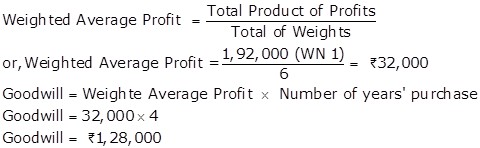
Working Notes:
|
Year |
Profit before Partners Remuneration |
- |
Partners Remuneration |
= |
Profit after Partners Remuneration |
|
2016-17 |
1,40,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
50,000 |
|
2017-18 |
1,01,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
11,000 |
|
2018-19 |
1,30,000 |
- |
90,000 |
= |
40,000 |
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2016-17 |
50,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
50,000 |
|
2017-18 |
11,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
22,000 |
|
2018-19 |
40,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
1,20,000 |
|
Total |
6 |
|
1,92,000 |
||
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.31
Solution Ex. 16
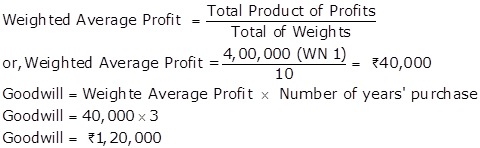
|
Working Note 1: Calculation Of Weighted Average Profits (31st March Closed) |
||||
|
Years |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
Profit /Loss |
25,000 |
27,000 |
46,900 |
53,810 |
|
Adjustments: Management Cost Plant Repair Expenses Depreciation Overvaluation of Closing Stock Overvaluation of Opening Stock |
(5,000) - - - - |
(5,000) 10,000 (1,000) (1,000) - |
(5,000) - (900) (2,000) 1,000 |
(5,000) - (810) - 2,000 |
|
Normal Profit |
20,000 |
30,000 |
40,000 |
50,000 |
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2015-16 |
20,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
20,000 |
|
2016-17 |
30,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
60,000 |
|
2017-18 |
40,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
1,20,000 |
|
2018-19 |
50,000 |
× |
4 |
= |
2,00,000 |
|
Total |
10 |
|
4,00,000 |
||
Solution Ex. 17
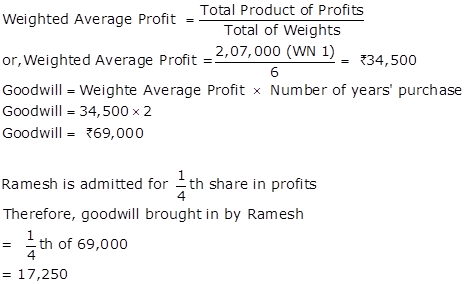
Working Note 1: Calculation Of Weighted Average Profits (31st March Closed)
|
Years |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
Profit /Loss |
50,000 |
(20,000) |
70,000 |
|
Adjustments: Profit on Sale of Asset (Abnormal Gain) Loss by fire (Abnormal Loss) Insurance Claim (Non-Recurring Income) Interest Received (Non-Recurring Income) |
(5,000) - - - |
- 35,000 - - |
- - (18,000) (8,000) |
|
Normal Profit |
45,000 |
15,000 |
44,000 |
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2016-17 |
45,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
45,000 |
|
2017-18 |
15,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
30,000 |
|
2018-19 |
44,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
1,32,000 |
|
Total |
10 |
|
2,07,000 |
||
Solution Ex. 18
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profit × Number of years' Purchase
Goodwill = Rs.1,39,000 ×3 = Rs.4,17,000
Working Notes:
