Class 9 R S AGGARWAL AND V AGGARWAL Solutions Maths Chapter 8 - Triangles
Triangles Exercise MCQ
Solution 1

Solution 2
Correct option: (c)
∠A - ∠B = 42°
⇒ ∠A = ∠B + 42°
∠B - ∠C = 21°
⇒ ∠C = ∠B - 21°
In ΔABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠B + 42° + ∠B + ∠B - 21° = 180°
⇒ 3∠B = 159
⇒ ∠B = 53°
Solution 3
Correct option: (b)
∠ACD = ∠B + ∠A (Exterior angle property)
⇒ 110° = 50° + ∠A
⇒ ∠A = 60°
Solution 4
Correct option: (d)
Solution 5
Correct option: (a)
Solution 6

Solution 7
Correct option: (b)
∠EAF = ∠CAD (vertically opposite angles)
⇒ ∠CAD = 30°
In ΔABD, by angle sum property
∠A + ∠B + ∠D = 180°
⇒ (x + 30)° + (x + 10)° + 90° = 180°
⇒ 2x + 130° = 180°
⇒ 2x = 50°
⇒ x = 25°
Solution 8
Correct option: (a)
∠ABF + ∠ABC = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ x + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ∠ABC = 180° - x
∠ACG + ∠ACB = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ y + ∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠ACB = 180° - y
In ΔABC, by angle sum property
∠ABC + ∠ACB + ∠BAC = 180°
⇒ (180° - x) + (180° - y) + ∠BAC = 180°
⇒ ∠BAC - x - y + 180° = 0
⇒ ∠BAC = x + y - 180°
Now, ∠EAD = ∠BAC (vertically opposite angles)
⇒ z = x + y - 180°
Solution 9
Correct option: (b)
In ΔOAC, by angle sum property
∠OCA + ∠COA + ∠CAO = 180°
⇒ 80° + 40° + ∠CAO = 180°
⇒ ∠CAO = 60°
∠CAO + ∠OAE = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 60° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 120°
∠COA = ∠BOD (vertically opposite angles)
⇒ ∠BOD = 40°
In ΔOBD, by angle sum property
∠OBD + ∠BOD + ∠ODB = 180°
⇒ ∠OBD + 40° + 70° = 180°
⇒ ∠OBD = 70°
∠OBD + ∠DBF = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 70° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 110°
∴ x + y = 120° + 110° = 230°
Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12
Correct option: (a)
∠ACB + ∠ACD = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 5y + 7y = 180°
⇒ 12y = 180°
⇒ y = 15°
Now, ∠ACD = ∠ABC + ∠BAC (Exterior angle property)
⇒ 7y = x + 3y
⇒ 7(15°) = x + 3(15°)
⇒ 105° = x + 45°
⇒ x = 60°
Triangles Exercise Ex. 8
Solution 1
Since, sum of the angles of a triangle is 180o
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() A + 76o
+ 48o = 180o
A + 76o
+ 48o = 180o
![]()
![]() A = 180o - 124o = 56o
A = 180o - 124o = 56o
![]()
![]() A = 56o
A = 56o
Solution 2
Let the measures of the angles of a triangle are (2x)o, (3x)o and (4x)o.
Then, 2x + 3x + 4x = 180 [sum of the angles of a triangle is 180o ]
![]() 9x = 180
9x = 180
![]()
![]()
![]() The measures of the required angles are:
The measures of the required angles are:
2x = (2 ![]() 20)o = 40o
20)o = 40o
3x = (3 ![]() 20)o = 60o
20)o = 60o
4x = (4 ![]() 20)o = 80o
20)o = 80o
Solution 3
Let
3![]() A = 4
A = 4![]() B = 6
B = 6![]() C = x (say)
C = x (say)
Then, 3![]() A = x
A = x
![]()
![]() A =
A = ![]()
4![]() B = x
B = x
![]()
![]()
and 6![]() C = x
C = x
![]()
![]() C =
C = ![]()
As
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
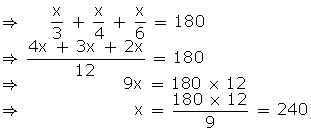
![]()
![]() A =
A = ![]()
![]() B =
B = ![]()
![]() C =
C = ![]()
Solution 4
![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 108o [Given]
B = 108o [Given]
But
as ![]() A,
A, ![]() B and
B and ![]() C are the angles of a triangle,
C are the angles of a triangle,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 108o +
108o + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() C = 180o - 108o = 72o
C = 180o - 108o = 72o
Also, ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 130o [Given]
C = 130o [Given]
![]()
![]() B + 72o = 130o
B + 72o = 130o
![]()
![]() B = 130o - 72o = 58o
B = 130o - 72o = 58o
Now
as, ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 108o
B = 108o
![]()
![]() A + 58o = 108o
A + 58o = 108o
![]()
![]() A = 108o - 58o = 50o
A = 108o - 58o = 50o
![]()
![]() A = 50o,
A = 50o, ![]() B = 58o and
B = 58o and ![]() C = 72o.
