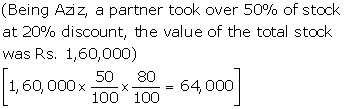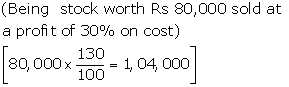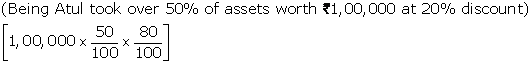Class 12-commerce NCERT Solutions Accountancy Chapter 4: Dissolution of Partnership Firm
The NCERT solutions for CBSE Class 12 Commerce Accountancy Chapter Dissolution of Partnership Firm at TopperLearning help students study better and perform better in the exam. The NCERT textbook solutions are detailed and have answers for every exercise and unit in the chapter. They help students in grasping the chapter better. They are not only great for writing answers but also for understanding the concepts of the chapter in detail. Along with the NCERT solutions, students can also refer to our sample papers, past years’ papers, revision notes, video lessons etc.
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 244
Solution SA 1
|
Basis of Difference |
Dissolution of Partnership |
Dissolution of Partnership Firm |
|
Meaning |
It means change in the partnership deed (or agreement) among partners. |
It means that the business is wound up and the firm is dissolved. |
|
Discontinuation |
Business is not discontinued. |
Business is discontinued as the firm is dissolved. |
|
Closure of Books of Accounts |
Books of accounts are not closed, as there is only change in the existing agreement between partners. |
Books of accounts are closed, as the business is discontinued. |
|
Assets and Liabilities |
Assets and liabilities are re-valued and a new balance sheet is drawn. |
Assets are sold off to pay the liabilities of the business. |
|
Role of Court |
The court does not intervene as the partnership is dissolved by mutual agreement. |
The court has inherent power to intervene. By its order, a firm can be dissolved. |
|
Nature |
It is voluntary. |
It may be voluntary or compulsory (voluntary: according to discretion of the partners; compulsory: according to the order of the court). |
|
Effect |
It may or may not involve dissolution of the firm. |
It necessarily involves the dissolution of both partnership and partnership firm. |
Solution SA 2
Accounting treatment for
- Unrecorded Assets: Unrecorded assets are omitted from the books or are assets whose value has been written off in the books of accounts but are still in working condition. The accounting treatment for unrecorded asset is
|
a) When the unrecorded asset is sold for cash |
|
|
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
------To Realisation A/c |
|
|
(Being unrecorded assets sold for cash) |
|
|
|
|
|
b) When the unrecorded asset is taken over by any partner |
Dr. |
|
Partner's Capital A/c |
|
|
-----To Realisation A/c |
|
|
(Being unrecorded asset taken over by the partner) |
|
- Unrecorded Liabilities: Unrecorded liabilities are not recorded in the books of accounts. The accounting treatment for unrecorded liability is
|
a. When the unrecorded liability is paid through Realisation A/c |
|
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
------To Cash A/c |
|
|
(Being unrecorded liability paid in cash) |
|
|
|
|
|
b. When the unrecorded liability is taken over by a partner |
Dr. |
|
Realisation A/c |
|
|
------To Partner's Capital A/c |
|
|
(Being unrecorded liability taken over by the partner) |
|
Solution SA 3
- If a partner's loan appears on the assets side of the balance sheet, then it means that a partner has taken a loan from the firm and is liable to repay the amount to the firm. In such a situation, the loan amount is transferred to his/her capital account. Thus, the accounting entry will be
|
Partner's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
-----To Partner's Loan A/c |
|
|
(Being partner's loan transferred to partner's Capital A/c) |
|
- If a partner's loan appears on the liabilities side of the balance sheet, then it means that the partner has lent a loan to the firm and the firm is liable to pay back the amount to the partner. In such a situation, the partner's loan is paid off after paying all the external liabilities of the firm. The partner's loan will be paid in cash and the following accounting entry will be passed:
|
Partner's Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
-----To Cash/Bank A/c |
|
|
(Being partner's loan paid in cash) |
|
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 245
Solution SA 4
|
Basis of Difference |
Firm's Debt |
Partner's Private Debts |
|
Meaning |
Debts which are borrowed against the name of the firm. |
Debts which are borrowed personally by the partner. |
|
Liability |
All the partners of the firm are jointly and severally liable. |
Only the concerned partner will be personally liable. |
|
Application of firm's assets |
Firm's debts are settled first against the firm's assets. Subsequently, if any surplus exists, then this is distributed among the partners. |
After paying off the firm's debts, the surplus of the firm's assets, if any, is distributed among the partners. The personal share of the partner in this surplus can be used to settle their own private debts. |
|
Application of private assets |
After paying off the partner's private debt, the surplus of the partner's private assets, if any, can be used to pay back the firm's debt only if the firm's debts exceed the firm's assets. |
Private debts are settled first against the partner's private assets. Subsequently, if any surplus exists, then this may be used to settle the firm's debts. |
Solution SA 5
According to Section 48 of the Partnership Act, 1932, following are the rules of the settlement of accounts on dissolution:
- Application of Assets: Proceeds received from the sale (realisation) of the assets shall be applied in the following order:
- First, all external liabilities and expenses are to be paid.
- Second, all loans and advances lent by partners to the firm should be paid.
- Lastly, the capital of each partner should be paid off.
If any surplus remains after the payment of (a), (b) and (c), then it should be distributed among the partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
- Treatment of Loss: In case of any loss and deficiency, the treatment for the same should be made in the following order:
- First, it should be adjusted against the firm's profits.