1.
|
|
Calculation Of Normal Profits (31st March Closed) |
|||||
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
|
Profit /Loss |
70,000 |
1,40,000 |
1,00,000 |
1,60,000 |
1,65,000 |
|
|
Adjustment |
20,000 |
(30,000) |
---- |
(10,000) |
10,000 |
|
|
Normal Profit |
90,000 |
1,10,000 |
1,00,000 |
1,50,000 |
1,75,000 |
|
2.
|
|
Calculation Of Weighted Average Profit (31st March Closed) |
|||||
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
|
i. Normal Profit |
90,000 |
1,10,000 |
1,00,000 |
1,50,000 |
1,75,000 |
|
|
ii. Adjustment (i ×ii) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
Product |
90,000 |
2,20,000 |
3,00,000 |
6,00,000 |
8,75,000 |
|
Total of weight = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
Total of Product Profit = 90,000 + 2,20,000 + 3,00,000 + 6,00,000 + 8,75,000
= Rs.20,85,000
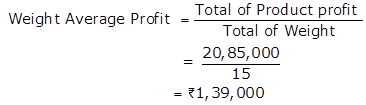
Solution Ex. 19
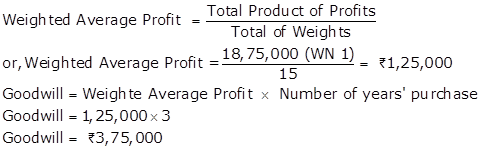
Working Note 1: Calculation Of Weighted Average Profits (31st March Closed)
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
Profit /Loss |
1,25,000 |
1,40,000 |
1,20,000 |
55,000 |
2,57,000 |
|
Adjustments: Repairs to Machine Depreciation Undervaluation of Stock Overvaluation of Stock Remuneration to Partners |
- - - - (40,000) |
- - - - (40,000) |
- - - - (40,000) |
1,00,000 (15,000) 50,000 - (40,000) |
(17,000)
(50,000) (40,000) |
|
Normal Profit |
85,000 |
1,00,000 |
80,000 |
1,50,000 |
1,50,000 |
|
Year |
Profit |
× |
Weight |
= |
Product |
|
2014-15 |
85,000 |
× |
1 |
= |
85,000 |
|
2015-16 |
1,00,000 |
× |
2 |
= |
2,00,000 |
|
2016-17 |
80,000 |
× |
3 |
= |
2,40,000 |
|
2017-18 |
1,50,000 |
× |
4 |
= |
6,00,000 |
|
2018-19 |
1,50,000 |
× |
5 |
= |
7,50,000 |
|
Total |
15 |
|
18,75,000 |
||
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.32
Solution Ex. 20
|
Particulars |
2015-16 |
2016-17 |
2017-18 |
2018-19 |
|
Profits |
1,01,000 |
1,24,000 |
1,00,000 |
1,40,000 |
|
Repair Capitalised |
|
|
+30,000 |
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
(1,000) |
(2,900) |
|
Overvaluation of Closing Stock |
|
(12,000) |
12,000 |
|
|
Management Cost |
(24,000) |
(24,000) |
(24,000) |
(24,000) |
|
Sale Proceeds |
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
Wrong Depreciation |
|
|
900 |
810 |
|
Adjusted Profits |
77,000 |
78,000 |
1,17,900 |
1,13,910 |
|
Weights |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Product |
77,000 |
1,56,000 |
3,53,700 |
4,55,640 |
Working Notes:
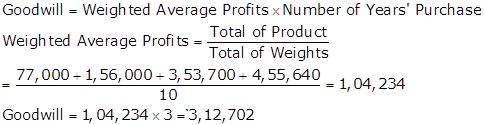
Note 1: Sale proceeds wrongly credited in 2016-17 have been deducted after adjusting for profit of Rs.1,000.
Solution Ex. 21

