Class 12-commerce NCERT Solutions Business Studies Chapter 4: Planning
Planning Exercise 109
Solution SA 4
Planning always helps in promoting innovation. Formulating policies and plans is an intellectual process and it requires creativity and some innovation from the managers. Once a plan is formulated, it is not possible for a manager to change it. Such type of rigidity creates hurdles when changes are uncertain and therefore it reduces creativity.
Solution SA 5
The type of plan that is adopted by Bharti Airtel is Strategy. Strategy is devised by keeping the business environment prevalent at the time.
The three dimensions of strategy are:
1. It helps determine long term objectives
2. It helps to determine a particular course of action
3. It guides on allocating resources which are necessary for achieving the objective.
Solution SA 6
a. Budget: It is one type of plan that works as a controlling device. Budget is a single use plan developed specifically for a project of one time or any such similar event.
b. Method: It is a type of plan that is based on analysis and research. It is mostly involved with technical and physical tasks. Method is a type of standing plan which happens at regular intervals.
Solution SA 1
Organisation, despite being a private or a government one, needs a proper planning to acquire success, high profit, and increase in sale. Planning implies to state in advance where to go and in which direction to move in order to achieve target. Planning is a psychological process of 'thinking and deciding in advance about 'what is to be done' and 'how it is to be done. It is a mental activity, in which the manager decides about the goals to be achieved, and actions through which they are to be accomplished. Being a continuous process which helps in reducing the risk of uncertainty, planning provides the rationale for undertaking policies in the direction of achieving goals. It is based on anticipating the future course of action and deciding the best course of action. The following points define planning:
- Setting objectives: This should include a detailed overview of each objective factors needed to achieve those goals, where, when and how it should be performed and the expected outcome of it. Managers need to state these objectives very clearly for each and every department in the organisation so that right direction can be taken for achieving goals.
- Time period: The plan must be formulated for a definite time period. If planning is not done within a time frame, it may prove futile. This is because with time business environment changes and requires fresh planning and action.
- Formulating alternatives for course of action: A plan, when made, should have multiple alternatives to it which can be followed. There can be number of ways to achieve a defined objective. The managers need to think carefully about these various routes while developing alternatives and should screen out most viable alternatives.
- Deciding on a course of action: After coming up with all possible alternatives and its outcome, the managers need to evaluate them. Selecting the best alternative involves opting for a method which is most viable as per the objective. The managers should utilise their skills and knowledge for judging and selecting the best alternative in terms of profitability, costs and workability.
Solution SA 2
It is true that planning is a forward looking function and is based on analysing and predicting the future elements. However, future involves uncertainty and cannot be predicted. There are various external forces which affect the functioning of an organisation. These forces are complex and ever changing in nature. For example, social trends, political conditions, technology, government rules and regulations change continuously. Because of such uncertainties, one cannot be sure of the success rate of the plans. Rather, the plans need to be modified to adapt to the changing environment. Thus, a good planning does not guarantee success. Also, the probability of attaining success once the plans have been put into action is odd. Often, the managers tend to rely on previously tried and tested successful plans. However, business environment is dynamic in nature and a pretested plan may or may not work in the future. Managers tend to over think that planning can prevent problems from occurring. However, they neglect the fact that planning just provides a base for predicting the future and does not give straight away solutions to the problems. For example, because of fierce competition, the demand for a company's product has taken a back seat. Here, the unforeseen entry of a competitor was not anticipated because of which there was a major dip in the sales. In such cases, the company now has to formulate new plan so as to get back in the business keeping in mind the change in demand. The previous marketing plan put into use for that product won't be of any use here. Thus, it can be said that despite the fact that planning involves working out details for the future, it does not ensure success.
Solution VSA 3
Rules refer to standard or specific statements which inform us about what is to be done. It is quite similar to plans because both of them facilitate the achievement of objectives. Rule states what not to be done and what needs to be done, whereas planning points out what to do and how to do. They can be viewed as the simplest of plans. However, rules are rigid in nature i.e. does not allow flexibility or discretion and are to be followed as it is, unless a change is stated by the organisation. Non-compliance of the rules leads to disciplinary actions by the organisation. For example, an organisation may have rules regarding the punch-in timings of the employees and every employee of the organisation must follow this rule. Rules act as a guide for general behaviour of the employees in the organisation.
Solution SA 3
Strategic decisions are concerned with the whole business environment in which the organisation works, the resources used, the stakeholders and the concerned departments. In order to survive in the ever-evolving environment, organisations have to keep on updating and evolving their strategic methods and procedures. This would have an impact not only on the entire organisation but also on the stakeholders involved. Thus, strategy refers to a broad outline for the business of an organisation. Strategic decisions mainly include the decision whether to continue on the same business lines or to adapt new organizational activities or to bring about any major kind of change so as to make a dominant stand for itself in the competitive market. It has three broad objectives:
- To determine the objectives
- To decide the course of action
- To allocate of necessary resources for the achievement of the objectives
Following are a few strategic decisions which a business organisation may look out for:
- Deciding about which line of business should be taken
- Whether a new line of production should be adopted or not
- What position should the company aim for in the existing market
- What kind of pricing policy should be used
- Decisions regarding the advertising policy and costs
Solution LA 1
Being the key function of any organisation, planning implies to state in advance where to go and in which direction to move in order to achieve target. Being a continuous process which helps in reducing the risk of uncertainty, planning provides the rationale for undertaking policies in the direction of achieving goals. One of the main agendas of planning is to predict or anticipate any future risk or unfortunate events which can cause major damage to a business. However, uncertainty always hovers around an organizational planning; things do not go as per the plan because of unforeseen changes in the business environment. Also, we can never develop a plan which is 100% fool-proofs; it will always have its own limitations which will hinder the accomplishment of all the objectives of an organisation.
