Class 9 NCERT Solutions Chemistry Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise 3
Solution 1
Air - It is matter
Love - It is not matter
Smell - It is not matter
Hate - It is not matter
Almonds - It is matter
Thought - It is not matter
Cold - It is not matter
Lemon water - It is matter
Smell of perfume - It is matter
Solution 2
Particles of matter possess kinetic energy and keep moving constantly. At lower temperature, particles have low kinetic energy and thus move slowly. Particles in cold food have low kinetic energy due to low temperature. At higher temperature, particles have high kinetic energy and move faster hence, the particles of hot vapors from hot food move faster.
Solution 3
Concept insight: Key to this answer is that a diver will be able to pass through water if there is availability of space between the particles and the forces of attraction between the liquid particles are not very strong. The diver will not be able to cut through solid ice because of less spaces between the solid particles and strong forces of attraction.
Solution 4
(i) All matter is composed of very small particles which can exist independently.
(ii) Particles of matter have spaces between them.
(iii) Particles of matter are continuously moving.
(iv) Particles of mater attract each other.
Concept insight: Mention all the charateristics of particles of matter.
Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise 6
Solution 1
Exhaust from chimney < Air < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Concept insight: Remember that gases have lowest densities, liquids have higher densities than gases but lower than that of solids and solids have highest densities.
Solution 2
(a) Characteristics of states of matter:
(b)
Concept insight: For answering this question, you need to remember all the properties of solids, liquids and gases and how do the properties vary when we compare them in solids, liquids and gases.
Solution 3
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid because it has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert because the particles of air have large intermolecular spaces and least force of attraction between them. Thus, one can easily move the hand in air and push the particles of air apart. However, the particles of solid have minimum amount of intermolecular space and maximum force of attraction between them. Thus, a greater amount of force is required to move the particles of solid apart. Thus, a much greater force is required to move hand through a solid block of wood.
Concept insight: For answering reasoning questions, the complete reason should be mentioned. For answering this question, you need to remember all the properties of solids, liquids and gases.
Solution 4
Though ice is a solid, but it has a cage like structure hence there are large number of empty spaces between its particles. These spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water. Thus for a given mass of water, volume of ice is greater than that of water. Hence, the density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with lower density than water can float on water. Therefore, ice floats on water.
Concept insight: For answering this question, link density with floating and sinking. A substance with lower density than water will float on water. A substance with higher density than water will sink in water.
Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise 9
Solution 1
= 27 C
(b) 573 K = (573 - 273)
= 300 C
Concept insight: Remember the relationship:
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in C + 273
Substitute the given value in the equation and then calculate the other unknown value.
Solution 2
(b) At 100 C, water exists in liquid state. At this stage, if we keep on supplying heat energy, water can change to gaseous state.
Concept insight: For answering this question you should recall the melting and boiling points of water.
Solution 3
Solution 4
Concept insight: To answer this question, you should think in which way you can change a gas to liquid. For this conversion, you need to decrease the intermolecular space between the particles and increase the intermolecular forces of attraction between them.
Matter In Our Surroundings Exercise 10
Solution 1
Concept insight: The key to this answer is evaporation. If the particles evaporate more, it will lead to more cooling. This is because evaporation causes cooling.
Solution 2
Concept insight: The key to this answer is evaporation and the property of evaporation that it causes cooling.
Solution 3
Concept insight: The key to this answer is evaporation and the property of evaporation that it causes cooling.
Solution 4
Solution 5
Concept insight: The key to this answer is evaporation and the property of evaporation that it causes cooling. Link evaporation to the types of clothes.
Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise 12
Solution 1
= 20 C
(b) 470 K = (470 - 273)
= 197 C
Concept insight: Remember the relationship:
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in C + 273
Substitute the given value in the equation and then calculate the other unknown value.
Solution 2
= 298 K
(b) 373°C = (373 + 273) K
= 646 K
Concept insight: Remember the relationship:
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in oC + 273
Substitute the given value in the equation and then calculate the other unknown value.
Solution 3
(a) Naphthalene undergoes sublimation easily i.e., the change of state of naphthalene from solid to gas without intervention of liquid state. Thus, naphthalene balls keeps on forming naphthalene vapours which disappear into the air with time without leaving any solid.
(b) Gaseous particles possess high speed and move very rapidly in all directions. When perfume is sprayed, its particles diffuse into the particles of air at a very fast rate and reach our nostrils. This enables us to smell the perfume from a distance.
Concept insight: For answering reasoning questions, the complete reason should be mentioned. Remember the properties of all the three states of matter and their state conversion processes.
Solution 4
Concept insight: The key to this answer is the strength of the forces of attraction in the different states of matter. Oxygen is a gas, water is a liquid and sugar is a solid.
Solution 5
NOTE: At 0 C temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of fusion, the solid form of water i.e., ice starts changing into its liquid form i.e., water.
(c) At 100 C, water exists in liquid state at 100oC. At this stage, if we keep on supplying heat energy, water can change to gaseous state.
Concept insight: For answering this question, you should recall the melting and boiling point of water.
Solution 6
(i) At room temperature, water has no shape but has a fixed volume i.e., it occupies the shape of the container in which it is kept.
(ii) At room temperature, water flows easily.
(i) It has a definite shape and volume like a solid at room temperature.
(ii) It is rigid as solid at room temperature.
Concept insight: For answering reasoning questions, the complete reason should be mentioned. Remember the characteristics of all the three states of matter to answer such questions.
Solution 7
Solution 8
Concept insight: The key to this answer is that in comparison to water, steam contains more heat in the form of latent heat of vaporisation.
Solution 9
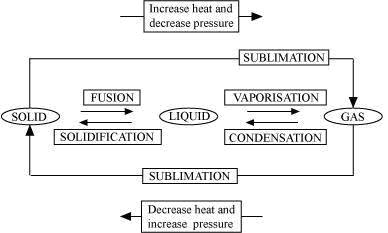
B. Vaporisation
C. Condensation
D. Solidification
E. Sublimation
F. Sublimation
Concept insight: The key to this answer is to recall the names of the processess of conversion of one state to another.