Solution Ex. 22

Solution Ex. 23

Solution Ex. 24

Solution Ex. 25

Solution Ex. 26

Solution Ex. 27
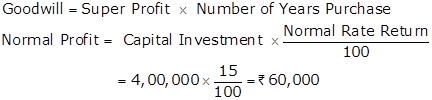
|
Year |
Profit before Partners' Remuneration |
_ |
Partners' Remuneration |
= |
Profit after Partners' Remuneration |
|
2017 |
1,70,000 |
- |
1,00,000 |
= |
70,000 |
|
2018 |
2,00,000 |
- |
1,00,000 |
= |
1,00,000 |
|
2019 |
2,30,000 |
- |
1,00,000 |
= |
1,30,000 |

Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.33
Solution Ex. 28
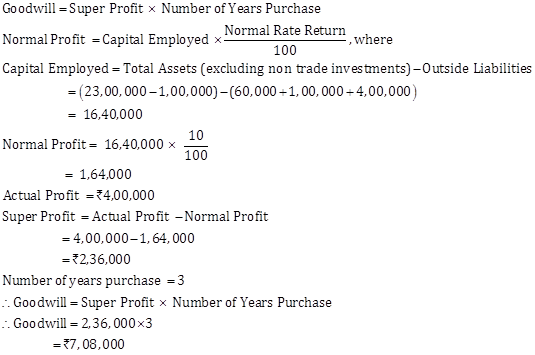 Note:
Since, no specific information has been given in the question with respect to
the Investments, such Investments are considered as non-trade investments
while computing the value of Capital Employed.
Note:
Since, no specific information has been given in the question with respect to
the Investments, such Investments are considered as non-trade investments
while computing the value of Capital Employed.
Solution Ex. 29
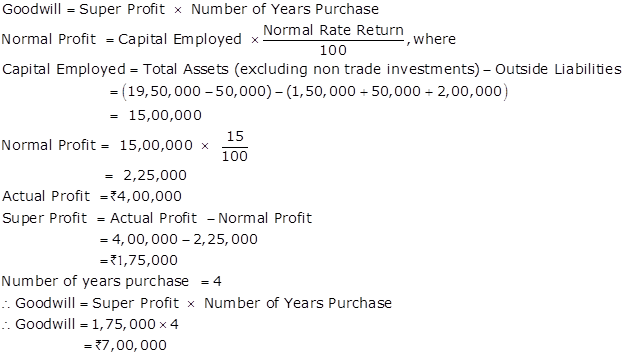
Solution Ex. 30

Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.34
Solution Ex. 31
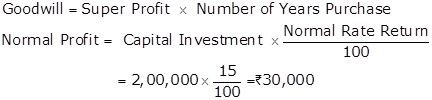
|
Year |
Profit before Partners' Salary |
_ |
Partners' Salary |
= |
Actual Profit after Salary |
|
1 |
60,000 |
- |
24,000 |
= |
36,000 |
|
2 |
72,000 |
- |
24,000 |
= |
48,000 |
|
2 |
84,000 |
- |
24,000 |
= |
60,000 |