- Then, it should be adjusted against total capital of the firm.
- If any loss and deficiencies still exist, then it should be borne by all the partners individually in their profit-sharing ratio.
Solution SA 6
|
Basic of Difference |
Realisation Account |
Revaluation Account |
|
Meaning |
It records the proceeds due to sale of various assets and payment of various liabilities. |
It records the effect of revaluation of assets and liabilities on the event of admission, retirement or death of a partner. |
|
Time |
It is prepared at the time of dissolution of the firm. |
It is prepared at the time of admission, retirement or death of a partner. |
|
Objective |
To ascertain profit or loss on realisation (sale) of assets and payment of liabilities. |
To ascertain profit or loss on revaluation of assets and liabilities. |
|
Profit/Loss Distribution |
Realisation profit or loss will be distributed among all the partners in their profit-sharing ratio. |
Revaluation profit or loss will be distributed among the old partner of the firm in the old profit-sharing ratio. |
|
Amount |
Assets and liabilities are shown at the book value. |
Increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities are shown in this account. |
|
Records |
All assets and liabilities are recorded here. |
Only those assets and liabilities are recorded whose values have changed over a period of time. |
|
Effect |
All accounts of assets and liabilities are closed. |
No account is closed on revaluation of assets and liabilities. |
Solution LA 1
The process of discontinuation of a partnership business is known as dissolution of partnership. According to Section 39 of the Partnership Act, dissolution of partnership between all partners of a firm is called dissolution of a partnership firm. Dissolution involves winding up of business, disposal of assets, paying off liabilities and distribution of any surplus or loss by partners of the firm. According to the Partnership Act 1932, a partnership firm may be dissolved on any of the following grounds:
- Dissolution by Agreement (Sec. 40)
- Compulsory Dissolution (Sec. 41)
- Dissolution due to Certain Contingencies (Sec. 42)
- Dissolution by Notice of Partnership at Will (Sec. 43)
- Dissolution by Court (Sec. 44)
Although the process of dissolution remains the same, the ways and modes in all five are different.
1. Dissolution by Agreement:
A firm may be dissolved with
a. Consent of all partners
b. Contract between partners
2. Compulsory Dissolution:
A firm may be dissolved by
a. Adjudication of all partners or of all partners but one as involved
b. Happening of an event or change in government policies which make the business unlawful
3. Dissolution due to Certain Contingencies:
Subject to the contract between partners, a firm is dissolved
a. If formed for a specific period, then on the expiry of the period
b. If formed for a specific purpose, then on completion of the purpose
c. On the death of partner/partners
d. On insolvency of a partner/partners
4. Dissolution by Notice:
If a partnership is at will, then the partnership firm is dissolved if any partner gives a written notice to all the other partners expressing his/her intention to dissolve the firm.
5. Dissolution by Court:
The court may order dissolution of a partnership firm when
a. A partner becomes insane or a lunatic.
b. A partner becomes permanently incapable of performing duties.
c. A partner is guilty of misconduct and affects business activities.
d. A partner repeatedly breaks the terms of agreement.
e. A partner transfers his interest to a third party without the consent of other partners.
f. A business persistently incurs losses.
Besides these circumstances, a partnership firm may be dissolved if the court at any stage finds dissolution of the firm to be justified and inevitable.
Dissolution of a firm is carried out in three steps:
- Preparation of a balance sheet of the firm to be dissolved
- Realisation of assets and liabilities
- Distribution of cash to creditors and partners
Also, for the settlement of accounts, Section 48 of the Partnership Act 1932 would be applicable.
- Application of Assets: Amount received by the realisation (sale) of assets shall be used in the following order:
- Debts of the firm towards third parties, or first, external liabilities and expenses are to be paid.
- Then all loans and advances forwarded by partners should be paid.
- Then the capital of each partner should be paid off. Any surplus remaining after the payment of (a), (b) and (c) should be distributed among partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
- Treatment of Loss: Loss and any deficiency of capital should be paid in the following order:
- First, these should be adjusted against the firm's profits.
- Then against the total capital of the firm.
- If there is still any loss and deficiency, then it should be borne by all partners individually in their profit-sharing ratio.
Solution LA 2
Dissolution of a partnership firm leads to discontinuation of business activities wherein all the books of accounts are to be closed. All the assets of business are sold off and all liabilities are paid off. To record the sale of assets and discharge of liabilities, a nominal account named realisation account is opened. The main purpose of this account is to ascertain the profit or loss due to the realisation of assets and liabilities. Realisation profit (i.e. credit side exceeding debit side) or realisation loss (i.e. debit side falling short of credit side) would be transferred to the partner's capital account in the profit-sharing ratio.
