Class 11-commerce NCERT Solutions Accountancy Part I Chapter 3: Recording of Transactions - I
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 87
Solution SA 1
The fundamental steps in the accounting process are:
- Identifying and analysing the business transactions
- Recording those transactions in journal
- Classifying account individually and posting it in a ledger
- Preparing and summarizing financial statement
- Communicating it to the interested users
The pictorial representation of the same is given below:

Solution SA 2
Source document can be termed as an evidence providing document. The evidence provided by the source document is important because it:
- Provides relevant and detailed information of a particular transaction such as parties involved in the transaction, amount and date
- Verifies transactions during auditing
- Acts as a evidence in the court of law
- Summation of each account which culminates into financial statements
Solution SA 3
To make sound business decisions, it is very important to have an accounting system which generates complete and error-free financial records. Although a journal and ledger are parts of an accounting system, they both serve extremely important and different purpose. A journal records transactions permanently in one entry using the source document and is listed as per their occurrences. It comes under the double-entry system and is called the book of original entry. Once the transactions are recorded in the journal, they are then posted into the ledger so as to assign each transaction to individual accounts,
The process of recording the transactions in journal and then in ledger is presented in the below given flow chart.
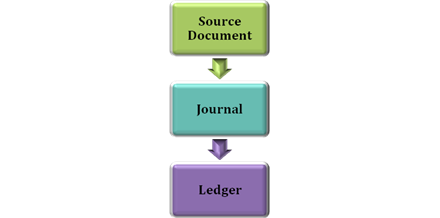
Solution SA 4
There are four columns for a journal entry; namely, Date, Particulars, L.F., Debit and Credit Amount. A journal entry format is as shown:
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. Rs. |
Cr. Rs. |
|
XXX |
Vehicle A/c |
Dr. |
|
XXX |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
XXX |
|
|
(Being vehicle bought by the business) |
|
|
|
|
The debit amount column always comes before/left to the credit amount column as a credit is a right-sided entry and debit is a left-sided entry. Credit accounts are indented and listed last. Indentation is leaving a space before writing any word. In the 'Particulars' column of journal format, debited account is written first and credited account is written on the next line leaving some space which is indentation.
Solution SA 5
An accounting system is of two types, single entry accounting system and double entry accounting system. Majority of the business uses the double entry accounting system as it consists of dual effect i.e. two kinds of amount and accounts, debit and credit which affect each transaction.
Solution SA 6
_________ Account
|
Dr. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cr. |
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount (Rs.) |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 88
Solution SA 7
Short term liabilities- Liabilities incurred with an intention to be paid or are payable within a year is termed as short-term liabilities. For example, short-term loans, outstanding wages, bills payable and bank overdraft creditors.
Capital- It refers to the amount invested in the form of cash or asset by the owner in a firm's business or organisation of his choice. It is a claim on the assets of the business and also it will be an obligation of the business towards the owner of the firm. On the balance sheet, the capital is shown on the liabilities side.
Business owners and business are treated differently. In case of closure, the business has to repay the owner, the capital amount, as the capital is treated as a liability to the business. An increase in liability is credited, the fresh capital introduced and its net profit increases the owner's capital; the capital along with the liability is increased. Similarly, if the liabilities are paid off, the liability is debited and withdrawals from the capital and its net loss decrease the capital; so capital along with liabilities is debited. Thus, the rules of debit and credit are same for both liability and capital.
Solution SA 8
J.F. (Journal Folio) number is the journal's page number on which the transaction was recorded originally. The J.F. number is entered in the ledger at the time of posting entries into their respective accounts and not at the time of recording the transactions. It acts as a tracker to the original record.
The purpose of entering J.F. number in the ledger is because of the below given benefits:
- It helps in locating the original transaction records in the journal. In other words, J.F. number helps to locate the position of the related journal entry and subsidiary book in the journal book.
- J.F. number in accounts ensures that recording in the books of original entry has been posted or not.
Solution SA 9
-
Increase in revenue
Increase in revenue is credited as it increases the capital. Capital has credit balance and if capital increases, then it is credited.
-
Decrease in expense
Decrease in expense is credited as all expenses have debit balance. If expense decreases, then it is credited.
-
Record drawings
Capital has credit balance; if the capital increases, then it is credited. If capital decreases, then it is debited. Drawings are debited as they decrease the capital.
-
Record of fresh capital introduced by the owner- credit
Capital has credit balance, if capital increases, then it is credited. The introduction of fresh capital increases the balance of capital, and so, it is credited.
Solution SA 10
Assets have debit balance which when decreased is considered credited. Thus, a decrease is recorded as a credit, if the transaction has a decreasing effect on the asset.
For example, sale of books results in decrease in books (asset); so, the sale of books will be credited.