C = 72o.
Solution 5
Since.
![]() A ,
A , ![]() B and
B and ![]() C are the angles of a triangle .
C are the angles of a triangle .
So, ![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
Now, ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 125o [Given]
B = 125o [Given]
![]() 125o +
125o + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() C = 180o - 125o = 55o
C = 180o - 125o = 55o
Also, ![]() A +
A + ![]() C = 113o [Given]
C = 113o [Given]
![]()
![]() A + 55o = 113o
A + 55o = 113o
![]()
![]() A = 113o - 55o = 58o
A = 113o - 55o = 58o
Now
as ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 125o
B = 125o
![]() 58o +
58o + ![]() B = 125o
B = 125o
![]()
![]() B = 125o - 58o = 67o
B = 125o - 58o = 67o
![]()
![]() A = 58o,
A = 58o, ![]() B = 67o and
B = 67o and ![]() C = 55o.
C = 55o.
Solution 6
Since, ![]() P,
P, ![]() Q and
Q and ![]() R are the angles of a triangle.
R are the angles of a triangle.
So,![]() P +
P + ![]() Q +
Q + ![]() R = 180o(i)
R = 180o(i)
Now,![]() P -
P - ![]() Q = 42o[Given]
Q = 42o[Given]
![]()
![]() P = 42o +
P = 42o + ![]() Q(ii)
Q(ii)
and![]() Q -
Q - ![]() R = 21o[Given]
R = 21o[Given]
![]() R =
R = ![]() Q - 21o(iii)
Q - 21o(iii)
Substituting the value of ![]() P and
P and ![]() R from (ii) and (iii) in (i), we get,
R from (ii) and (iii) in (i), we get,
42o + ![]() Q +
Q + ![]() Q +
Q + ![]() Q - 21o = 180o
Q - 21o = 180o
![]() 3
3![]() Q + 21o = 180o
Q + 21o = 180o
![]() 3
3![]() Q = 180o - 21o = 159o
Q = 180o - 21o = 159o
![]()
![]() Q =
Q = ![]()
![]()
![]() P = 42o +
P = 42o + ![]() Q
Q
= 42o + 53o = 95o
![]() R =
R = ![]() Q - 21o
Q - 21o
= 53o - 21o = 32o
![]()
![]() P = 95o,
P = 95o, ![]() Q = 53o and
Q = 53o and ![]() R = 32o.
R = 32o.
Solution 7
Given that the sum of the angles A and B of a ![]() ABC is 116o, i.e.,
ABC is 116o, i.e., ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 116o.
B = 116o.
Since, ![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
So, 116o + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() C = 180o - 116o = 64o
C = 180o - 116o = 64o
Also, it is given that:
![]() A -
A - ![]() B = 24o
B = 24o
![]()
![]() A = 24o +
A = 24o + ![]() B
B
Putting, ![]() A = 24o +
A = 24o + ![]() B in
B in ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 116o, we get,
B = 116o, we get,
24o + ![]() B +
B + ![]() B = 116o
B = 116o
![]() 2
2![]() B + 24o = 116o
B + 24o = 116o
![]() 2
2![]() B = 116o - 24o = 92o
B = 116o - 24o = 92o
![]()
![]() B =
B = ![]()
Therefore, ![]() A = 24o + 46o = 70o
A = 24o + 46o = 70o
![]()
![]() A = 70o,
A = 70o, ![]() B = 46o and
B = 46o and ![]() C = 64o.
C = 64o.
Solution 8
Let the two equal angles, ![]() A and
A and ![]() B, of the triangle be xo each.
B, of the triangle be xo each.