Important objectives of preparing a realisation account:
- Closure of all the books of accounts
- To record transactions relating to the sale of assets and discharge of liabilities
- To determine profit or loss due to the realisation of assets and liabilities
Accounting treatment of items related to a realisation account
|
1) For transfer of assets |
Dr. |
|
Realisation A/c |
|
|
-----To Sundry Assets A/c (Individually) |
|
|
(Being all assets transferred to realisation account, except cash or bank, PandL debit balance and loan to a partner) |
|
|
|
|
|
2) For transfer of liabilities |
Dr. |
|
Sundry Liabilities A/c (Individually) |
|
|
-----To Realisation A/c |
|
|
(Being all liabilities transferred to realisation account, except partner's capital, PandL credit balance, loan from a partner) |
|
|
|
|
|
3) For sale of assets |
Dr. |
|
Bank A/c (Amount received) |
|
|
-----To Realisation A/c |
|
|
(Being assets sold for cash) |
|
|
|
|
|
4) For payment of liabilities |
Dr. |
|
Realisation A/c |
|
|
-----To Bank A/c |
|
|
(Being expenses paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
5) For payment of realisation expenses |
|
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
-----To Bank A/c |
|
|
(Being expenses paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
6) For transfer of profit on realisation |
|
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
-----To Partner's Capital A/c |
|
|
(Being profit on realisation transferred to partner's capital account) |
|
|
|
|
|
7) For transfer of loss realisation |
|
|
Partner's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
-----To Realisation A/c |
|
|
(Being loss transferred to partner's capital account) |
|
Solution LA 4
Dissolution of a firm calls for closure of all accounts and realisation of assets and making payment to meet liabilities. At the time of dissolution of a firm, the amount received from the sale of the firm's assets is used to pay off creditors. If the amount received from the sale falls short, then the partner's private assets are used for settling the dues of the firm's creditors. Even if some portion of the amount due to creditors is left unpaid, then there arises deficiency of creditors. This deficiency can be treated in the following two ways:
- Transferring deficiency to the Deficiency Account
- Transferring deficiency to the Partner's Capital Account
In case the amount of deficiency is to be transferred to the Deficiency Account, then a separate account is prepared for the firm's creditors. A Cash Account is prepared to ascertain the firm's cash balance accruing from the sale of the firm's assets and partner's private assets. After ascertaining the cash availability with the firm, creditors and external liabilities are paid proportionately. The remaining unpaid creditors or the deficiency is transferred to the Deficiency Account.
In the second case, creditors are paid by the cash available with the firm, including the partner's individual contribution. The deficiency or unpaid creditor's amount is transferred to the Partner's Capital Account. Thus, the deficiency of creditors is borne by all partners in their profit-sharing ratio. If any partner becomes insolvent and is unable to bear the deficiency, then this will be regarded as a capital loss to the firm. If the partnership deed is silent about such capital loss in the facet of insolvency of a partner, then according to the Garner vs. Murray case, such capital loss needs to be borne by the solvent partners in their capital ratio.
Solution Num 1
|
Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
(a) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
2,500 |
|
|
|
------To Bank A/c |
2,500 |
||||
|
(Being realization expenses paid) |
|||||
|
(b) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
3,000 |
||
|
------To Ashok's Capital A/c |
3,000 |
||||
|
(Being realization expenses paid by Ashok) |
|||||
|
(c) |
No entry as all realization expenses are borne personally by Tarun |
||||
|
(d) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
4,000 |
||
|
------To Amit's Capital A/c |
4,000 |
||||
|
(Being realization expenses paid to Amit) |
|
||||
|
|
|
Dr. |
|
|
|
Solution Num 2
|
Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
(a) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||
|
------To Cash A/c |
40,000 |
||||
|
(Being creditors worth Rs.85,000 accepted Rs.40,000 as cash and investment worth Rs.43,000 in their full settlement) |
|||||
|
(b) |
No Entry |
|
|||
|
(Being creditors Rs.16,000 accepted Machinery Rs.18,000 in the full settlement. No entry is required since both asset and liability are already transferred to the Realization Account) |
|||||
|
(c) |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||
|
------To Realization A/c |
30,000 |
||||
|
(Being creditors worth Rs. 90,000 accepted buildings worth Rs. 1,20,000 and returned Rs.30,000 as cash after settlement of claim to the firm) |
|||||
Solution Num 3
|
Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
Nitin's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
3,000 |
|||
|
------To Realization A/c |
3,000 |
||||
|
(Being unrecorded computer taken over by Nitin) |
|||||
Solution Num 4
|
Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
a) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
3,200 |
||
|
-----To Bank A/c |
3,200 |
||||
|
(Being unrecorded liabilities paid) |
|||||
|
b) |
Rohit's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
7,500 |
||
|
-----To Realisation A/c |
7,500 |
||||
|
(Being stock is taken over by Rohit) |
|||||
|
c) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
18,000 |
||
|
-----To Ashish's Capital A/c |
7,500 |
||||
|
|
-----To Tarun's Capital A/c |
|
|
|
10,500 |
|
|
(Being profit on Realization is transferred to Partner's Capital Account) |
|
|
|
|
|
d) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,500 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
5,500 |
|
|
(Being unrecorded asset sold) |
|
|
|
|
Solution Num 5
|
Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
1) |
|||||
|
a) |
For Transfer of Assets |
||||
|
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
||||
|
