Class 12-science NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 11 - Organisms and Populations
Organisms and Populations Exercise 204
Solution 1
(i)Population density
(ii)Natality or birth rate
(iii)Mortality or death rate
(iv)Population growth
(v)Sex ratio
(vi)Age distribution
Solution 2

Solution 3
Modification of leaves into thorns and development of spiny margins on leaves. Many plants produce and store chemicals which make herbivores sick. Example: Calotropis produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides. Some other chemical substances such as nicotine, quinine, opium etc. are produced by plants and provide defence against grazing animals.
Solution 4
It is an example of commensalism, where the orchid gets space (benefitted) and the mango tree is neither benefitted nor harmed.
Solution 5
The ecological principle behind the biological control of pest insects is based on the ability of a predator to regulate the prey population in that habitat. Example: Gambusia fish prey upon the larvae of mosquito and acts as biological controller of malaria.
Solution 6
Population: A population is the collection of interbreeding organisms of a particular species living together in the same geographical area at a time.
Community: A community is a group of organisms belonging to several different species which live together in the same area or habitat and interact through trophic and spatial relationships.
Solution 7
(a) Commensalism: Commensalism is an interspecific interaction between two species where one species is benefitted and the other remains unaffected. Example: Orchid and mango tree.
(b) Parasitism: It is a relationship between two organisms where the larger animal is at harm and the smaller animal is benefitted. Example: Malarial parasite and human beings.
(c) Camouflage: Camouflage is the ability of animals to blend with the surroundings or background. In this way, animals remain unnoticed for protection or aggression. Example: Stick insect.
(d) Mutualism: It is relationship between two organisms where both organisms are benefitted. Example: Fungal symbiotic association with algae in lichens.
(e) Interspecific Competition: It is an interaction between individuals of two species where both the interacting species are affected. Example: Monarch butterfly and Queen Monarch.
Solution 8
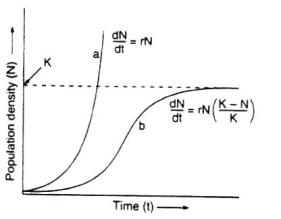
Diagram: Population growth curve
a - When responses are not limiting the growth, the plot is exponential.
b - When responses are limiting, the growth plot is logistic. K is the carrying capacity.
Solution 9
(d) One organism is benefitted, other is affected.
Solution 10
Three important characteristics of a population are
i.Density: It is expressed as the total number of individuals per unit area or volume at a given time. The size of the population is determined by the available resources nutrients, water etc. at a given time and other group properties such as natality, mortality and age structure.
ii.Natality: It is the increase in the number of individuals in a population under given environmental conditions. Birth, hatching, germination and even vegetative propagation cause increase in the number of individuals.
iii.Mortality: The loss of individuals due to death in a population under given environmental conditions is called mortality.