We know,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() xo + xo +
xo + xo + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 2xo +
2xo + ![]() C = 180o(i)
C = 180o(i)
Also, it is given that,
![]() C = xo + 18o(ii)
C = xo + 18o(ii)
Substituting ![]() C from (ii) in (i), we get,
C from (ii) in (i), we get,
2xo + xo + 18o = 180o
![]() 3xo = 180o - 18o = 162o
3xo = 180o - 18o = 162o
![]() x =
x = ![]()
Thus, the required angles of the triangle are 54o, 54o and xo + 18o = 54o + 18o = 72o.
Solution 9
Let ![]() C be the smallest angle of
C be the smallest angle of ![]() ABC.
ABC.
Then,
![]() A = 2
A = 2![]() C and
C and ![]() B = 3
B = 3![]() C
C
Also,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 2
2![]() C + 3
C + 3![]() C +
C + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 6
6![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() C = 30o
C = 30o
So, ![]() A = 2
A = 2![]() C = 2
C = 2 ![]() 30o
= 60o
30o
= 60o
![]() B = 3
B = 3![]() C = 3
C = 3 ![]() 30o
= 90o
30o
= 90o
![]() The required angles of the triangle are 60o,
90o, 30o.
The required angles of the triangle are 60o,
90o, 30o.
Solution 10
Let
ABC be a right angled triangle and ![]() C = 90o
C = 90o
Since,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 180o -
B = 180o - ![]() C = 180o - 90o = 90o
C = 180o - 90o = 90o
Suppose ![]() A = 53o
A = 53o
Then, 53o + ![]() B = 90o
B = 90o
![]()
![]() B = 90o - 53o = 37o
B = 90o - 53o = 37o
![]() The required angles are 53o, 37o
and 90o.
The required angles are 53o, 37o
and 90o.
Solution 11
Let
ABC be a right angled triangle and ![]() C = 90o
C = 90o
Since,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 180o -
B = 180o - ![]() C = 180o - 90o = 90o
C = 180o - 90o = 90o
Suppose ![]() A = 53o
A = 53o
Then, 53o + ![]() B = 90o
B = 90o
![]()
![]() B = 90o - 53o = 37o
B = 90o - 53o = 37o
![]() The required angles are 53o, 37o
and 90o.
The required angles are 53o, 37o
and 90o.
Solution 12
Let ABC be a triangle.
So, ![]() A <
A < ![]() B +
B + ![]() C
C
Adding ![]() A to both sides of the inequality,
A to both sides of the inequality,
![]() 2
2 ![]() A <
A < ![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C
C
![]() 2
2 ![]() A < 180o [Since
A < 180o [Since ![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o]
C = 180o]
![]()
Similarly, ![]() B <
B <![]() A +
A + ![]() C
C
![]()
![]() B < 90o
B < 90o
and ![]() C <
C < ![]() A +
A + ![]() B
B
![]()
![]() C < 90o
C < 90o
![]() ABC is an acute angled triangle.
ABC is an acute angled triangle.
Solution 13
Let
ABC be a triangle and ![]() B >
B > ![]() A +
A + ![]() C
C
Since,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() A +
A + ![]() C = 180o -
C = 180o - ![]() B
B
Therefore, we get,
![]() B > 180o -
B > 180o - ![]() B
B
Adding
![]() B on both sides of the inequality, we get,
B on both sides of the inequality, we get,
![]() B +
B + ![]() B > 180o -
B > 180o - ![]() B +
B + ![]() B
B
![]() 2
2![]() B > 180o
B > 180o
![]()
![]() B >
B > ![]()
i.e.,
![]() B > 90o which means
B > 90o which means ![]() B is an obtuse angle.
B is an obtuse angle.
![]()
![]() ABC is an obtuse angled triangle.
ABC is an obtuse angled triangle.
Solution 14
Since
![]() ACB and
ACB and ![]() ACD form a linear pair.
ACD form a linear pair.
So, ![]() ACB +
ACB + ![]() ACD = 180o
ACD = 180o
![]()
![]() ACB + 128o = 180o
ACB + 128o = 180o
![]()
![]() ACB = 180o - 128 = 52o
ACB = 180o - 128 = 52o
Also, ![]() ABC +
ABC + ![]() ACB +
ACB + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]() 43o + 52o
+
43o + 52o
+ ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]() 95o +
95o + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]()
![]() BAC = 180o - 95o = 85o
BAC = 180o - 95o = 85o
![]()
![]() ACB = 52o and
ACB = 52o and ![]() BAC = 85o.