-----To Assets A/c (Individually) |
|||||
|
(Being assets transferred to Realization Account) |
|
||||
|
b) |
For Transfer of Liabilities |
||||
|
Liabilities A/c (Individually) |
Dr. |
||||
|
-----To Realizations A/c |
|||||
|
(Being liabilities transferred to realization account) |
|||||
|
c) |
For sale of Asset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash/Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
|
|
|
-----To Realizations A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Being assets sold) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d) |
For liabilities paid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
|
|
|
-----To Cash/Bank A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Being liabilities paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2) |
Aziz's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
64,000 |
|
|
|
-----TO Realization A/c |
|
|
|
64,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,04,000 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
1,04,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Being land and building sold for Rs.3,00,000 and 2% commission paid to broker) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
No entry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Being plant and machinery Rs. 60,000 handed over to the creditors at a discount of 10%. No entry is required as both the asset and liability are already transferred to the Realization Account) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being investment worth Rs.4,000 were realized at 50%) |
|
|
|
|
Solution 3
| Specimen Realisation Account | |||||
| Dr. | Cr. | ||||
| Particulars | Amount Rs. |
Particulars | Amount Rs. |
||
| To Sundry Assets A/c (Excluding cash/bank, fictitious assets, debit balance of PandL A/c and loan to partner) |
- | By Various Liabilities A/c (Excluding partner's capital account, reserves, PandL A/c, current A/c, loan to partner) |
- | ||
| To Reserve for Discount on Creditors A/c | - | By Provision on Assets (like provision for doubtful debts, provision for depreciation) |
- | ||
| To Cash/Bank A/c (Payment to outside and unrecorded liabilities) |
- | By Cash/Bank (Amount received from realisation of assets and unrecorded assets) |
- | ||
| To Partner's Capital A/c (If any liabilities taken on expenses paid by him or remuneration payment to him) |
- | By Partner's Capital A/c (If any assets taken over by any partner) |
- | ||
| To Profit Transferred to Partner's Capital A/c | - | By Loss Transferred to Partner's Capital A/c | - | ||
| - | - | ||||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 246
Solution Num 6
|
Books of Rashim and Bindiya Journal Entries |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
1) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
1,00,000 |
||
|
-----To bank A/c |
1,00,000 |
||||
|
(Being realization expenses paid) |
|||||
|
2) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||
|
-----To Rashim's Capital A/c |
30,000 |
||||
|
(Being realization expenses borne by Rashim) |
|||||
|
3) |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
70,000 |
||
|
------To Rashim's Capital A/c |
70,000 |
||||
|
|
(Being realization expenses borne by Rashim and remuneration to him for dissolution Rs.70,000) |
|
|
|
|
Solution Num 7
|
Journal |
||||
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
Realization A/c |
1,00,000 |
|||
|
-----To Sundry Assets A/c |
Dr. |
1,00,000 |
||
|
(Being assets other than cash and bank transferred to Realization Account) |
||||
|
Atul's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||
|
-----To Realization A/c |
40,000 |
|||
|
|
||||
|
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
26,000 |
||
|
-----To Realization A/c |
26,000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No entry is made for obsolescence of the assets and the assets given to the creditors in the full settlement as these are already transferred to the Realization Account and adjusted) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solution Num 8
|
Books of Paras and Priya Journal |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
1) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
3,000 |
||
|
-----To reallistion A/c |
3,000 |
||||
|
(Being unrecorded furniture sold) |
|||||
|
2) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
600 |
||
|
-----To Realization A/c |
600 |
||||
|
(Being bad debts recovered which was previously written off as bad) |
|||||
|
3) |
Paras's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||
|
------To Realization A/c |
30,000 |
||||
|
(Being unrecorded goodwill taken over by Paras) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4) |
Priya's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
300 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
(Being unrecorded Typewriter estimated Rs.400 taken over by Priya at 25% less price) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5) |
Paras's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
300 |
|
|
|
Priya's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
300 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
600 |
|
|
(Being 100 share of Rs.10 each which were not recorded in the books taken @ Rs.6 each by Paras and Priya and divided between them in their profit sharing ratio) |
|
|
|
|
Solution Num 9
According to section 48 of Partnership Act, 1932 at the time of dissolution, loans and advances from the partners must be paid off before the settlement of their capital accounts. Hence, Yastin's argument is correct that her loan of Rs.2,00,000 must be paid off before the payment of partners' capital.
Solution Num 10
|
Books of Paras and Priya Journal |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
1 |
Arti's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
68,000 |
||
|
-----To, Realization A/c |
68,000 |
||||
|
(Being Arti took over stock worth Rs.80,000 at Rs. 68,000) |
|||||
|
2. |
Karim's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||
|
-----To Realization A/c |
40,000 |
||||
|
(Being Karim took over an unrecorded bike of Rs. 40,000) |
|||||
|
3. |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||