Liabilities have credit balance which is credited if the liability increase and is debited with a decrease in liability. Thus, a decrease is recorded as a debit if the transaction has a decreasing effect on the liability.
For example, payment to the creditors results in a decrease in the creditors (liability); so, the creditors account will be debited.
Solution NUM 1
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets = |
Liabilities + Capital |
||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Debtors+ |
Furniture |
Creditors |
+ Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
= NIL + |
2,00,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Stock |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(40,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,60,000 + |
40,000 |
|
|
= NIL + |
2,00,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Debtors |
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Profit |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
1,60,000 + |
30,000 + |
12,000 |
|
= NIL + |
2,02,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Furniture |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
1,60,000 + |
30,000 + |
12,000 + |
7,000 |
= 7,000 |
+ 2,02,000 |
Solution NUM 2
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= Liabilities + Capital |
|||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Furniture + |
Stock |
Creditors |
+ Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in cash |
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
= NIL + |
2,50,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Furniture |
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(35,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,15,000 + |
35,000 |
|
= NIL + |
2,50,000 |
|
c. |
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
(2,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(2000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,13,000 + |
35,000 |
|
= NIL + |
2,48,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Stock |
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
2,13,000 + |
35,000 |
+ 40,000 |
= 40,000 + |
2,48,000 |
|
e. |
Increase in Cash |
26,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
2,39,000 + |
35,000 |
+ 20,000 |
= 40,000 + |
2,54,000 |
Solution LA 1
Irrespective whether a business is small or big, there would be n-amount of financial transactions which would take place. A human mind cannot grasp this much amount of information. So in such instances, the source documents come in handy. A source document always enables verifiability and acts as evidence in court. They ensure that transactions recorded in the books are free from personal biases.
Source document in accounting is important because of the below given reasons.
- Systematic track of records
- Detect and prevent frauds and errors
- Alternative memory box
- Verifying the transaction during the auditing process
- Evidence in the count of law
Scenarios which are supported by source document are
- Return of goods purchased on credit worth Rs. 500, supported by debit note
- Deposits into bank worth Rs. 1000, supported by pay-in slips
- Purchase of goods worth Rs. 1000 on credit, supported by purchase invoice/bill
- Cash sales worth Rs. 2,000, supported by cash memo
The books of accounts only record events expressed in monetary terms and not the non-monetary events. For example, promotion of an employee is not recorded in the book but the salary increment is recorded at the time when salary is paid or due.
Solution LA 2
An accounting system is of two types, single entry accounting system and double entry accounting system. Majority of the business use the double entry accounting system as it consists of dual aspect. Double entry system is a complete system of recording transaction in the books of accounts. Each transaction reveals two aspects, receiving aspect or incoming aspect or expenses/loss aspect known as debit aspect and giving aspect or outgoing aspect or income/gain aspect known as credit aspect. The dual aspect can be better understood by the help of an example; bought goods worth Rs.1000 on cash. This transaction affects two accounts with the same amount simultaneously. As goods are brought in exchange of cash, the cash balances in the business reduce by Rs.1000 i.e. the cash account is credited. Simultaneously, the amount of goods increases by Rs.1000, so purchase account will be debited.
Debit and credit depend on the nature of accounts involved; such as assets, expenses, income, liabilities and capital. There are five types of accounts.
-
Assets- This increases the profit earning capacity of the business over a long-term across various accounting periods. Examples of fixed assets are furniture, machinery, land, plant and buildings.
For example, machinery purchased and payment is made by cheque. The journal entry is
Machinery A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
Here, machinery and bank balance, both are assets to the firm. As machinery is purchased, so machinery account will increase, and will be debited. On the other hand, payment of machinery is being made by cheque that reduces the bank balance of the business, so bank account will be credited.
-
Expense- It is the costs incurred to maintain the profitability of business in the process of earning profits. This help in the generating revenues, business operations and production such as rent, wages, depreciation, interest, salaries. They are measured by the services rendered or the cost of assets during an accounting period. For example, rent paid. The journal entry is:
Rent A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
Here, rent is an expense. All expenses have debit balance. Hence, rent is debited. On the other hand, as rent is paid in cash that reduces the cash balances, so cash account is credited.
-
Liability- Liabilities refer to the financial obligations or debt which a business owes to others such as loans from banks, other persons or creditors for goods supplied. Long term liabilities are loans which are payable after a period of 1 year. Short term liabilities are obligations which are payable within a period of time.
The journal entry is:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Bank Loan A/c
Here, loan from bank is a liability to the firm. As all liabilities have credit balance, so loan from bank has been credited because it increases the liabilities.
-
Income- It refers to the amount received from selling the products or providing services to customers, royalty and commission received; they are added to the capital.