BAC = 85o.
Solution 15
As ![]() DBA and
DBA and ![]() ABC form a linear pair.
ABC form a linear pair.
So,![]() DBA +
DBA + ![]() ABC = 180o
ABC = 180o
![]() 106o +
106o + ![]() ABC = 180o
ABC = 180o
![]()
![]() ABC = 180o - 106o = 74o
ABC = 180o - 106o = 74o
Also, ![]() ACB and
ACB and ![]() ACE form a linear pair.
ACE form a linear pair.
So,![]() ACB +
ACB + ![]() ACE = 180o
ACE = 180o
![]()
![]() ACB + 118o = 180o
ACB + 118o = 180o
![]()
![]() ACB = 180o - 118o = 62o
ACB = 180o - 118o = 62o
In ![]() ABC, we have,
ABC, we have,
![]() ABC +
ABC + ![]() ACB +
ACB + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
74o + 62o + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]() 136o +
136o + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]()
![]() BAC = 180o - 136o = 44o
BAC = 180o - 136o = 44o
![]() In triangle ABC,
In triangle ABC, ![]() A = 44o,
A = 44o, ![]() B = 74o and
B = 74o and ![]() C = 62o
C = 62o
Solution 16
(i) ![]() EAB +
EAB + ![]() BAC = 180o [Linear pair angles]
BAC = 180o [Linear pair angles]
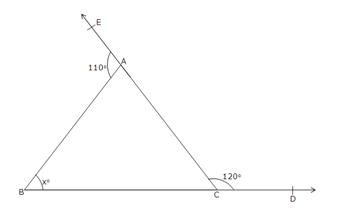
110o + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
![]()
![]() BAC = 180o - 110o = 70o
BAC = 180o - 110o = 70o
Again, ![]() BCA +
BCA + ![]() ACD = 180o [Linear
pair angles]
ACD = 180o [Linear
pair angles]
![]()
![]() BCA + 120o
= 180o
BCA + 120o
= 180o
![]()
![]() BCA = 180o - 120o = 60o
BCA = 180o - 120o = 60o
Now,
in ![]() ABC,
ABC,
![]() ABC +
ABC + ![]() BAC +
BAC + ![]() ACB = 180o
ACB = 180o
xo + 70o + 60o = 180o
![]() x + 130o
= 180o
x + 130o
= 180o
![]() x = 180o - 130o
= 50o
x = 180o - 130o
= 50o
![]() x = 50
x = 50
(ii)
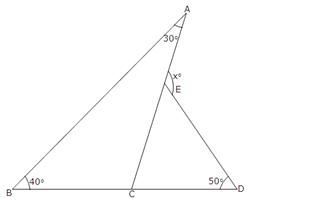
In
![]() ABC,
ABC,
![]() A
+
A
+ ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 30o + 40o
+
30o + 40o
+ ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 70o
+
70o
+ ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]()
![]() C = 180o - 70o = 110o
C = 180o - 70o = 110o
Now ![]() BCA +
BCA + ![]() ACD = 180o [Linear pair]
ACD = 180o [Linear pair]
![]() 110o
+
110o
+ ![]() ACD = 180o
ACD = 180o
![]()
![]() ACD = 180o - 110o = 70o
ACD = 180o - 110o = 70o
In
![]() ECD,
ECD,
![]() ECD +
ECD + ![]() CDE +
CDE + ![]() CED = 180o
CED = 180o
![]() 70o + 50o
+
70o + 50o
+ ![]() CED = 180o
CED = 180o
![]() 120o
+
120o
+ ![]() CED = 180o
CED = 180o
![]()
![]() CED = 180o - 120o = 60o
CED = 180o - 120o = 60o
Since
![]() AED and
AED and ![]() CED from a linear pair
CED from a linear pair
So, ![]() AED +
AED + ![]() CED = 180o
CED = 180o
![]() xo
+ 60o = 180o
xo
+ 60o = 180o
![]() xo
= 180o - 60o = 120o
xo
= 180o - 60o = 120o
![]() x =
120
x =
120
(iii)
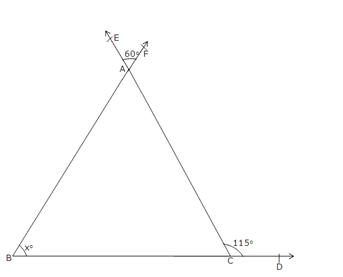
![]() EAF
=
EAF
= ![]() BAC
[Vertically opposite angles]
BAC
[Vertically opposite angles]
![]()
![]() BAC = 60o
BAC = 60o
In
![]() ABC, exterior
ABC, exterior ![]() ACD is equal to the sum of two opposite interior
angles.
