Class 9 NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 6 - Tissues
61
65
69
70
71
Tissues Exercise 61
Solution 1
A group of cells common in origin and structure and perform similar function is called a tissue. Example: blood, xylem.
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic
Solution 2
A multi-cellular organism is made up of many different types of cells. Each cell carries out a specific function. A group of cells that carries out a specific function is called a tissue. Different tissues carry out different functions. This is called division of labour. A tissue gives the highest possible efficiency of function in multi-cellular organisms.
Concept insight: Different tissues carry out different types of functions, hence they show division of labour.
Tissues Exercise 65
Solution 1
Simple tissues are of three types:
i. Parenchyma
ii. Collenchyma
iii. Sclerenchyma
Concept insight: Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cells. Remember the chart for tissues and its types.
Solution 2
Apical meristem is found at the growing tips of stems and roots. It helps in increasing the length of stem and root.
Concept insight: Remember the types of meristem and their location and function. Do not get confused between them.
Solution 3
The husk of coconut is made up of sclerenchymatous tissue.
Concept insight: Suggested Exam type question.
Solution 4
Phloem is made up four types of elements. They are:
(i) Sieve tubes
(ii) Companion cells
(iii) Phloem parenchyma
(iv) Phloem fibres.
Concept insight: Remember all the components of phloem tissue and do not get confused with xylem components.
Tissues Exercise 69
Solution 1
Muscular tissue helps in the movement of our body.
Concept insight: Suggested Exam types question.
Solution 2
A neuron or a nerve cell consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm. It is also called as cyton. Many long thin hair-like cytoplasmic extensions arise from the cell body called as dendrites. A single long extension is called the axon.
Concept insight: Structure of nerve cell or neuron should be clear along with labels and description.
Solution 3
Features of cardiac muscles:
i. Cardiac muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the life.
ii. They are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated.
iii. Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
ii. They are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated.
iii. Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
Concept insight: Do not get confused between different types of connective tissues. Remember the structure, location and functions of various types of connective tissue.
Solution 4
Areolar tissues are found between the skin and muscle as well as around the blood vessels. This tissue fills the gap between the organs and protects the internal organs. It also repairs the damaged tissues.
Concept insight: Do not get confused between different types of connective tissues. Remember the structure, location and functions of various types of connective tissues.
Tissues Exercise 70
Solution 1
A group of cells common in origin and structure and performs similar function is called a tissue. Example: blood, xylem.
Concept insight: Most popular exam question from this topic.
Solution 2
Four types of elements together make up xylem tissue. These are:
(i) Tracheids (ii) Vessels (iii) Xylem parenchyma (iv) Xylem fibres.
(i) Tracheids (ii) Vessels (iii) Xylem parenchyma (iv) Xylem fibres.
Concept insight: Students generally get confused between xylem and phloem components. Remember all the elements of xylem and phloem tissues.
Solution 3
Differences between simple and complex plant tissues-
| Simple tissues | Complex tissues |
| 1.Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cells. 2.All cells have same origin and are similar in structure. 3.Example-Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. |
1.Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. 2.The cells of complex tissues have different origin as well as structure. 3.Example-Xylem and phloem. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should always be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Solution 4
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| i. Cells of prenchyma tissues are unspecialised with thin cell walls. ii. It is made up of cellulose. |
i. Cells of collenchyma tissues are elongated and irregularly thicknend at the corners. ii. It has deposition of pectin at corner. |
i. Cells of sclerenchyma are dead and have thick cell wall. ii. The cell walls have deposition of lignin. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should always be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Give example wherever possible.
Solution 5
The two main functions of stomata are:
- Exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
- Loss of water during transpiration.
Solution 6
(a) Striated Muscle
(b) Smooth Muscle
(c) Cardiac Muscle
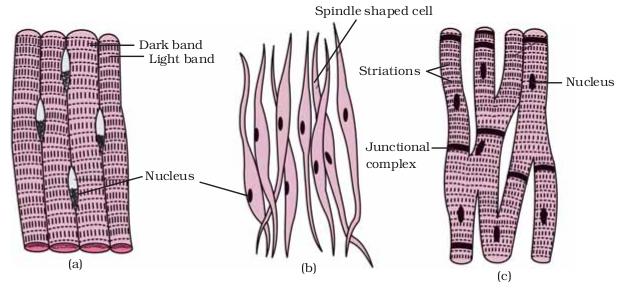
Concept insight:
- Recall the differences in the diagram of the types of muscular tissues.