|
-----To Bank A/c |
40,000 |
||||
|
|
(Being compensation paid to the employees) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,600 |
|
|
|
-----To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
30,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Arti's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,000 |
|
|
|
Karim's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
24,000 |
|
|
|
-----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
|
(Being loss on realization transferred to Partner's Capital Account) |
|
|
|
|
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 247
Solution Num 11
|
Books of Rose and Lily Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
80,000 |
By Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c |
|
3,600 |
||
|
To Inventory A/c |
|
1,09,000 |
By Creditors A/c |
|
40,000 |
||
|
To Bills Receivables A/c |
|
40,000 |
By Cash A/c |
|
|
||
|
To Buildings A/c |
|
2,80,000 |
By Assets: |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Motor cycle |
10,000 |
|
||
|
To Cash: |
|
|
Other Assets |
4,84,000 |
4,94,000 |
||
|
Outstanding Electricity Bill |
5,000 |
|
By Rose's Capital A/c (Bills Receivable) |
|
33,000 |
||
|
Creditors |
38,000 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Expenses |
2,400 |
45,400 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
To Profit transferred to: |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Rose's Capital A/c |
6,240 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Lily's Capital A/c |
9,360 |
15,600 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
5,70,600 |
|
|
5,70,600 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Rose |
Lily |
Particulars |
Rose |
Lily |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Bills Receivable) |
33,000 |
|
By Balance b/d |
2,40,000 |
1,60,000 |
||
|
To Cash A/c |
2,33,240 |
1,99,360 |
By Profit and Loss A/c |
20,000 |
30,000 |
||
|
|
By Realization A/c (Profit) |
6,240 |
9,360 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
2,66,240 |
1,99,360 |
2,66,240 |
1,99,360 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Lily's Loan Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Cash A/c |
32,000 |
By Balance c/d |
32,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
32,000 |
|
32,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Cash Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Balance b/d |
|
16,000 |
By Realization: |
|
|
||
|
To Realization: |
|
|
Creditors |
38,000 |
|
||
|
Motor Cycle |
10,000 |
|
Outstanding Electricity Bill |
5,000 |
|
||
|
Other Assets |
4,84,000 |
4,94,000 |
Expenses |
2,400 |
45,400 |
||
|
|
|
|
By Lily's Loan |
|
32,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
By Rose's Capital A/c |
|
2,33,240 |
||
|
|
|
|
By Lily's Capital A/c |
|
1,99,360 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
5,10,000 |
|
|
5,10,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Solution Num 12
|
In the Books of Shilpa ,Meena and Nanda Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Land A/c |
|
81,000 |
By Bank loan A/c |
|
20,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
56,760 |
By Creditors A/c |
|
37,000 |
||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
18,600 |
By Provision for doubtful debts A/c |
|
1,200 |
||
|
To Shilpa's Capital A/c |
|
20,000 |
By Shilpa's Capital A/c (Stock) |
|
35,000 |
||
|
To Cash: |
|
|
By Cash: |
|
|
||
|
To Creditors |
31,000 |
|
Stock |
14,000 |
|
||
|
To Realization Expenses |
1,200 |
32,200 |
Debtors |
12,300 |
|
||
|
To Profit transferred to |
|
|
land |
1,10,000 |
1,36,300 |
||
|
Shilpa's Capital A/c |
10,470 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Meena's Capital A/c |
6,980 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Nanda's Capital A/c |
3,490 |
20,940 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
2,29,500 |
|
|
2,29,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Shilpa |
Meena |
Nanda |
Particulars |
Shilpa |
Meena |
Nanda |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
- |
- |
23,000 |
By Balance b/d |
80,000 |
40,000 |
- |
||
|
To Realzation A/c (Stock) |
35,000 |
|
By General Reserve A/c |
6,000 |
4,000 |
2,000 |
|||
|
To Cash A/c |
81,470 |
50,980 |
|
By Realization A/c (Bank Loan) |
20,000 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
By Realization A/c (Profit) |
10,470 |
6,980 |
3,490 |
||||
|
|
|
By Cash A/c |
|
|
17,510 |
||||
|
1,16,470 |
50,980 |
23,000 |
1,16,470 |
50,980 |
23,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Cash Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
10,840 |
By Realization (Expenses) |
32,200 |
||
|
To Realization A/c(Assets) |
1,36,300 |
By Shilpa capital A/c |
81,470 |
||
|
To Nanda's Capital A/c |
17,510 |
By Meena's Capital A/c |
50,980 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,64,650 |
|
1,64,650 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 248
Solution Num 13
|
Books of Surjit and Rahi Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
6,000 |
By Creditors A/c |
|
38,000 |
||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
19,000 |
By Mrs. Surjit's Loan A/c |
|
10,000 |
||
|
To Furniture A/c |
|
4,000 |
By Surjit's Capital A/c (Investment) |
|
8,000 |
||
|
To Plant A/c |
|
28,000 |
By Bank : |
|
|
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
10,000 |
Stock |
5,000 |
|
||
|
To Surjit's Capital A/c (Mrs. Surjit's Loan) |
|
10,000 |
Debtors |
18,500 |
|
||
|
To Bank: |
|
|
Furniture |
4,500 |
|
||
|
Expenses |
1,600 |
|
Plant |
25,000 |
53,000 |
||
|
Creditors |
37,000 |
38,600 |
By Loss transferred to: |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Surjit's Capital A/c |
3,960 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Rahi's Capital A/c |
2,640 |
6,600 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
1,15,600 |
|
|
1,15,600 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Surji |
Rahi |
Particulars |
Surjit |
Rahi |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Investment) |
8,000 |
|
By Balance b/d |
10,000 |
8,000 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Loss) |
3,960 |
2,640 |
By Realization A/c (Mrs. Surjit Loan) |
10,000 |
|
||
