Class 11-commerce NCERT Solutions Economics Chapter 1 - Introduction
Introduction Exercise 7
Solution 1
The central problems of an economy are the allocation of scarce resources to fulfil unlimited wants and the distribution of final goods and services. The central problems of an economy are summarised as
What to produce: This is the main problem which an economy has to face. As there are limited resources with alternative uses, a country has to decide what to produce and in what quantity. For example, a country has to decide on whether to produce necessity goods or luxury goods.
How to produce: This is an important problem which an economy has to face. A government has to decide whether to use capital-intensive technology or labour-intensive technology.
For whom to produce: This is an important element of an economy to make appropriate distribution of goods and services. The government has to decide for whom to produce and how much to produce.
Solution 2
The production possibilities of an economy means a set of all possible combinations of goods and services which an economy can produce by using available resources and technology.
The production possibilities of an economy indicate the capacity of an economy to optimally utilise the available resources and technology to produce maximum goods and services.
Solution 3
A production possibility frontier is a curve indicating various possibilities of two goods which can be produced by using available resources and the stock of technology. It shows that all the available resources and technology are optimally utilised if a country is producing maximum goods and services.
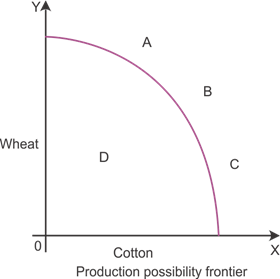
The diagram indicates the production possibility frontier of wheat and cotton. The curve shows that any combination of goods which lie on the production possibility frontier can be achieved if all the resources are fully utilised. Anything below the production possibility frontier indicates that the resources are not optimally utilised in the production process.
Solution 4
The subject matter of economics is categorised under microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics studies the behaviour of individual, whereas macroeconomics studies the behaviour of an economy as a whole.
Determination of price and quantities of goods and services in the individual market is the subject matter of microeconomics.
Determination of aggregate price level and the quantities of goods and services in an economy is the subject matter of macroeconomics.
The main focus of microeconomics is equilibrium of prices and quantities of goods and services in the individual market.
The main focus of macroeconomics is a general equilibrium of all markets in an economy.
Solution 5
|
Centrally Planned Economy |
Market Economy |
|
All the factors of production are fully owned by the government. |
All the factors of production are fully owned by the private sector. |
|
Social welfare is the main aim of production. |
Profit maximisation is the main aim of the production process. |
|
Planning mechanism advocates the production process. |
Market demand and supply determine the production process. |
|
There is comparatively lower income inequality. |
There is comparatively higher income inequality. |
|
Price of goods and services is determined by the government. |
Price of goods and services is determined by market demand and supply. |
Solution 6
In positive economic analysis, we deal with what is, what was and how a particular mechanism functions in a particular economy.
Normally, facts are described in positive economics. For example, India has opted for a liberalised policy in 1991. The Indian economy is a developing economy.
Thus, personal value judgements are not analysed in a positive economic analysis, rather importance is given to the facts.
Solution 7
In normative economic analysis, we deal with 'ought to be', 'what should be' and 'how a particular mechanism should solve economic problems'.
Normally, facts are not described in normative economics. For example, India should allow 100% FDI to increase economic growth development.
Thus, personal value judgements are analysed in a normative economic analysis. Importance is given to analytical judgements.
Solution 8
|
Microeconomics |
Macroeconomics |
|
Studies the behaviour of individuals. |
Studies the behaviour of the economy as a whole. |
|
Deals with the determination of prices and quantities of goods and services in the individual market. |
Deals with the determination of the aggregate price level and the quantities of goods and services in an economy. |
|
The main focus is the equilibrium of prices and quantities of goods and services in the individual market. |
The main focus is a general equilibrium of all markets in an economy. |
|
Price determination and allocation of resources are central economic problems. |
Income and employment level determination are central economic problems. |
|
Individual demand, individual supply, rent, wages, profit and price are main variables. |
Inflation, aggregate demand, aggregate supply and employment level are main variables. |