Solution Ex. 32

Solution Ex. 33

Solution Ex. 34
Average Profit earned by a firm = Rs.1,00,000
Undervaluation of Stock = Rs.40,000
Average Actual Profit
= Average Profit earned by a firm + Undervaluation of Stock
= 1,00,000 + 40,000
= Rs.1,40,000
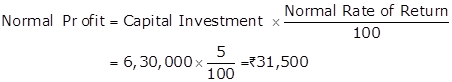
Super Profit
= Actual Average Profit -Normal Profit
= 1,40,000 -31,500 = Rs.1,08,500
Goodwill
= Super Profit × Number of Times
= 1,08,500 × 5
= Rs.5,42,500
Solution Ex. 35
Average Profit earned by a firm = Rs.7,50,000
Overvaluation of Stock = Rs.30,000
Average Actual Profit
= Average Profit earned by a firm - Overvaluation of Stock
= 7,50,000 - 30,000
= Rs.7,20,000
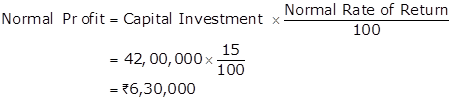
Super Profit = Actual Average Profit - Normal Profit
= 7,20,000 - 6,30,000
=Rs. 90,000
Goodwill = Super Profit × Number of Times
= 90,000 × 3
= Rs.2,70,000
Solution Ex. 36
1.
|
|
Calculation Of Normal Profits (31st March) |
|||||
|
Years |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
|
Profit /Loss |
1,50,000 |
1,80,000 |
1,00,000 |
2,60,000 |
2,40,000 |
|
|
Adjustment |
--- |
--- |
1,00,000 |
(40,000) |
--- |
|
|
Normal Profit |
1,50,000 |
1,80,000 |
2,00,000 |
2,20,000 |
2,40,000 |
|
Total of Normal Profit = 1,50,000 + 1,80,000 + 2,00,000 + 2,20,000 + 2,40,000
= Rs.9,90,000
2.
Calculation of Capital Employed
Capital employed = Total Assets - Outside liabilities
Capital employed = Rs.20,00,000 - Rs.5,00,000 = Rs.15,00,000
3.
Calculation Super Profit
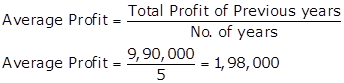
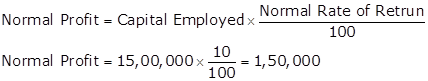
Super Profit = Average Profit - Normal Profit
Super Profit = 1,98,000 - 1,50,000 = 48,000
Goodwill = Super Profit × Number of Year Purchase
= 48,000 × 3
= Rs.1,44,000
Solution Ex. 37
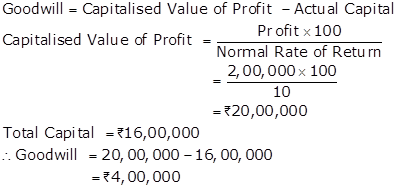
Solution Ex.38
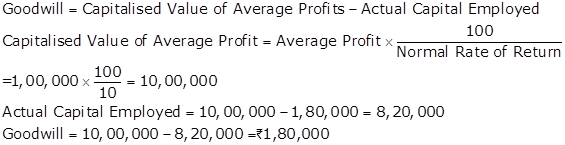
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.35
Solution Ex. 39
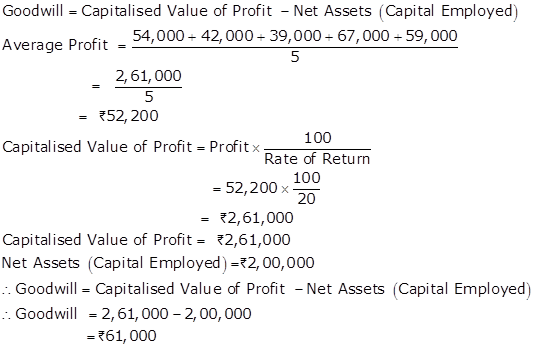
Solution Ex. 40
Given:
Average Profit - Rs.4,00,00
Normal Rate of Return -10%
(i) Goodwill by Capitalisation of super profit
Capital Employed = Assets -External Liabilities
= 40,00,000 -7,20,000
= Rs.32,80,000
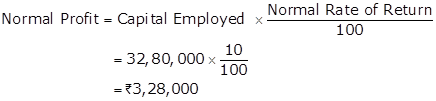
Super Profit =Actual Profit -Normal Profit
= 4,00,000 -3,28,000 = Rs.72,000
![]()
![]()
= Rs.7,20,000
(ii) Super Profit Method if the goodwill is valued at 3 years purchase of super profits
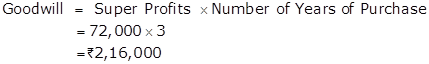
Therefore, Goodwill is valued at Rs.2,16,000
Solution Ex. 41
(i) Calculation of goodwill by capitalization of super profit method