ACD is equal to the sum of two opposite interior
angles.
So, ![]() ACD =
ACD = ![]() BAC +
BAC + ![]() ABC
ABC
![]() 115o = 60o
+ xo
115o = 60o
+ xo
![]() xo = 115o
- 60o = 55o
xo = 115o
- 60o = 55o
![]() x = 55
x = 55
(iv)
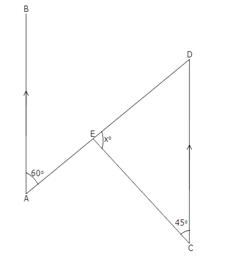
Since AB || CD and AD is a transversal.
So, ![]() BAD =
BAD = ![]() ADC
ADC
![]()
![]() ADC = 60o
ADC = 60o
In
![]() ECD, we have,
ECD, we have,
![]() E +
E + ![]() C +
C + ![]() D = 180o
D = 180o
![]() xo + 45o +
60o = 180o
xo + 45o +
60o = 180o
![]() xo + 105o
= 180o
xo + 105o
= 180o
![]() xo =
180o - 105o = 75o
xo =
180o - 105o = 75o
![]() x = 75
x = 75
(v)
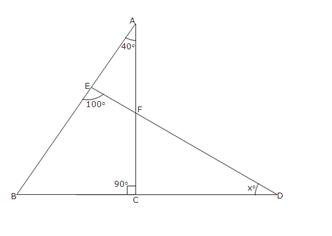
In
![]() AEF,
AEF,
Exterior
![]() BED =
BED = ![]() EAF +
EAF + ![]() EFA
EFA
![]() 100o = 40o
+
100o = 40o
+ ![]() EFA
EFA
![]()
![]() EFA = 100o - 40o = 60o
EFA = 100o - 40o = 60o
Also, ![]() CFD =
CFD = ![]() EFA [Vertically
Opposite angles]
EFA [Vertically
Opposite angles]
![]()
![]() CFD = 60o
CFD = 60o
Now
in ![]() FCD,
FCD,
Exterior
![]() BCF =
BCF = ![]() CFD +
CFD + ![]() CDF
CDF
![]() 90o = 60o +
xo
90o = 60o +
xo
![]() xo = 90o -
60o = 30o
xo = 90o -
60o = 30o
![]() x = 30
x = 30
(vi)
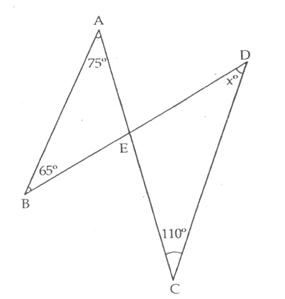
In
![]() ABE, we have,
ABE, we have,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() E = 180o
E = 180o
![]() 75o + 65o
+
75o + 65o
+ ![]() E = 180o
E = 180o
![]() 140o +
140o + ![]() E = 180o
E = 180o
![]()
![]() E = 180o - 140o = 40o
E = 180o - 140o = 40o
Now, ![]() CED =
CED = ![]() AEB [Vertically
opposite angles]
AEB [Vertically
opposite angles]
![]()
![]() CED = 40o
CED = 40o
Now,
in ![]() CED, we have,
CED, we have,
![]() C +
C + ![]() E +
E + ![]() D = 180o
D = 180o
![]() 110o + 40o
+ xo = 180o
110o + 40o
+ xo = 180o
![]() 150o + xo =
180o
150o + xo =
180o
![]() xo = 180o -
150o = 30o
xo = 180o -
150o = 30o
![]() x = 30
x = 30
Solution 17
AB ∥ CD and AC is the transversal.
⇒ ∠BAC = ∠ACD = 60° (alternate angles)
i.e. ∠BAC = ∠GCH = 60°
Now, ∠DHF = ∠CHG = 50° (vertically opposite angles)
In ΔGCH, by angle sum property,
∠GCH + ∠CHG + ∠CGH = 180°
⇒ 60° + 50° + ∠CGH = 180°
⇒ ∠CGH = 70°
Now, ∠CGH + ∠AGH = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 70° + ∠AGH = 180°
⇒ ∠AGH = 110°
Solution 18
Produce CD to cut AB at E.
