Class 11-commerce NCERT Solutions Economics Chapter 5 - Market Equilibrium
Market Equilibrium Exercise 86
Solution 1
Market equilibrium is a situation of the market where the demand for goods and services equals the supply with the given price.
The market equilibrium is automatically achieved in the marketplace as there is no incentive to deviate from the market equilibrium situation.
In a state of market equilibrium, the excess of demand and supply does not exist. The price which prevails in the market is considered the market equilibrium price.
Solution 2
At a given price, when the demand for a commodity is greater than the supply of that commodity, there is excess of demand for the commodity.
Excess demand occurs in the market when producers are not willing to supply goods as compared to the demand in the market at a particular price.
Solution 3
At a given price, when the supply for a commodity is greater than the demand of that commodity, there is excess of supply for the commodity.
Excess supply occurs in the market when producers are willing to supply more goods as compared to the demand in the market at a particular price.
The decline in the demand for a commodity as compared to the quantity supplied causes an excess supply for a commodity in the market.
Solution 4
(i) If the market price is above the equilibrium price, then there will be decline in the quantity demanded for a commodity. Consumers are likely to buy comparatively less goods. At a higher price, producers are likely to increase the quantity supplied.
Thus, if the price prevailing in the market is above the equilibrium price, then there will be excess supply in the market.
(ii) If the market price is below the equilibrium price, then there will be an increase in the quantity demanded for a commodity. Consumers are likely to buy comparatively more goods and services. At a lower price, producers are unwilling to supply goods.
Thus, if the price prevailing in the market is below the equilibrium price, then there will be excess demand in the market.
Solution 5
In a perfectly competitive market, price is determined by market demand and market supply. Market demand is the summation of all individual demands in the market. Market supply is also the summation of all individual supply schedules in the market.
The intersection of market demand and market supply determines the price in a perfectly competitive market.
Graphical representation of the determination of price in a perfectly competitive market
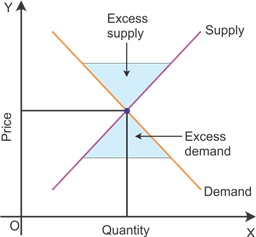
The figure indicates that the price is determined at the point where the market demand curve intersects the market supply curve. Any point above the equilibrium price creates excess supply, and the price below the equilibrium level creates excess demand, as indicated in the figure.
Solution 6
Firms earn supernormal profit if the equilibrium price is greater than the minimum average cost of the firms. New firms are likely to enter the market considering supernormal profit. An increase in the number of firms in the market causes a rise in the total supply, causing a decline in the market equilibrium price.
Supernormal profits are wiped out when the price becomes equal to the average cost. Firms start earning normal profits when the market equilibrium price equals the average cost.
Thus, the market price equals the average cost when there is free entry and exit in the market.
Solution 7
Firms in a perfectly competitive market supply goods when the price is equal to the minimum of average cost in the long run.
The characteristics of free entry and free exit enforce firms to earn normal or zero economic profit. Firms in the market cannot earn either abnormal losses or abnormal profits. If there is an abnormal profit in the market, then more firms enter the market and the abnormal profit will be wiped out.
Therefore, the characteristics of free entry and free exit ensure that the price is equal to the minimum of average cost in the long run.
Graphical representation of the equilibrium quantity determined in a perfectly competitive market
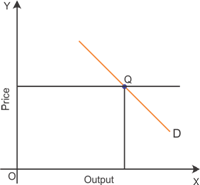
The figure indicates that the equilibrium quantity is determined at the level where the average cost equals the market demand.
Solution 8
The characteristics of free entry and free exit enforce firms to earn normal or zero economic profit.
Firms in the market cannot earn either abnormal losses or abnormal profits. If there is an abnormal profit in the market, then more firms enter the market and the abnormal profit will be wiped out.
New firms will not enter the market or existing firms will not exit from the market if the price is equal to the minimum of average cost in the long run.
Therefore, the equilibrium number of firms is determined in a market where the price equals the minimum of the long-run average cost.