For example, rent received from tenant. The journal entry is:
Cash A/c Dr.
To Rent A/c
Here, rent is an income; hence, rent account has been credited and cash has been debited, as rent received increases the cash balances.
-
Capital- It refers to the amount invested in form of cash or asset by the owner in a firm's business or organisation of his choice. It is a claim on the assets of the business and also it will be an obligation of the business towards the owner of the firm. On the balance sheet, the capital is shown on the liabilities side.
For example, additional capital introduced by owner. The journal entry is:
Cash A/c Dr.
To Capital A/c
The amount of capital increases i.e. credited when additional capital is introduced. On the other hand, the cash account is debited when the cash balances decrease i.e. capital introduced in form of cash.
Solution LA 3
In a business, recording each and every transaction is of utmost importance. Not doing so, can notably affect the financial status of the business.
A transaction is first recorded in the journal, the book of original entry. However, if the further details on expense, revenue, equity, liability or increase or decrease in assets are needed, an account is brought in use. A detailed record of the information relating to a financial transaction can be termed as an account. It helps in determining the financial position of the business.
There are some steps to record transactions in accounts; it can be easily understood with the help of an example.
Sold goods to Mr. X worth Rs. 40,000 on 12th April and received payment Rs. 40,000 on 25th April. The following journal entries will be recorded:
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
Apr. 12
Apr 25. |
X' A/c Dr To Sales (Goods sold on credit to Mr. X)
Cash A/c Dr To X's A/c (Cash received from Mr. X) |
22 18
13 22 |
40,000
40,000 |
40,000
40,000 |
Step 1- Locate the account in ledger, i.e. Mr. X's Account.
Step 2- Enter the date of transaction in the date column of the debit side of Mr. X's Account.
Step 3- In the 'Particulars' column of the debit side of Mr. X's Account, the name of corresponding account is to be written, i.e. 'Sales'.
Step 4- Enter the page number of the ledger in the Journal Folio (J.F.) column of Mr. X's Account.
Step 5- Enter the amount in the 'Amount' column.
Step 6- Same steps are to be followed to post entries in the credit side of Mr. X's Account.
Step 7- After entering all the transactions for a particular period, balance the account by totaling both sides and write the difference in shorter side, as 'Balance c/d'.
Step 8- Total of account is to be written on either sides.
Solution LA 4
Journal is known to be the book of original entry. Any financial transaction which takes place is recorded first in a journal so that they can be used for future references. The recording is done as and when a transaction occurs i.e. in a chronological order.
Performa of Journal
In the books of.....
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs. |
Credit Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date- Date of the transaction is entered in the first column. This date is entered only once unless and until there is a change in the date of transaction. It should be entered in proper sequence.
Particulars- Details of business transactions like, name of the parties involved and the name of related accounts, are recorded.
L.F. - Page number of ledger account when entry is posted.
Debit Amount- Amount of debit account is written.
Credit Amount- Amount of credit account is written.
Example:
|
Date |
Transactions by Mr. Ram |
|
April 01 |
Started business with cash Rs.1,13,000 |
|
April 06 |
Open a bank account Rs.40,000 |
|
April 12 |
Purchase goods for cash Rs.5,000 |
|
April 19 |
Goods sold for cash Rs.4,500 |
|
April 25 |
Goods sold to Mr. X Rs.3,400 |
Journal in the books of Mr. Ram
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr.(Rs.) |
|
2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr. 01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,13,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
1,13,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr.02 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
(Being bank account opened with cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr.12 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr.19 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,500 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
4,500 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr.25 |
Mr. X's A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,400 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
3,400 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Mr. X on credit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
1,62,900 |
1,62,900 |
|
Solution LA 5
|
Basis of Difference |
Source Documents |
Vouchers |
|
Meaning |
It refers to the documents in writing, containing the details of events or transactions |
When source document is considered as evidence of an event or transaction, then it is called voucher |
|
Purpose |
It is used for preparing accounting vouchers |
It is used for analysing the transactions |
|
Recording |
It acts as a basis for preparing accounting voucher which helps in recording |
It acts as a basis for recording transactions |
|
Legality/Validity |
It can be used as evidence in the court of law |
It can be used for authenticating transactions |
|
Prepared By |
It is prepared by the those directly involved in the transactions or who are authorised to prepare or approve these documents |
It is prepared by the authorised persons or by the accountants |
|
Examples |
Cash memo, invoice, and pay-in-slip |
Cash memo, invoice, pay-in-slip (if used as evidence), debit note, credit note, cash vouchers, transfer vouchers |
Solution LA 6
Majority of the business prefers the double entry accounting system i.e. the dual aspect concept over single entry system as it consists of dual effect i.e. two kinds of amount, debit and credit which affects each transaction. It is based on the fact that if there is receiver, there should be a giver. However, at any point of time, the assets of a business entity will always be equal to the total of its liabilities and capital i.e. total claims.