|
To Profit and Loss A/c |
4,500 |
3,000 |
By Reserve A/c |
9,000 |
6,000 |
||
|
To Bank A/c |
12,540 |
8,360 |
|
|
|||
|
29,000 |
14,000 |
29,000 |
14,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Rahi's Loan Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Bank A/c |
5,000 |
By Balance b/d |
5,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
5,000 |
|
5,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Bank Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
11,500 |
By Realization A/c (Creditors and Expenses) |
38,600 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets realized) |
53,000 |
By Rahi's Loan A/c |
5,000 |
||
|
|
|
By Surjit's Capital A/c |
12,540 |
||
|
|
|
By Rahi's Capital A/c |
8,360 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
64,500 |
|
64,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Solution Num 14
|
In the Books of Rita,Geeta and Ashish Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
52,300 |
By Creditors A/c |
|
65,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
36,000 |
By Bills payable A/c |
|
26,000 |
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
69,000 |
By Cash: |
|
|
||
|
To Plant A/c |
|
91,200 |
Debtors |
30,000 |
|
||
|
To Cash: |
|
|
Stock |
26,000 |
|
||
|
Outstanding Salaries |
7,200 |
|
Plant |
42,750 |
|
||
|
Discounted Bill |
9,800 |
|
Investment |
58,650 |
1,57,400 |
||
|
Creditors |
65,000 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Bill's Payable |
26,000 |
1,08,000 |
By Loss transferred to |
|
|
||
|
To Rita's capital A/c |
|
7,870 |
Rita's Capital A/c |
57,985 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Geeta's Capital A/c |
38,657 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Ashish's Capital A/c |
19,328 |
1,15,970 |
||
|
|
|
3,64,370 |
|
|
3,64,370 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Rita |
Geeta |
Ashish |
Particulars |
Rita |
Geeta |
Ashish |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Loss) |
57,985 |
38,657 |
19,328 |
By Balance b/d |
80,000 |
50,000 |
30,000 |
||
|
To Bank A/c |
39,885 |
18,010 |
14,005 |
By General Reserve A/c |
10,000 |
6,667 |
3,333 |
||
|
|
|
By Realization A/c |
7,870 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
97,870 |
56,667 |
33,333 |
97,870 |
56,667 |
33,333 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Cash Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
22,500 |
By Realization A/c |
1,08,000 |
||
|
To Realization A/c |
1,57,400 |
By Rita's Capital A/c |
39,885 |
||
|
|
|
By Geeta's Capital A/c |
18,010 |
||
|
|
|
By Ashish's Capital A/c |
14,005 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,79,900 |
|
1,79,900 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 249
Solution Num 15
|
Books of Anup and Sumit Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Sundry Debtors A/c |
|
12,000 |
By Sundry Creditors A/c |
|
27,000 |
||
|
To Plant A/c |
|
47,000 |
By Loan A/c |
|
40,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
42,000 |
By Bank: |
|
|
||
|
To Lease hold land A/c |
|
60,000 |
Lease hold Land |
72,000 |
|
||
|
To Furniture A/c |
|
25,000 |
Furniture |
22,500 |
|
||
|
To Bank: |
|
|
Stock |
40,500 |
|
||
|
Creditors |
25,500 |
|
Plant |
48,000 |
|
||
|
Loan |
40,000 |
|
Sundry Debtors |
10,500 |
1,93,500 |
||
|
Expenses |
2,500 |
68,000 |
|
|
|
||
|
To Profit transferred to |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Anup's Capital A/c |
3,250 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Sumit's Capital A/c |
3,250 |
6,500 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
2,60,500 |
|
|
2,60,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Anup |
Sumit |
Particulars |
Anup |
Sumit |
||
|
To Bank A/c |
68,250 |
68,250 |
By Balance b/d |
60,000 |
60,000 |
||
|
|
By Reserve Fund A/c |
5,000 |
5,000 |
||||
|
|
By Realization A/c |
3,250 |
3,250 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
68,250 |
68,250 |
68,250 |
68,250 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Bank Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
11,000 |
By Realization A/c (Expenses and Liabilities) |
68,000 |
||
|
|
|
By Anup's Capital A/c |
68,250 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets) |
1,93,500 |
By Sumit's Capital A/c |
68,250 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
2,04,500 |
|
2,04,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 250
Solution Num 16
|
Books of Ashu and Harish Realisation Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
|||
|
To Building A/c |
|
80,000 |
By Creditors A/c |
88,000 |
||
|
To Machinery A/c |
|
70,000 |
By Bank overdraft A/c |
50,000 |
||
|
To Furniture A/c |
|
14,000 |
By Ashu's Capital A/c (Assets taken) |
1,43,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
20,000 |
By Harish's capital A/c (Assets taken) |
1,12,000 |
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
60,000 |
By Cash A/c (Debtors) |
46,000 |
||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
48,000 |
|
|
||
|
To Ashu's Capital A/c (Creditors) |
|
88,000 |
|
|
||
|
To Harish's Capital A/c (Bank Overdraft) |
|
50,000 |
|
|
||
|
To Cash A/c (Expenses) |
|
3,000 |
|
|
||
|
To Profit transferred to |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Ashu's Capital A/c |
3,600 |
|
|
|
||
|
Harish's Capital A/c |
2,400 |
6,000 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
4,39,000 |
|
4,39,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Ashu |
Harish |
Particulars |
Ashu |
Harish |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets taken) |
1,43,000 |
1,12,000 |
By Balance b/d |
1,08,000 |
54,000 |
||
|
To Cash A/c |
56,600 |
|
By Realization A/c (Liabilities) |
88,000 |
50,000 |
||
|
|
By Realization A/c (Profit) |
3,600 |
2,400 |
||||
|
|
By Cash A/c |
|
5,600 |
||||
|
1,99,600 |
1,12,000 |
1,99,600 |
1,12,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Cash Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
8,000 |
By Realization A/c (Expenses) |
3,000 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Debtors) |
46,000 |
By Ashu's Capital A/c |
56,600 |
||
|
To Harish's Capital A/c |
5,600 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
59,600 |
|