Solution 9
(a) An increase in consumer income leads to a rise in the equilibrium price assuming that the number of firms is constant in the market. Consumers are likely to increase their demand considering a rise in their level of income. A rise in demand causes an increase in the equilibrium price.
Graphical representation of the effects of an increase in the level of income on the equilibrium price and quantity
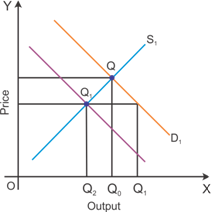
The figure indicates that the equilibrium price is likely to increase due to a rise in the consumer's income level.
(b) A decrease in consumer's income leads to a decline in the equilibrium price assuming that the number of firms is constant in the market. Consumers are likely to decrease their demand considering a decline in their level of income. A decline in the demand causes a fall in the equilibrium price due to the availability of excess supply in the market.
Graphical representation of the effects of a decrease in the level of income on the equilibrium price and quantity
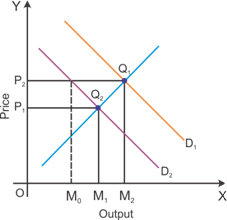
The figure indicates that the equilibrium price is likely to decrease due to a decrease in the consumer's income level.
Solution 10
Shoes and a pair of socks are complementary goods which are demanded together. A rise in the price of shoes leads to a decrease in the demand for the pair of socks as these goods are demanded together.
Graphical representation of the rise in the price of shoes on the quantity bought and sold of the pairs of socks
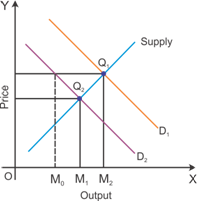
The image indicates the changes in the demand for a pairs of socks with respect to changes in the price of shoes.
Market Equilibrium Exercise 87
Solution 11
An increase in the price of coffee is likely to increase the demand for tea and a decrease in the price of coffee reduces the demand for tea. Tea and coffee are considered substitute goods.
The positive change in the price of one substitute good increases the demand for another substitute good.
Graphical representation of the effect on equilibrium quantity
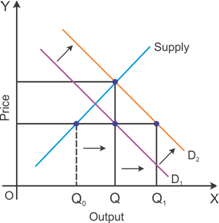
The graph indicates a rise in the demand for tea caused by an increase in the price of coffee.
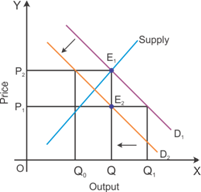
The graph indicates a decline in the demand for tea caused by a decrease in the price of coffee.
Solution 12
An increase in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price. Producers tend to produce comparatively less goods and services. The market demand remains the same, and due to this, the equilibrium price tends to increase.
Thus, a rise in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price.
A decrease in the price of inputs causes an increase in the equilibrium quantity and a decrease in the equilibrium price. Producers tend to produce comparatively more goods and services. The market demand increases due to a decline in the price. Producers reduce the price for their goods and services considering a decline in the price of inputs.
Thus, a decrease in the price of inputs causes an increase in the equilibrium quantity and a decrease in the equilibrium price.
Solution 13
The equilibrium price and quantity are likely to increase if there is an increase in the price of a substitute (Y) of Good X. Changes in the price of one substitute good tends to change the demand for another substitute good.
The demand for Good X is likely to increase due a rise in the price of Good Y. This situation causes an increase in the price of Good X due to excessive demand.
The equilibrium quantity level also tends to increase due to a rise in the demand for Good X.
Graphical representation of changes in price and quantity
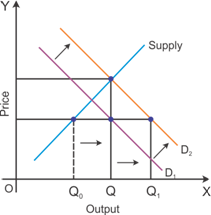
An increase in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price. Producers tend to produce comparatively less goods and services. The market demand remains the same, and due to this, the equilibrium price tends to increase.
Solution 14
An increase in the demand causes a rightward shift in the demand curve. If the number of firms is fixed in the market, then a rise in the demand will causes an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity. This change is described in the figure below.