The equation between the assets and claims can be read as follows:
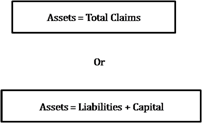
or Liabilities = Asset - Capital
or Capital = Assets - Liabilities
The equation can also be represented as:
Assets - Liabilities = Capital
Assets - Capital = Liabilities
The above equation cannot be altered. For example,
1. Business started with cash Rs.1,00,000
Cash A/c Dr
To Capital A/c
|
Assets |
= |
Liabilities |
+ |
Capital |
|
Cash (1,00,000) |
|
|
|
1,00,000 |
Assets decrease, as cash is invested into the business and capital increases. Thus the equality between LHS and RHS remains intact.
2. Goods purchased on credit Rs.20, 000
|
Assets |
= |
Liabilities |
+ |
Capital |
|
|
Cash
1,00,000 |
Stock
20,000 |
= |
Creditors
20,000 |
+ |
1,00,000 |
Assets increase as well as liability increases, without disturbing the equality.
3. Goods purchased with cash Rs.25,000
|
Assets |
= |
Liabilities |
+ |
Capital |
|
|
Cash 1,00,000 (25,000) |
Stock 20,000 25,000 |
= |
20,000 |
+ |
1,00,000 |
As goods are purchased for cash, so cash balance reduces by Rs.25,000, but on the other hand, stock balance increases by Rs.25,000. Thus the total balance of LHS remains equal to the total claims.
Solution LA 7
Majority of the business prefers the double entry accounting system i.e. the dual aspect concept over single entry system as it consists of dual effect i.e. two kinds of amount, debit and credit which affects each transaction. It is based on the fact that if there is receiver, there should be a giver.
If a business firm acquires an asset for cash, it has to give some other asset say cash or the obligation to pay for it in future. Thus, giver necessarily implies a receiver and a receiver necessarily implies a giver.
In double entry system, accounts are classified as shown below:
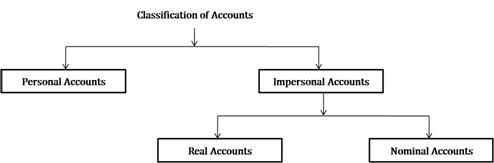
-
Personal Accounts: Accounting transactions relating to persons such as individuals, firms, bank and companies are known as personal accounts, such as Mr. A, M/s ABC and Co. etc.
Rule of double entry system for personal accounts: Debit the receiver and credit the giver.
For example: Cash paid to Mr. A.
Mr. A's A/c
Dr.
To Cash A/c
(Being cash paid to Mr. A)
-
Impersonal Accounts: It relates to non living things. Impersonal accounts are further classified as real accounts and nominal accounts.
-
Real Account- Accounting transactions relating to tangible assets such as properties, goods and cash and intangible assets such as patents and trademark are known as real accounts.
Rule of double entry system for real accounts: Debit what comes in and credit what goes out.
For example: Furniture purchased for cash.
Furniture A/c
Dr.
To Cash A/c
(Being furniture purchased for cash)
-
Nominal Account: Accounting transactions relating to incomes and expenses and gains and losses of the firm are known as nominal accounts.
Rule of double entry system for nominal accounts:Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains.
For example : Rent paid
Rent A/c
Dr.