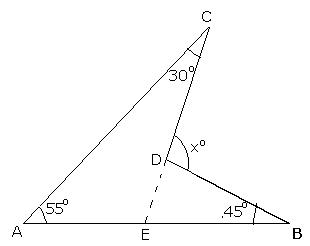
Now, in ![]() BDE, we have,
BDE, we have,
Exterior ![]() CDB =
CDB = ![]() CEB +
CEB + ![]() DBE
DBE
![]() xo =
xo = ![]() CEB + 45o .....(i)
CEB + 45o .....(i)
In ![]() AEC, we have,
AEC, we have,
Exterior ![]() CEB =
CEB = ![]() CAB +
CAB + ![]() ACE
ACE
= 55o + 30o = 85o
Putting ![]() CEB = 85o in (i), we get,
CEB = 85o in (i), we get,
xo = 85o + 45o = 130o
![]() x = 130
x = 130
Solution 19
The angle ![]() BAC is divided by AD in the ratio 1 : 3.
BAC is divided by AD in the ratio 1 : 3.
Let ![]() BAD and
BAD and ![]() DAC be y and 3y, respectively.
DAC be y and 3y, respectively.
As BAE is a straight line,
![]() BAC +
BAC + ![]() CAE = 180o [linear pair]
CAE = 180o [linear pair]
![]()
![]() BAD +
BAD + ![]() DAC +
DAC + ![]() CAE = 180o
CAE = 180o
![]() y + 3y + 108o = 180o
y + 3y + 108o = 180o
![]() 4y = 180o - 108o = 72o
4y = 180o - 108o = 72o
![]()
![]()
Now, in ![]() ABC,
ABC,
![]() ABC +
ABC + ![]() BCA +
BCA + ![]() BAC = 180o
BAC = 180o
y + x + 4y = 180o
[Since, ![]() ABC =
ABC = ![]() BAD (given AD = DB) and
BAD (given AD = DB) and ![]() BAC = y + 3y = 4y]
BAC = y + 3y = 4y]
![]() 5y + x = 180
5y + x = 180
![]() 5
5 ![]() 18 + x = 180
18 + x = 180
![]() 90 + x = 180
90 + x = 180
![]() x = 180 - 90 = 90
x = 180 - 90 = 90
Solution 20
Given : A ![]() ABC in which BC, CA and AB are produced to D, E and F respectively.
ABC in which BC, CA and AB are produced to D, E and F respectively.
To prove : Exterior ![]() DCA + Exterior
DCA + Exterior ![]() BAE + Exterior
BAE + Exterior ![]() FBD = 360o
FBD = 360o
Proof : Exterior ![]() DCA =
DCA = ![]() A +
A + ![]() B(i)
B(i)
Exterior ![]() FAE =
FAE = ![]() B +
B + ![]() C(ii)
C(ii)
Exterior ![]() FBD =
FBD = ![]() A +
A + ![]() C(iii)
C(iii)
Adding (i), (ii) and (iii), we get,
Ext. ![]() DCA + Ext.
DCA + Ext. ![]() FAE + Ext.
FAE + Ext. ![]() FBD
FBD
= ![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C +
C + ![]() A +
A + ![]() C
C
= 2![]() A +2
A +2![]() B + 2
B + 2![]() C
C
= 2 (![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C)
C)
= 2 ![]() 180o
180o
[Since, in triangle the sum of all three angle is 180o]
= 360o
Hence, proved.
Solution 21
In ![]() ACE, we have,
ACE, we have,
![]() A +
A + ![]() C +
C + ![]() E = 180o (i)
E = 180o (i)
In ![]() BDF, we have,
BDF, we have,
![]() B +
B + ![]() D +
D + ![]() F = 180o (ii)
F = 180o (ii)
Adding both sides of (i) and (ii), we get,
![]() A +
A + ![]() C+
C+![]() E +
E + ![]() B +
B + ![]() D +
D + ![]() F = 180o + 180o
F = 180o + 180o
![]()
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C +
C + ![]() D +
D + ![]() E +
E + ![]() F = 360o.
F = 360o.