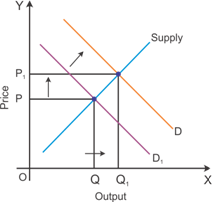
According to the graph, the firms are likely to earn super-normal profit as there is an increase in the market equilibrium price.
If the entry-exit is allowed for new firms, then there will be a decrease in the market equilibrium price. More firms will enter the market considering the availability of super normal profit.
Entry of new firms in the market causes a decrease in the super-normal profits of existing firms. All firms start earning normal profit as indicated in the below figure.
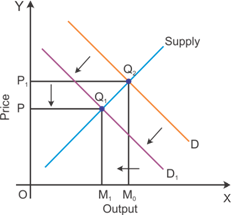
Solution 15
If the demand and supply increase by the same proportion, then there will not be any changes in the market equilibrium price.
Graphical representation of the effect of a rightward shift of both demand and supply curves on equilibrium price and quantity
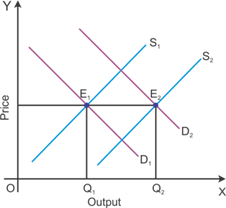
The figure indicates that the market equilibrium price remains unchanged when there are equal changes in the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded. If an increase in the quantity demanded is more than the quantity supplied, then there will be a rise in the market equilibrium price.
If a rise in the quantity supplied is more than the quantity demanded, then there will be a decline in the market equilibrium price.
Solution 16
(a) Both demand and supply curves shift in the same direction.
If the demand and supply increase by the same proportion, then there will not be any changes in the market equilibrium price.
Graphical representation of the effect of a rightward shift of both demand and supply curves on equilibrium price and quantity
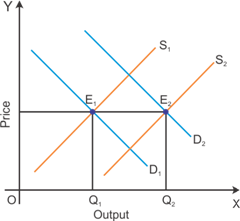
The figure indicates that the market equilibrium price remains unchanged when there are equal changes in the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded.
(b) Demand and supply curves shift in opposite directions
If the demand supply curve shifts in the same direction, then the there will be an increase in the demand and decrease in the supply. This causes an increase in the price. The equilibrium quantity remains unchanged.
If the demand decreases and the supply increases, then the equilibrium price remains unchanged and the equilibrium quantity increases.
Solution 17
The demand for goods and services comes from consumers in the goods market, whereas the demand for labour comes from employers in the labour market.
The supply of goods and services comes from producers in the goods market, whereas the supply for labour comes from the households in the labour market.
Thus, households play the role of suppliers in the labour market and firms play the role of suppliers in the goods market.
Solution 18
The optimal amount of labour is determined in a perfectly competitive market considering the cost and benefit incurred from employing additional labour.
A firm is likely to employ labourers up to the point where the cost of employing additional labour equals the benefits incurred from it.
The following equation is used to determine the optimal amount of labour in a perfectly competitive market:
![]()
Here, VMP = value of marginal product
The optimum amount of labour is determined when the value of marginal product from the labour equals the wage rate.
Graphical representation of the determination of the optimal amount of labour in a perfectly competitive market
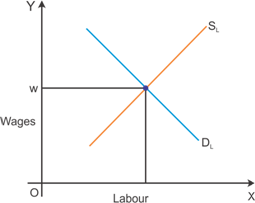
The graph indicates the wage determination in the perfectly competitive market. Intersection of demand and supply determines the wage rate.
Solution 19
Equilibrium of demand and supply of labour determines the wage rate. Marginal product of labour plays an important role in determining the demand for labour.
Graphical representation of the wage determination in a perfectly competitive labour market
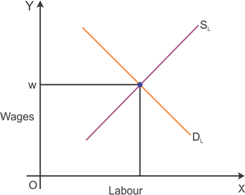
The graph indicates the wage determination in a perfectly competitive market. Intersection of demand and supply determines the wage rate.
Solution 20
Price ceiling is the process of determining the price of some necessary goods at a lower level so that they can be made available for the poor.