59,600 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Note: However, the answer mentioned in the book is Rs. 14,000. But, as per the solution, the Profit on Realization is Rs. 6,000;
Working Notes:
|
|
Ashu |
Harish |
|
Building |
95,000 |
|
|
Machinery |
|
80,000 |
|
Stock (3:2) |
12,000 |
8,000 |
|
Investment (3:2) |
36,000 |
24,000 |
|
|
Rs.1,43,000 |
Rs.1,12,000 |
|
|
|
|
Solution Num 17
|
Books of Sanjay, Tarun and Vineet Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Plant A/c |
|
90,000 |
By Creditors A/c |
|
80,000 |
||
|
To Debtors A/c |
|
60,000 |
By Bills Payable A/c |
|
30,000 |
||
|
To Furniture A/c |
|
32,000 |
By Cash: |
|
|
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
60,000 |
Plant |
72,000 |
|
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
70,000 |
Debtors |
54,000 |
|
||
|
To Bills Receivable A/c |
|
36,000 |
Furniture |
18,000 |
|
||
|
To Cash: |
|
|
Stock |
54,000 |
|
||
|
Creditors |
80,000 |
|
Investments |
76,000 |
|
||
|
Bills Payable |
30,000 |
1,10,000 |
Bills Receivable |
31,000 |
3,05,000 |
||
|
To Sanjay's Capital A/c |
|
18,300 |
By Loss transferred to |
|
|
||
|
(6% commission) |
|
|
Sanjay's Capital A/c |
30,650 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Tarun's Capital A/c |
20,433 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Vineet's Capital A/c |
10,217 |
61,300 |
||
|
|
|
4,76,300 |
|
|
4,76,300 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Sanjay |
Tarun |
Vineet |
Particulars |
Sanjay |
Tarun |
Vineet |
||
|
To Realization A/c (loss) |
30,650 |
20,433 |
10,217 |
By Balance b/d |
1,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
||
|
To Cash A/c |
87,650 |
79,567 |
59,783 |
By Realization A/c |
18,300 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
(commission) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1,18,300 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
1,18,300 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Cash Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
32,000 |
By Realization A/c |
1,10,000 |
||
|
To Realization A/c |
3,05,000 |
By Sanjaya's Capital A/c |
87,650 |
||
|
|
|
By Tarun's Capital A/c |
79,567 |
||
|
|
|
By Vineet Capital A/c |
59,783 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
3,37,000 |
|
3,37,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 251
Solution Num 18
|
Books of Gupta and Sharma Journal |
||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
||
|
2017 |
||||||
|
Mar.31 |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
2,35,500 |
|||
|
-----To Sundry Debtors A/c |
55,000 |
|||||
|
-----To Stock A/c |
44,000 |
|||||
|
-----To Bills Receivable A/c |
19,000 |
|||||
|
-----To Machinery A/c |
52,000 |
|||||
|
-----To Investment A/c |
38,500 |
|||||
|
-----To Fixtures A/c |
27,000 |
|||||
|
(Being assets transferred to Realization Account) |
||||||
|
Mar. 31 |
Sundry Creditors A/c |
Dr. |
|
38,000 |
|
|
|
|
Mrs. Gupta's Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
Mrs. Sharma's Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
92,000 |
|
|
|
(Being liabilities transferred to Realization Account) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar. 31 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,59,000 |
|
|
|
|
----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
1,59,000 |
|
|
|
(Being assets realized: sundry Debtors Rs.52,000, Stock Rs.42,000, bills receivable Rs.16,000, Machinery Rs.49,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar.31 |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
----To Gupta's Capital A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
(Being Gupta took over Mrs. Gupta's Loan) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar. 31 |
Gupta's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
36,000 |
|
|
|
|
----To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
36,000 |
|
|
|
(Being investment taken over by Gupta) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar.31 |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
|
66,860 |
|
|
|
|
--------To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
66,860 |
|
|
|
(Being liabilities paid: Mrs. Shrama's loan Rs. 30,000 and Creditors Rs. 38,000 paid off less 3% discount) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar. 31 |
Realization A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
|
-----To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
(Being realization expenses paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar. 31 |
Gupta's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,280 |
|
|
|
|
Sharma's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,280 |
|
|
|
|
--------To Realization A/c |
|
|
|
36,560 |
|
|
|
(Being Loss on Realization transferred to Partner's capital Account) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar. 31 |
Reserve Fund A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
|
--------To Gupta's Capital A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
--------To Sharma's Capital A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
(Being reserve fund distributed among partners ratio) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar 31 |
Gupta's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
58,720 |
|
|
|
|
Sharma's Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
44,720 |
|
|
|
|
--------To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
1,03,440 |
|
|
|
(Being final payment made to partners) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Books of Gupta and Sharma Realization Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Sundry Debtors A/c |
|
55,000 |
By Sundry Creditors A/c |
|
38,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
44,000 |
By Mrs. Gupta's loan A/c |
|
20,000 |
||
|
To Bills Receivable A/c |
|
19,000 |
By Mrs. Sharma Loan A/c |
|
30,000 |
||
|
To Machinery A/c |
|
52,000 |
By Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c |
|
4,000 |
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
38,500 |
By Bank: |
|
|
||
|
To Fixtures A/c |
|
27,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
52,000 |
|
||
|
To Gupata's Capital A/c (Mrs. Gupta Loan) |
|
