Class 6 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 4: Getting To Know Plants
Getting To Know Plants Exercise 43
Solution 1
(a) Root absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
Concept insight: Stem is the aerial part of plant and roots are underground part of the plant which perform the function of absorption.
(b) Stem holds the plant upright.
Concept insight: Stem is the aerial part of plant which supports branches and leaves.
(c) Stem conducts water to the leaves.
Concept insight: Roots absorb water from soil. Then it transfers water to the stem which conducts it to leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower may be different in different plants.
Concept insight: The number of petals and sepals in a flower is not always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, then its petals may or may not be joined together.
Concept insight: Petals may be either separate from one another or joined together to form a tubular flower.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the stamen may or may not be joined to the petal.
Concept insight: Recall the structure of stamen and pistil.
Solution 2
Concept insight: Recall the structure and types of leaves, roots and flowers.
Solution 3
Yes, a plant having long and weak stem is called a climber. As it has a weak stem it readily climbs up a neighbouring support or a tree. Grape vine is a climber.
Concept insight: Recall the different types of plants.
Solution 4
Functions of a stem are:
i. The main function of a stem in plants is that it helps in the conduction of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of plants.
ii. It also provides support to branches, leaves, flowers, fruits, and buds of the plant.
Concept insight: Students should know the functions of a stem.
Solution 5
Arrangement of veins in the lamina of a leaf is called venation.
There are two types of venation: reticulate and parallel.
Leaves of Tulsi, Coriander and China rose have reticulate venation.
Concept insight: In reticulate venation, the veins in a leaf occur in an irregular way forming a net-like design while in parallel venation, the veins in a leaf are arranged parallel to each other.
Solution 6
Plants with fibrous roots have parallel venation in their leaves. For example, grass, wheat, maize etc. have fibrous roots with parallel venation.
Concept insight: Fibrous roots have thin and moderately growing branches arising from the stem. Parallel venation, on the other hand, has leaves in which the veins are arranged parallel to each other.
Solution 7
Plants with reticulate venation in their leaves are likely to have tap roots. For example, a carrot or a rose plant has leaves with reticulate venation and its roots are called tap roots.
Taproots and reticulate venation
Concept insight: In tap roots, there is one main root known as the tap root that grows straight down from the stem. It also has smaller roots known as lateral roots. In leaves with reticulate venation, the veins are arranged in a net-like pattern.
Solution 8
Yes, it is possible to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper.
Concept insight: The plants having leaves with reticulate venation have tap roots while the plants having leaves with parallel venation have fibrous roots.
Solution 9
Flower consists of sepals, petals, stamens and pistil.
i. Sepals are green, leaf-like parts in the outermost circle of a flower.
ii. Petals are coloured leaf-like part of a flower.
iii. Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower and has two parts - anther and filament.
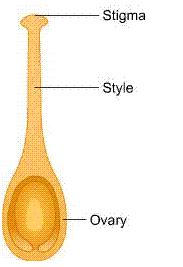
iv. Pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower and consists of three parts - stigma, style and ovary.
Concept insight: Recall the structure of a flower.
Solution 10
The given examples are flowering plants. But, in some plants such as tulsi, pipal, sugarcane, etc. flowers are very small so they are not visible.
Concept insight: Recall examples of flowering plants.
Solution 11
Leaves of a plant prepare food in the presence of sunlight.
The process of making food by utilizing water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Concept insight: Only leaves perform the function of photosynthesis as they contain chlorophyll pigment.
Solution 12
Ovary is present at the base of pistil.
Concept insight: Recall the structure of pistil.
Solution 13
Flowers with joined sepals are Periwinkle (Sadabahar) and Hibiscus (China rose).
Flowers with separated sepals are Rose and Magnolia.
Concept insight: Important from Exam Point of View.