To Cash A/c
(Being rent paid)
-
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 89
Solution NUM 3
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
=Liabilities + Capital |
||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Debtors |
Furniture |
Creditors |
+ Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
1,75,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
1,75,000 |
|
|
|
1,75,000 |
|
|
|
= NIL + |
1,75,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Stock |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors (Rohit) |
|
|
|
|
= 50,000+ |
1,75,000 |
|
|
|
1,75,000 + |
50,000 |
|
|
= 50,000 + |
1,75,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Debtors (Manish) |
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(17,500) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
1,75,000 + |
32,500 + |
20,000 |
|
= 50,000 + |
1,77,500 |
|
d. |
Increase in Furniture |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,65,000 + |
32,500 + |
20,000 + |
10,000 |
=50,000 + |
1,77,500 |
|
e. |
Decrease in Creditors (Rohit) |
|
|
|
|
(50,000) |
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(48,500) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Discount received) |
|
|
|
|
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
1,16,500 + |
32500 + |
20,000 + |
10,000 |
=NIL + |
1,79,000 |
|
f. |
Increase in Cash |
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Debtors (Manish) |
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,36,500 + |
32500 + |
NIL + |
10,000 |
=NIL + |
1,79,000 |
|
g. |
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
(1,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(1,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,35,500 + |
32500 + |
NIL + |
10,000 |
=NIL + |
1,78,000 |
|
h. |
Decrease in Capital (Drawings) |
|
|
|
|
|
(3,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(3,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,32,500 + |
32500 + |
NIL + |
10,000 |
=NIL + |
1,75,000 |
Solution NUM 4
|
S.No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
|||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Machinery + |
Stock |
|
Creditors + |
Unaccured Income |
+ |
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
1,50,000 |
|
|
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
1,50,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Machinery |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
= |
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,50,000+ |
40,000 |
|
= |
40,000 |
|
|
1,50,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Stock |
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,30,000 + |
40,000 + |
20,000 |
= |
40,000 |
|
+ |
1,50,000 |
|
d. |
Decrease in Cash |
(80,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Drawings) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(80,000) |
|
|
|
50,000 + |
40,000 |
+20,000 |
= |
40,000 |
|
+ |
70,000 |
|
e. |
Decrease in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
(40,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(38,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Discount received) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
12,000 + |
40,000 + |
20,000 |
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
72,000 |
|
f. |
Increase in Cash |
4,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
|
(5000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(500) |
|
|
|
16,500 + |
40,000 + |
15,000 |
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
71,500 |
|
g. |
Decrease in Cash |
(1000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1000) |
|
|
|
15,500 + |
40,000 + |
15,000 |
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
70,500 |
|
h. |
Increase in Cash |
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Unaccrued Income |
|
|
|
= |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
17,500 |
40,000 |
15,000 |
= |
NIL |
2,000 |
+ |
70,500 |
Solution NUM 5
|
S.No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Prepaid Expenses |
= |
Outstanding Expenses |
+ |
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in cash |
1,20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,20,000 |
|
|
|
1,20,000 |
|
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,20,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in stock |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in cash |
(10,000) |
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,10,000 + |
10,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,20,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in cash |
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
1,15,000 + |
10,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,25,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in outstanding expenses |
|
|
|
= |
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
Decrease in capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2,000) |
|
|
|
1,15,000 + |
10,000 |
|
= |
2,000 |
+ |
1,23,000 |
|
e. |
Increase in prepaid expenses |
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in cash |
(1,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,14,000 + |
10,000 |
+ 1,000 |
= |
2,000 |
+ |
1,23,000 |
|
f. |
Increase in cash |
700 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
700 |
|
|
|
1,14,700 + |
10,000 |
+ 1000 |
= |
2,000 |
+ |
1,23,700 |
|
g. |
Increase in cash |
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in stock |
|
(5,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
1,21,700+ |
5,000 + |
+ 1000 |
= |
2000 |
+ |
1,25,700 |
|
h. |
Decrease in stock |
|
(500) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in capital (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(500) |
|
|
|
1,21,700+ |
4500 + |
1000 |
= |
2000 |
+ |
1,25,200 |
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 90
Solution NUM 6
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
|||||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Building + |
Debtors |
|
Creditors + |
Outstanding Exp + |
Unaccured Income + |
|
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
5,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Stock |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,00,000 |
|
|
|
5,00,000+ |
1,00,000 |
|
|
= |
NIL |
|
|
+ |
6,00,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Building |
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(2,00,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,00,000+ |
1,00,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
|
|
+ |
6,00,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Stock |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,00000+ |
1,50,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
= |
50,000 |
|
|
+ |
6,00,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Debtors |
|
|
|
36,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(25,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,000 |
|
|
|
3,00,000+ |
1,25,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
50,000 + |
|
|
+ |
6,11,000 |
|
e. |
Decrease in Cash |
(3000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3000) |
|
|
|
2,97,000+ |
1,25,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
50,000 + |
|
|
+ |
6,08,000 |
|
f. |
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5,000) |
|
|
|
2,97,000+ |
1,25,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
50,000 + |
5,000 |
|
|
6,03,000 |
|
g. |
Decrease in Building |
|
|
(8,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8,000) |
|
|
|
2,97,000+ |
1,25,000 + |
1,92,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
50,000 + |
5,000 |
|
+ |
5,95,000 |
|
h. |
Decrease in Cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
2,77,000+ |
1,25,000 + |
1,92,000 + |
36000 |
= |
50,000 + |
5,000 |
|
+ |
5,75,000 |
|
i. |
Increase in Cash |
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,82,000 + |
1,25,000 + |
1,92,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
50,000 + |
5,000 + |
5,000 |
+ |
5,75,000 |
|
j. |
Decrease in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,62,000 + |
1,25,000 + |
1,92,000 + |
36,000 |
= |
30,000 + |
5,000 + |
5,000 |
+ |
5,75,000 |
|
k. |
Increase in Cash |
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Debtors |
|
|
|
(30,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,92,000 + |
1,25,000 + |
1,92,000 + |
6,000 |
= |
30,000 + |
5,000 + |
5,000 |
+ |
5,75,000 |
Solution NUM 7
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
|||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Investment + |