20,000 |
Stock |
42,000 |
|
||
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
Bills Receivable |
16,000 |
|
||
|
Creditors |
36,860 |
|
Machinery |
49,000 |
1,59,000 |
||
|
Mrs. Sharma's Loan |
30,000 |
|
By Gupta's Capital A/c (Investment) |
|
36,000 |
||
|
Expenses |
1,200 |
68,060 |
By Loss transferred to |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Gupta's Capital A/c |
18,280 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sharma's Capital A/c |
18,280 |
36,560 |
||
|
|
|
3,23,560 |
|
|
3,23,560 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Gupta |
Sharma |
Particulars |
Gupta |
Sharma |
||
|
Realization(Investment) |
36,000 |
|
By Balance b/d |
90,000 |
60,000 |
||
|
Realization A/c (Loss) |
18,280 |
18,280 |
By Realization (Mrs. Gupta Loan) |
20,000 |
|
||
|
Bank A/c |
58,720 |
44,720 |
By Reserve Fund |
3,000 |
3,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1,13,000 |
63,000 |
1,13,000 |
63,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Bank Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
Balance b/d |
12,500 |
By Realization A/c (Payment of expenses and liabilities) |
68,060 |
||
|
Realization A/c (Assets realized) |
1,59,000 |
By Gupta's Capital A/c |
58,720 |
||
|
|
|
By Sharama's Capital A/c |
44,720 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,71,500 |
|
1,71,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Solution Num 19
|
Realization Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||||
|
To Sundry Debtors A/c |
|
58,000 |
By Sundry Creditors A/c |
|
20,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
|
39,500 |
By Bill's payable A/c |
|
25,500 |
||
|
To Machinery A/c |
|
48,000 |
By Ashok's Current A/c (Investment) |
|
40,000 |
||
|
To Investment A/c |
|
42,000 |
By Babu's Current A/c (Machinery) |
|
45,000 |
||
|
To Freehold property A/c |
|
50,500 |
By Chetan's Current A/c (Freehold property) |
|
55,000 |
||
|
To Bank: |
|
|
By Bank: |
|
|
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
18,600 |
|
Sundry Debtors |
56,500 |
|
||
|
Bills payable |
25,500 |
|
Stock |
36,500 |
|
||
|
Expenses |
3,000 |
47,100 |
Unrecorded computer |
9,000 |
1,02,000 |
||
|
To Profit transferred to |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Ashok's Current A/c |
1,200 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Babu's Current A/c |
800 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Chetan's Current A/c |
400 |
2,400 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
2,87,500 |
|
|
2,87,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Current Accounts |
|||||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets taken) |
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
By Balance b/d |
10,000 |
5,000 |
3,000 |
||
|
|
|
By Realization A/c (Profit) |
1,200 |
800 |
400 |
||||
|
|
|
By Ashoks's capital A/c |
28,800 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
By Babu's capital A/c |
|
39,200 |
|
||||
|
|
|
By Chetan capital A/c |
|
|
51,600 |
||||
|
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
||
|
To Ashok's Current A/c |
28,800 |
|
By Balance b/d |
70,000 |
55,000 |
27,000 |
|||
|
To Babu's Current A/c |
|
39,200 |
|
By Bank A/c |
|
|
24,600 |
||
|
To Chetan's Current A/c |
|
51,600 |
|
|
|
||||
|
To Bank A/c |
41,200 |
15,800 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
70,000 |
55,000 |
51,600 |
70,000 |
55,000 |
51,600 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Babu's Loan Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Cash A/c |
30,000 |
By Balance b/d |
30,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
30,000 |
|
30,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Bank Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
7,500 |
By Realization A/c (Expenses and Liabilities) |
47,100 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets realized) |
1,02,000 |
By Babu's Loan A/c |
30,000 |
||
|
To Chetan's Capital A/c |
24,600 |
By Ashok's Capital A/c |
41,200 |
||
|
|
|
By Babu's Capital A/c |
15,800 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,34,100 |
|
1,34,100 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Exercise 252
Solution Num 20
|
Books of Tanu and Manu Realisation Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
|||
|
To Sundry Debtors A/c |
55,000 |
By Sundry Creditors A/c |
|
62,000 |
||
|
To Stock A/c |
75,000 |
By Bills Payable A/c |
|
32,000 |
||
|
To Motor Ca A/c r |
90,000 |
By Bank Loan A/c |
|
50,000 |
||
|
To Machinery A/c |
45,000 |
Tanu's Capital A/c |
|
|
||
|
To Investment A/c |
70,000 |
Sundry Debtors A/c |
55,000 |
|
||
|
To Fixtures A/c |
9,000 |
Motor Car A/c |
60,000 |
1,15,000 |
||
|
To Manu's Capital A/c (Bills Payable) |
30,400 |
By Bank: |
|
|
||
|
To Bank A/c (Expenses) |
2,200 |
Stock |
10,000 |
|
||
|
To Tanu's Capital A/c (Bank Loan) |
50,000 |
Investment |
76,000 |
|
||
|
|
|
Fixtures |
4,000 |
90,000 |
||
|
|
|
By Manu's Capital A/c (Machinery) |
|
40,000 |
||
|
|
|
By Loss transferred to |
23,500 |
|
||
|
|
|
Tanu's Capital A/c |
14,100 |
37,600 |
||
|
|
|
Manu's Capital A/c |
|
|
||
|
|
4,26,600 |
|
|
4,26,600 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Partner's Capital Accounts |
|||||||
|
Dr |
|
Cr |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Tanu |
Manu |
Particulars |
Tanu |
Manu |
||
|
To Realzation A/c (Assets taken) |
1,15,000 |
40,000 |
By Balance b/d |
1,10,000 |
90,000 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Loss) |
23,500 |
14,100 |
By Realization A/c (Liabilities) |
50,000 |
30,400 |
||
|
To Bank A/c |
31,500 |
72,300 |
By Reserve Fund A/c |
10,000 |
6,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1,70,000 |
1,26,400 |
1,70,000 |
1,26,400 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Bank Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
Particulars |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
To Balance b/d |
16,000 |
By Realization A/c (Expenses) |
2,200 |
||
|
To Realization A/c (Assets) |
90,000 |
By Tanu's Capital A/c |
31,500 |
||
|
|
|
By Manu's Capital A/c |
72,300 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,06,000 |
|
1,06,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||