Government of India imposes a price ceiling on the basic necessity goods which should be made available for the poor. For example, goods such as rice, wheat, sugar kerosene and pulses.
Imposition of the price ceiling has the following consequences:
Imposition of price ceiling leads an excessive increase in the demand. At lower price, people are likely to increase their demand for such commodities.
Poor consumers do not get access to unlimited goods. The quota is fixed for these goods.
Normally, the goods provided under the price ceiling system are of inferior quality.
Market Equilibrium Exercise 88
Solution 21
In the short run, shift in the demand curve has larger effects on price and smaller effects on the quantity because the quantity supplied cannot be changed according to the changes in quantity demanded. Producers try to change the market price according to changes in the market demand.
On the contrary, in the long run, free entry and exit are permitted for firms. This enables the market to change the quantity supplied according to the changes in the quantity demanded. This would have lesser effect on the price and more effect on the quantity. In the long run, price is equal to the minimum of average variable cost.
Thus, a shift in the demand curve has a larger effect on price and smaller effect on quantity considering that the quantity supplied remains inelastic during the short period.
Solution 22
Firms are not willing to supply any positive level of output at any price less than Rs 15 considering that this price is less than the minimum of average variable cost. If the price is less than that of the minimum of average variable cost, then the firms have to incur losses.
Calculation of the equilibrium price for this commodity:
The equilibrium price is determined at the level where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
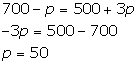
Thus, the equilibrium price is 50 rupees.
Equilibrium quantity is determined by considering the market price.
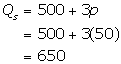
Therefore, 650 is the equilibrium quantity.
Solution 23
(a)
Firms are not willing to supply any positive level of output at any price between 0 and 20 considering that this price is less than the minimum of average variable cost. If the price is less than that of the minimum of average variable cost, then the firms have to incur losses.
(b)
The market for X will be in equilibrium at the price of Rs 20. During the long run, there is free entry and exit for firms. So, the equilibrium price equals to the minimum of the average variable cost. All the firms in the long run earn zero economic profit as the price equals the minimum of the average variable cost.
(c)
Equilibrium quantity is determined by considering the market equilibrium price. The following is a calculation of market equilibrium quantity and the number of firms in the market:
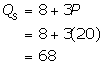
So, the quantity supplied is 68.
Quantity demanded
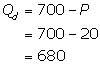
Thus, the equilibrium quantity is 680. The number of firms in the market can be calculated by considering the equilibrium quantity.

Thus, the number of firms in the market is 10.
Solution 24
(a)
The equilibrium price and quantity can be calculated by considering the given price and quantity level.
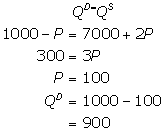
Therefore, the equilibrium quantity is 900 and the equilibrium price is 100.
(b)
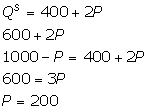
Thus, the equilibrium price is 200.
![]()
Thus, the equilibrium quantity is 800.
An increase in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price. Producers tend to produce comparatively less goods and services. The market demand remains the same, and due to this, the equilibrium price tends to increase.
Thus, a rise in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price. An increase in the price of inputs causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price.
(c)
Imposition of taxes increases the cost of production. An increase in the cost of production causes a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price.
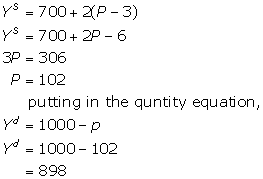
Thus, the equilibrium price is 102 and the equilibrium quantity is 898.
Solution 25
The demand for apartments on rent would likely increase if the government comes forward to help those seeking apartments.
Government uses the price ceiling on apartment rents. Price ceiling is the process of determining the price of some necessary goods at a lower level so that they can be made available for the poor.
If the government comes forward and decides a rent below the market equilibrium price, then the demand for the apartments on rent is likely to increase.
Imposition of price ceiling would lead to a practice of black marketing. Landlords can charge higher rents illegally.