Bank |
|
Creditors |
+ |
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
1,20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,20,000 |
|
|
|
1,20,000 + |
|
|
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,20,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Cash |
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
1,30,000 |
|
|
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,30,000 |
|
c. |
Decrease in Investment |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80,000 + |
|
50,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,30,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Cash |
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
85,000+ |
|
50,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,35,000 |
|
e. |
Increase in Stock |
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditor (Ragani) |
|
|
|
|
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
85,000 + |
35,000 + |
50,000 |
|
= |
35,000 |
+ |
1,35,000 |
|
f. |
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(7,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78,000 + |
35,000 + |
50,000 |
|
= |
35,000 |
+ |
1,28,000 |
|
g. |
Increase in Cash |
14,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
92,000+ |
25,000 + |
50,000 |
|
= |
35,000 |
+ |
1,32,000 |
|
h. |
Decrease in Creditors (Ragani) |
|
|
|
|
|
(35,000) |
|
|
|
|
Decrease in cash |
(35,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57,000+ |
25,000 + |
50,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,32,000 |
|
i. |
Decrease in cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in bank |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37,000 + |
25,000 + |
50,000 + |
20,000 |
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,32,000 |
Solution NUM 8
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
|||||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Building + |
Debtors + |
Prepaid Expenses |
|
Creditors + |
Outstanding Expenses |
+ |
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash, Stock and Building |
2,30,000 + |
1,00,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,30,000 |
|
|
|
2,30,000 + |
1,00,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
|
= |
|
|
+ |
5,30,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Stock |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,80,000 + |
1,50,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
|
= |
|
|
+ |
5,30,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Cash |
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in stock |
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
2,15,000 + |
1,30,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,45,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Stock |
|
55,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
= |
55,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,15,000 + |
1,85,000 + |
2,00,000 |
|
|
= |
55,000 |
|
+ |
5,53,000 |
|
e. |
Increase in Debtors |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(52,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
2,15,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000+ |
60,000 |
|
= |
55,000 |
|
+ |
5,53,000 |
|
f. |
Decrease in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(55,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(53,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Discount received) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
1,62,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
60,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
5,55,000 |
|
g. |
Decrease in Cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
|
1,42,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
60,000 |
|
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
5,35,000 |
|
h. |
Increase in Cash |
59,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Discount allowed) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1000) |
|
|
Decrease in Debtors |
|
|
|
(60,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,01,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
NIL |
|
= |
NIL |
|
+ |
5,34,000 |
|
i. |
Increase in Outstanding Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Capital (Expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3,000) |
|
|
|
2,01,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000 + |
NIL |
|
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,31,000 |
|
j. |
Decrease in Prepaid Expense |
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(2,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,99,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
200,000 + |
NIL + |
2,000 |
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,31,000 |
|
k. |
Increase in Cash |
13,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13,000 |
|
|
|
2,12,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000+ |
NIL + |
2000 |
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,44,000 |
|
l. |
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(20,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(20,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,92,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
2,00,000+ |
NIL + |
2000 |
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,24,000 |
|
m. |
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(10,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Building |
|
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,92,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
1,90,000+ |
NIL+ |
2000 |
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,14,000 |
|
n. |
Increase in Cash |
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
2,42,000 + |
1,33,000 + |
1,90,000+ |
NIL + |
2000 |
= |
NIL + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,64,000 |
|
o. |
Increase in Stock |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,42,000 + |
1,43,000 + |
1,90,000+ |
NIL+ |
2000 |
= |
10,000 + |
3,000 |
+ |
5,64,000 |
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 91
Solution NUM 9
|
S. No |
Explanation |
Assets |
= |
Liabilities + Capital |
|||||
|
|
|
Cash + |
Stock + |
Furniture + |
Debtors + |
|
Creditors |
+ |
Capital |
|
a. |
Increase in Cash |
1,25,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,25,000 |
|
|
|
1,25,000 + |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
1,25,000 |
|
b. |
Increase in Stock |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(50,000) |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
75,000 + |
50,000 |
|
|
= |
|
|
1,25,000 |
|
c. |
Increase in Furniture |
|
|
10,000 |
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
= |
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
75,000+ |
50,000 |
10,000 |
|
= |
10,000 |
+ |
1,25,000 |
|
d. |
Increase in Debtors |
|
|
|
9,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(7000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
75,000+ |
43,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
10,000 |
+ |
1,27,000 |
|
e. |
Decrease in Capital (Cartage Expenses) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(100) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(100) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
74,900 + |
43,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
10,000 |
+ |
1,26,900 |
|
f. |
Decrease in Creditors |
|
|
|
|
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(9,700) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Discount - received) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
65,200 + |
43,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,27,200 |
|
g. |
Increase in Cash |
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in Stock |
|
(10,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
77,200 + |
33,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,29,200 |
|
h. |
Increase in Cash |
4,000 + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in Capital (Income) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
81,200 + |
33,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,33,200 |
|
i. |
Decrease in Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3,000) |
|
|
Decrease in Cash |
(3,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78,200 + |
33,000 + |
10,000 + |
9,000 |
= |
NIL |
+ |
1,30,200 |
Solution NUM 10
a. The transaction (a) increases assets by Rs.5,50,000 (cash Rs.4,00,000 and office equipment Rs.1,5,000) it will be debited and on the other hand it will increase the capital by Rs. 5,50,000, so it will be credited in capital account.