Following are some of the limitations of planning which may result in the abandoning or reconsidering the organisational objectives:
- Rigidness: In case of any unforeseen conditions, the changes which can be made to a plan are limited. A major change to the already created plan is neither possible nor would do any good in the interest of an organisation. This rigid nature of a plan creates hurdles at times of unforeseen changes. The managers may, sometimes, require certain degree of flexibility so as to cope with the changes in an appropriate manner. Rigidity in plans sometimes causes huge loses to the organisation creates obstacles in the completion of the objectives.
- Unfavourable for a dynamic environment: Nothing is constant in a business environment; it is dynamic in nature. Planning, on the other hand, completely depends on the anticipation of future happenings. As a result, both do not go hand-in-hand. Planning cannot foresee such sudden changes in the business and fails of uncertainties. This may lead to failure in the accomplishment of objectives. An organisation must adapt its functioning to the changing environment; a long term planning will make this dynamic environment less effective.
- Gigantic costs: Planning involves analysis, research and scientific calculations which requires huge cost and time. As planning is based on future predictions, it requires a lot of thinking and analysing. It involves scientific calculations along with the figures and the facts, which are to be used in formulating the course of action. Companies, thus, need to hire professionals who would formulate plans. This involves high costs. Moreover, sometimes it might also happen that the benefits derived from planning fall short of the costs incurred.
- False security: A good planning does not guarantee success. The probability of attaining success once the plans have been put into action is odd. Often the managers tend to rely on previously tried and tested successful plans. However, business environment is dynamic in nature and a pretested plan may or may not work in the future. Managers tend to over think that planning can prevent problems from occurring. However, they neglect the fact that planning just provides a base for predicting the future and does not give straight away solutions to the problems.
- Time consuming: Formulating a plan involves analysis, research and scientific calculations which consumes too much of time. It is a boon while facing a definite situation. However, sudden unforeseen situation cannot be tackled; there is no short-term planning procedure. The time taken to formulate a complete plan may cause delay in the decision-making process.
Solution VSA 4
The type of plan that is adopted by Rama Stationery is a payment policy of making all payments by e-transfer.
Solution VSA 5
Planning has a less chance of working correctly in a changing environment. Nature of business is dynamic and it continuously changes. For example, factors like social, political, rules and regulations are prone to changes on a continuous basis. Planning cannot detect such changes and therefore prove not that effective. For example, a company has planned to make white bread but the market demand shifted to brown bread due to people becoming more health conscious. Here the company needed to change its previous plan as market factors were not as per the plan.
Planning Exercise 108
Solution VSA 1
Planning clearly states the predetermined course of action; guide the managers about things to be done, what route to take and how the objectives are to be achieved and provides a direction to the actions of different departments of the organisation. Thus, they come to know exactly what is to be done, and thereby moves in the right direction. It also ensures clarity in thoughts and that various departments of the organisation work in a coordinated manner towards the achievement of the desired objectives. Without planning work would be done in a haphazard manner with each department going in different directions. Thus, planning ensures smooth functioning towards the desired goals of an organization.
Solution VSA 2
The step that has been undertaken by Ms Rajni is identifying alternative courses of action. In this process Ms. Rajni has noted down all possible course of action that can be used for increasing the market share.
Planning Exercise 110
Solution LA 2
Organisation, despite being a private or a government one, needs a proper planning to acquire success, high profit, and increase in sale. Planning implies making predictions to achieve target. Being an intellectual process, planning seeks to bridge the gap between where we are and where we want to go; it is a trap to capture the future. It involves a few logical steps. Following are the steps to be followed by the management while making plans:
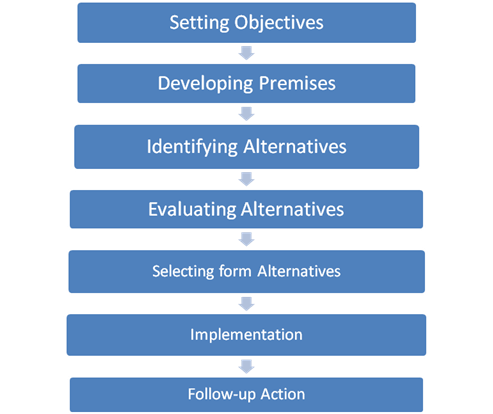
- Setting objectives: The first step in the planning process is to identify specific company objectives and goals. This should include a detailed overview of each objective factors needed to achieve those goals, where, when and how it should be performed and the expected outcome of it. Managers need to state these objectives very clearly for each and every department in the organisation so that right direction can be taken for achieving goals. It provides a guided direction to individual departments/units to work towards a common objective for the organisation. The functioning of an organisation depends on whether the goals are not met or not.