- Diagram should be neat and correctly drawn.
- Label the parts according to their significance.
Solution 7
The specific function of cardiac muscle is to contract and relax rhythmically throughout the life.
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic.
Solution 8
| Stariated muscle | Unstriated muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| Structure: 1. The fibres or cells are long and cylindrical with multiple nuclei present at the periphery. 2. The fibres or cells are unbranched. 3. Striations with light and dark band are present. Location: They are present in hand, feet and other skeletal muscles. |
Structure: 1. The cells are long, narrow, and spindle-shaped and uninucleate. 2. The fibres or cells are unbranched. 3. Strations are absent. Location: They are present in walls of stomach, intestine, ureter and bronchi. |
Structure: 1. The cells are shorts, cylindrical and unincleate. 2. The cells are branched. 3.Striations are present but not very distinct. Location: They are present in the heart. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should always be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Solution 9
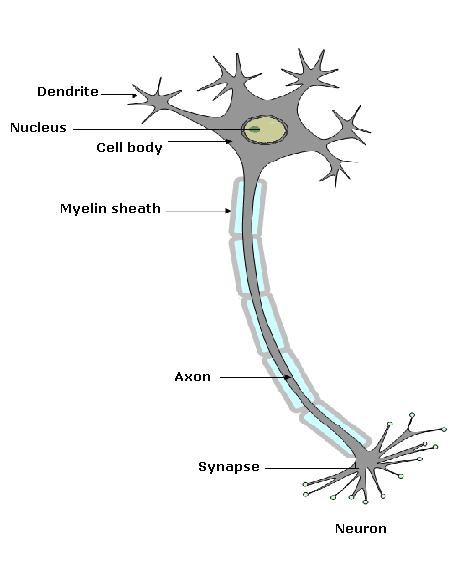
Concept insight:
- Diagram should be neat and correctly drawn.
- Label the parts according to significance.
Solution 10
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Tendon
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
(b) Tendon
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
Concept insight: Remember the various types of animal tissues, their location and function.
Solution 11
(i) Skin - Stratified squamous epithelium
(ii) Bark of tree - Cork or secondary epidermis
(iii) Bone - Connective tissue
(iv) Lining of kidney tubule - Cuboidal epithelium
(v) Vascular bundle - Conductive tissues (xylem and phloem)
(ii) Bark of tree - Cork or secondary epidermis
(iii) Bone - Connective tissue
(iv) Lining of kidney tubule - Cuboidal epithelium
(v) Vascular bundle - Conductive tissues (xylem and phloem)
Concept insight: Student should remember the various types of plant and animal tissues, their location and function.
Tissues Exercise 71
Solution 12
The cells of parenchyma are living cells and are usually loosely packed. This tissue is mainly found in all soft parts of the plant such as roots, stem, leaves, flowers, fruits, etc. It is also found in the ground tissue of petioles, mesophyll of leaves as well as in vascular bundles.
Concept insight: Remember the structure, location and function of parenchyma tissue. Students generally get confused with parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells.
Solution 13
Role of epidermis in plants:
i. Protection of the underlying cells and tissues.
ii. Prevention of water loss.
iii. Prevention of mechanical injury and attack by parasitic fungi.
iv. Exchange of gases and transpiration through stomata.
i. Protection of the underlying cells and tissues.
ii. Prevention of water loss.
iii. Prevention of mechanical injury and attack by parasitic fungi.
iv. Exchange of gases and transpiration through stomata.
Concept insight: Important from Exam point of view.
Solution 14
Several layers of epidermal cells constitute the cork. These cells are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also possess a chemical called suberin in their walls which makes them impervious to water and gases.
Concept insight: Students get confused between bark and cork. Cork is formed from the bark of oak tree.
Solution 15
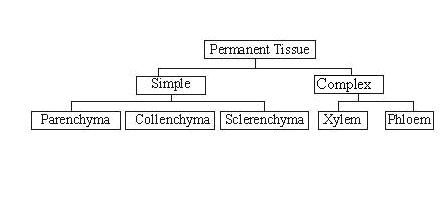
Concept insight: A child should remember the chart for the classification of plant tissues.