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
|
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 |
|
|
Office Equipment Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
|
|
(a) Rs.1,50,000 |
|
|
Capital Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (a) Rs.1,50,000 |
|
|
|
b. Purchase of land and small office building are assets. On one hand, the purchase of these items will increase their individual accounts and this will increase the total amount of the assets in the business; so, both the accounts will be debited. On the other hand, payment in cash on the purchase of these assets will decrease the cash balance, so cash account will be credited to the extent of amount paid. After payment for building in cash, the balance of building account will be transferred to creditors for building account. This will increase the amount of the creditors, which in turn will increase the total liabilities of the business. Long term payables are regarded as loan to the business that will increase both cash balance (due to loan taken) as well as liabilities of the business.
|
Land Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(b) Rs.1,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Building Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(b) Rs.3,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 |
(b) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 |
|
|
|
|
Long Term Payable Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(b) Rs.8,00,000 |
|
|
|
c. Payment for 'office supplies' is an expense. So, it will be debited on one hand while on the other hand, office supplies has been purchased on credit, so it will increase the liability and the supplier's account will be credited.
|
Office Supplies Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(c) Rs.12000 |
|
|
Supplier's Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(c) Rs. 12000 |
d. Amount invested (motor car) by the proprietor in the business would increase both the capital and assets.
|
Motor Car Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(d) Rs.90,000 |
|
|
Capital Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 |
|
|
(a) Rs.1,50,000 |
|
|
(d) Rs.90,000 |
e. Purchase of additional equipments increases the assets, hence, office equipments account will be debited. Further as the office equipments was purchased on credit, it increases the amount of the creditors for office equipments and the creditors account will be credited.
|
Office Equipment Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.30,000 |
|
|
Creditors for Office Equipment Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(e) Rs.30,000 |
f. Salary is an expense and it will be debited. Payment of salary to the manager will be debited to the salary account. And on the other hand the payment of the salary in cash decreases the cash balance (Assets), so the cash account would be credited.
|
Salary Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(f) Rs.7,500 |
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 |
(b) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 |
g. Amount received is income for the business. All revenues are to be credited, so client service account will be credited. On the other hand, cash received in exchange of services would increase the cash balance. It would be debited to the cash account.
|
Client Services Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(g) Rs.30,000 |
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 |
(b) Rs. 1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500
|
h. All expenses are to be debited. Amount paid for utilities would be debited to utilities account. Utilities have been paid in cash so the cash account will be credited (as this decreases assets).
|
Utilities Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(h) Rs.4,000 |
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 |
(b) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 (h) Rs.4,000
|
i. Payment to the supplier (creditors) will be debited. It results in the decrease in liabilities. Further as the payment has been made in cash, so it results in decrease in the cash balance (assets) and hence the cash account will be credited.
|
Supplier's Account (Creditors) |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(h) Rs.12,000 |
(c) Rs.12,000 |
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 |
(b) Rs. 1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 (h) Rs.4,000 (i) Rs.12,000
|
j. Purchase of the equipments will be debited in the Equipment Account (as there is increase in the assets).
|
Office Equipments Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.30,000 (g) Rs.1,00,000 |
(b) Rs.7,000
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 |
(b) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 (h) Rs.4,000 (i) Rs.12,000 (j) Rs.93,000 |
k. Receipt from 'Client services' is revenue. The client services account will be credited and client is considered as debtors, so the client account will be debited.
|
Client Services Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
|
(g) Rs.30,000 (k) Rs.26,000
|
|
Client Account (Debtors) |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(k) Rs.26,000 |
|
l. The client has been considered as Debtors. The amount received from the client will lead to the decrease in the debtors balance and the client account will be credited. Receipts from the client will increase the cash balance (asset) and hence the cash account will be debited.
|
Client Account (Debtors) |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(k) Rs.26,000 |
(f) Rs.19,000
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 (l) Rs.19,000 |
(b) Rs. 1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 (h) Rs.4,000 (i) Rs.12,000 (j) Rs.93,000
|
m. The amount withdrawn by the proprietor is considered as 'drawings'. Drawings account will be debited (as decrease in capital is debited). On the other hand as drawings have been made in cash, decrease in cash means cash account will be credited with the amount of drawings.