(ii) Calculation of Goodwill by capitalization of average profits method
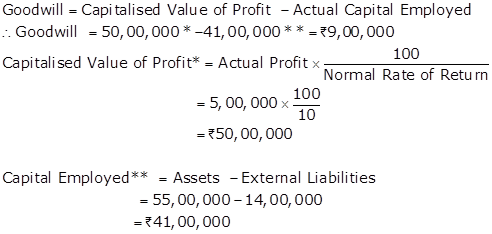
Solution Ex. 42
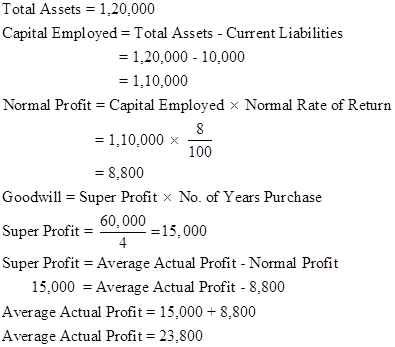
Solution Ex. 43
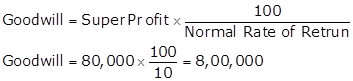
Working Notes:
Calculation Super Profit
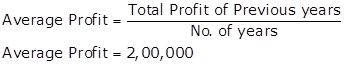
Capital Employed
Capital employed = Total Assets - Outside liabilities
Capital employed = Rs.15,00,000 - Rs.3,00,000 = Rs.12,00,000
Normal Profit
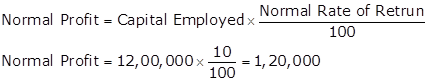
Super Profit
Super Profit = Average Profit - Normal Profit
Super Profit = 2,00,000 - 1,20,000 = 80,000
Solution Ex. 44
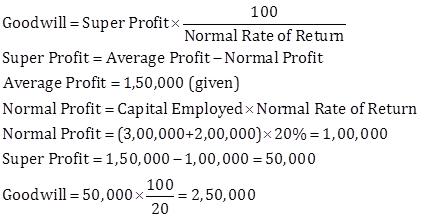
Solution Ex. 45
![]()
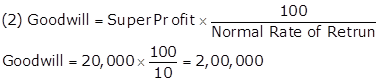
Working Notes:
Calculation Super Profit
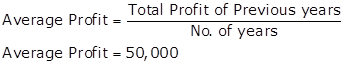
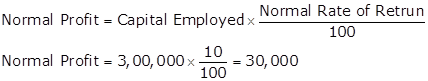
Super Profit = Average Profit - Normal Profit
Super Profit = 50,000 - 30,000 = 20,000
Solution Ex. 46
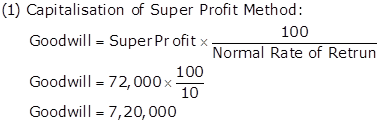
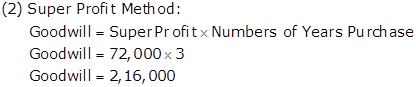
Working Notes:
Calculation Super Profit:
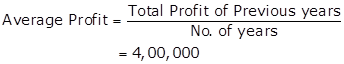
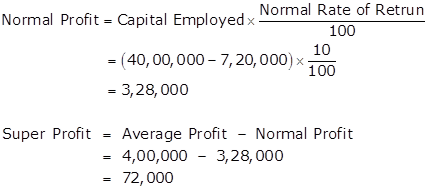
Goodwill: Nature and Valuation Exercise 3.36
Solution Ex. 47
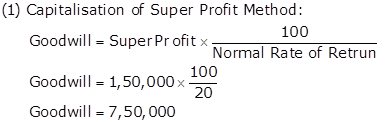
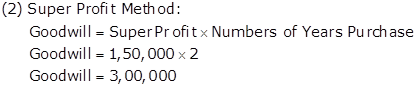
Working Notes:
Calculation Super Profit:
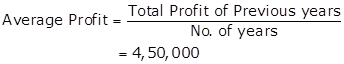
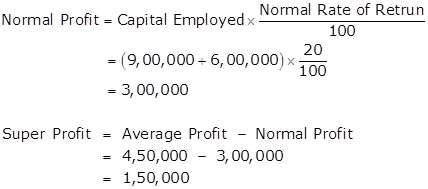
Solution Ex. 48
![]()
![]()
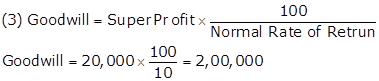
(4) Goodwill = Capitalised Value - Net Asset
Goodwill =8,00,000 - 6,00,000 = 2,00,000
Working Notes:
Calculation Super Profits
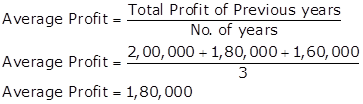
Capital employed = Total Assets - Outside liabilities
Capital employed = Rs.7,00,000 - Rs.1,00,000 = Rs.6,00,000
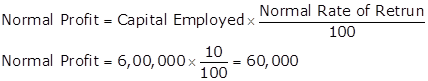
Super Profit = Average Profit (Adjusted) - Normal Profit
Super Profit = Rs.80,000 - Rs.60,000 = Rs.20,000