- Developing the planned premises: Planning is based on certain assumptions for an uncertain future. Certain assumptions have to be made for formulating the plans; they are known as premises. Forecasting is essential as assumptions are by verifying and referring to previous plans and current policies and facts. It helps in making realistic assumptions. These assumptions are essential for an organisation as they determine the path for the plans to be made. Thus, for successful planning, correct premises should be proposed.
- Identification of the alternatives: A plan, when made, should have multiple alternatives to it which can be followed. There can be number of ways to achieve a defined objective. The managers need to think carefully about these various routes while developing alternatives and should screen out most viable alternatives. This involves innovation and creative mind so that new ways can be developed in order to accomplish the goals. Best outcome is achieved only when best alternative for doing a work is selected.
- Evaluation and selection of the best alternatives: After coming up with all possible alternatives and its outcome, the managers need to evaluate them. This evaluation is based on the utility and the consequences of the options and the performance study of various actions. Various factors will be weighed against each other as they must assess the pros and cons of each alternative. For example, one plan might incur less cost, whereas another one would help in achieving the goals in lesser time and budget. In light of such aspects the right evaluation of different alternatives should be done. Selecting the best alternative involves opting for a method which is most viable as per the objective. The managers should utilise their skills and knowledge for judging and selecting the best alternative in terms of profitability, costs and workability.
- Implementation: It involves putting into action and organising the work according to the selected path, procedures, standards and policies. Implementation is concerned with following the opted path of action and deciding how that is to be used in order to be successful.
- Follow-up action: For assessing and ensuring that the plans and the whole working are proceeding along the right lines, a continuous supervision of the actions is required. Here, the actual performance is compared to that of the planned performance to determine if there are any short comings regarding the same. Keeping an eye on the activities to be performed is an important part of planning itself, as it helps to ensure the proper working of a plan. Thus, a thorough follow-up action increases the success of a plan.
Solution LA 3
- The types of plans that can be adopted are strategy and policy.
A strategy provides the broad contours of a plan for achieving the objectives of an organisation. It includes determining long-term objectives, adopting the required course of action and allocating the necessary resources. Policies, on the other hand, are the statements that act as a guide to channelise the efforts of the organisation in a particular direction. They provide the basis for the interpretation of the organisation's strategies and define broad parameters for the functions of the management. They are usually flexible in nature. With strategies and policies the company would be able to draft the plan and take steps to survive in the increased market competition.
- The following are the limitations of strategy and policy.
- Rigidness: In case of any unforeseen conditions, the changes which can be made to a plan are limited. A major change to the already created plan is neither possible nor would do any good in the interest of an organisation. This rigid nature of a plan creates hurdles at times of unforeseen changes. The managers may, sometimes, require certain degree of flexibility so as to cope with the changes in an appropriate manner. Rigidity in plans sometimes causes huge loses to the organisation creates obstacles in the completion of the objectives.
- Cannot Deal With Dynamic Environment: Nothing is constant in a business environment; it is dynamic in nature. Planning, on the other hand, completely depends on the anticipation of future happenings. As a result, both do not go hand-in-hand. Planning cannot foresee such sudden changes in the business and fails of uncertainties. This may lead to failure in the accomplishment of objectives.
- Gigantic Costs: Planning involves analysis, research and scientific calculations which requires huge cost and time. As planning is based on future predictions, it requires a lot of thinking and analysing. It involves scientific calculations along with the figures and the facts, which are to be used in formulating the course of action. Companies, thus, need to hire professionals who would formulate plans. This involves high costs.
- False Security: A good planning does not guarantee success. The probability of attaining success once the plans have been put into action is odd. Often the managers tend to rely on previously tried and tested successful plans. However, business environment is dynamic in nature and a pretested plan may or may not work in the future.
- Time Consuming: Formulating a plan involves analysis, research and scientific calculations which consumes too much of time. It is a boon while facing a definite situation. However, sudden unforeseen situation cannot be tackled; there is no short-term planning procedure. The time taken to formulate a complete plan may cause delay in the decision-making process. Managers tend to over think that planning can prevent problems from occurring. However, they neglect the fact that planning just provides a base for predicting the future and does not give straight away solutions to the problems.
- Following steps can be taken to eliminate the limitations of planning:
- The plans must not be too rigid in the sense that certain degree of flexibility must be provided to the managers to deal with the unforeseen changes that might come up in the course of planning.
- The planning must be done keeping in mind that the business environment is highly dynamic in nature. Plans should be such that they can be easily adjusted as per the need of the hour.
- The cost and the time invested in the course of planning should be curtailed.
- It must not be the case that only the pretested plans are relied upon. New plans can be drafted as per the situation and circumstances.