Solution 22
In ΔABC, by angle sum property,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠A + 70° + 20° = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 90°
In ΔABM, by angle sum property,
∠BAM + ∠ABM + ∠AMB = 180°
⇒ ∠BAM + 70° + 90° = 180°
⇒ ∠BAM = 20°
Since AN is the bisector of ∠A,
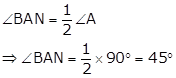
Now, ∠MAN + ∠BAM = ∠BAN
⇒ ∠MAN + 20° = 45°
⇒ ∠MAN = 25°
Solution 23
BAD ∥ EF and EC is the transversal.
⇒ ∠AEF = ∠CAD (corresponding angles)
⇒ ∠CAD = 55°
Now, ∠CAD + ∠CAB = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 55° + ∠CAB = 180°
⇒ ∠CAB = 125°
In ΔABC, by angle sum property,
∠ABC + ∠CAB + ∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠ABC + 125° + 25° = 180°
⇒ ∠ABC = 30°
Solution 24
In the given ![]() ABC, we have,
ABC, we have,
![]() A :
A : ![]() B :
B : ![]() C = 3 : 2 : 1
C = 3 : 2 : 1
Let ![]() A = 3x,
A = 3x, ![]() B = 2x,
B = 2x, ![]() C = x. Then,
C = x. Then,
![]() A +
A + ![]() B +
B + ![]() C = 180o
C = 180o
![]() 3x + 2x + x = 180o
3x + 2x + x = 180o
![]() 6x = 180o
6x = 180o
![]() x = 30o
x = 30o
![]()
![]() A = 3x = 3
A = 3x = 3 ![]() 30o = 90o
30o = 90o
![]() B = 2x = 2
B = 2x = 2 ![]() 30o = 60o
30o = 60o
and, ![]() C = x = 30o
C = x = 30o
Now, in ABC, we have,
Ext ![]() ACE =
ACE = ![]() A +
A + ![]() B = 90o + 60o = 150o
B = 90o + 60o = 150o
![]()
![]() ACD +
ACD + ![]() ECD = 150o
ECD = 150o
![]()
![]() ECD = 150o -
ECD = 150o - ![]() ACD
ACD
![]()
![]() ECD = 150o - 90o [since
ECD = 150o - 90o [since ![]() ,
, ![]() ]
]
![]()
![]() ECD= 60o
ECD= 60o
Solution 25
∠FGH + ∠FGE = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 120° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 60°
AB ∥ DF and BD is the transversal.
⇒ ∠ABC = ∠CDE (alternate angles)
⇒ ∠CDE = 50°
BD ∥ FG and DF is the transversal.
⇒ ∠EFG = ∠CDE (alternate angles)
⇒ ∠EFG = 50°
In ΔEFG, by angle sum property,
∠FEG + ∠FGE + ∠EFG = 180°
⇒ x + y + 50° = 180°
⇒ x + 60° + 50° = 180°
⇒ x = 70°
Solution 26
AB ∥ CD and EF is the transversal.
⇒ ∠AEF = ∠EFD (alternate angles)
⇒ ∠AEF = ∠EFG + ∠DFG
⇒ 65° = ∠EFG + 30°
⇒ ∠EFG = 35°
In ΔGEF, by angle sum property,
∠GEF + ∠EGF + ∠EFG = 180°
⇒ x + 90° + 35° = 180°
⇒ x = 55°
Solution 27
AB ∥ CD and AE is the transversal.
⇒ ∠BAE = ∠DOE (corresponding angles)
⇒ ∠DOE = 65°
Now, ∠DOE + ∠COE = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ 65° + ∠COE = 180°
⇒ ∠COE = 115°
In ΔOCE, by angle sum property,
∠OEC + ∠ECO + ∠COE = 180°
⇒ 20° + ∠ECO + 115° = 180°
⇒ ∠ECO = 45°
Solution 28
AB ∥ CD and EF is the transversal.
⇒ ∠EGB = ∠GHD (corresponding angles)
⇒ ∠GHD = 35°
Now, ∠GHD = ∠QHP (vertically opposite angles)
⇒ ∠QHP = 35°
In DQHP, by angle sum property,
∠PQH + ∠QHP + ∠QPH = 180°
⇒ ∠PQH + 35° + 90° = 180°
⇒ ∠PQH = 55°
Solution 29
AB ∥ CD and GE is the transversal.
⇒ ∠EGF + ∠GED = 180° (interior angles are supplementary)
⇒ ∠EGF + 130° = 180°
⇒ ∠EGF = 50°