|
Drawings Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(m) Rs.20,000 |
|
|
Cash Account |
|
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|
(a) Rs.4,00,000 (b) Rs.8,00,000 (g) Rs.30,000 (l) Rs.19,000 |
(b) Rs.1,50,000 (b) Rs.50,000 (f) Rs.7,500 (h) Rs.4,000 (i) Rs.12,000 (j) Rs.93,000 (m) Rs.20,000
|
T - Accounts
Capital Accounts
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) (a) (d) |
Cash Office Equipment Motor Car |
|
4,00,000 1,50,000 90,000 |
|
Office Equipments Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(a) (e)
(j) |
Capital Creditors for office equipment Cash (1,00,000 - 7,000) |
|
1,50,000 30,000 93,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(a) (b) (g) (i) |
Capital Long term payable Client Services Client |
|
4,00,000 8,00,000 30,000 19,000
|
(b) (b) (f) (h) (i) (j) (m)
|
Land Building Salaries Utilities Suppliers Office Equipments Drawings |
|
1,50,000 50,000 7,500 4,000 12,000 93,000 20,000 |
|
Land Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(b) |
Cash |
|
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Building Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(b) (b) |
Cash Creditors for Building |
|
50,000 3,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Office Supplies Account (Expense)
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(c) |
Supplier |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Motor Car Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(d) |
Capital |
|
90,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Supplier's Account (Creditors)
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(i) |
Cash |
|
12,000 |
(c) |
Office supplies |
|
12,000 |
|
Creditors for Office Equipment
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(e) |
Office equipment |
|
30,000 |
|
Salaries Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(i) |
Cash |
|
7,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Client Services Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(g) (k) |
Cash Client |
|
30,000 26,000 |
|
Utilities Account (Expenses)
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(h) |
Cash |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Client Accounts (Debtors)
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(k) |
Client Services |
|
26,000 |
(l) |
Cash |
|
19,000 |
|
Drawings Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
(m) |
Cash |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Long Term Payable Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Cash |
|
8,00,000 |
|
Creditors For Building Account
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
S.No |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Building |
|
3,00,000 |
|
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 92
Solution NUM 11
Books of Himanshu
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
(Being started business with cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.07 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.09 |
Swati A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold on credit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.12 |
Furniture A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being furniture purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.18 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales a/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Swati and discount Allowed)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.25 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
To Cash a/c |
|
|
|
1,500 |
|
|
(Being salary paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
1,00,500 |
1,00,500 |
Solution NUM 12
Books of Mudit
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
Building A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,75,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
2,75,000 |
|
|
(Being commenced with cash and building)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.02 |
Purchase A/c |
Dr. |
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.03 |
Ramesh A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To sales A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Ramesh)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
Wages A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
(Being wages paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.06 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.10 |
Trade Expenses A/c |
Dr. |
|
700 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
700 |
|
|
(Being trade expenses paid in cash) |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.12 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
29,500 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Ramesh A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Ramesh and discount allowed to him)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.14 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
27,000 |
|
|
|
To Sudhir |
|
|
|
27,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Sudhir on credit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.18 |
Cartage A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being cartage paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.20 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being cash drawn for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods drawn for business for households use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.25 |
Sudhir A/c |
Dr. |
|
27,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
26,700 |
|
|
To Discount Received A/c |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
(Being cash paid to Sudhir and discount received) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
4,83,200 |
4,83,200 |
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 93
Solution NUM 13
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.02 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being bank account opened with SBI)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.04 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Ashu A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Ashu)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.06 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.10 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.13 |
Suman A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Suman)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.16 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
19,500 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Suman A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Suman and discount allowed)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.20 |
Ashu A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque given to Ashu)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.22 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid by cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.23 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
16,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
16,000 |
|
|
(Being cash deposited into bank)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.25 |
Machinery A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Parigya A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being machinery purchased from Parigya)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.26 |
Trade Expenses A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being trade expenses paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
Parigya A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque issued to Parigya)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.29 |
Telephone expense A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
1,200 |
|
|
(Being telephone expenses paid by cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,500 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
4,500 |
|
|
(Being salary paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
3,00,700 |
3,00,700 |
Solution NUM 14
Books of Harpreet bros
Journal
|
S.No |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Bad debts A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Rohit A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being due from Rohit became bad debts)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c) |
Depreciation A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Machinery A/c |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
(Being depreciation charged on machinery for two months)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) |
Interest on Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,750 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
6,750 |
|
|
(Being interest on capital at 6% due for 9 months)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(e) |
Bad debts A/c |
Dr. |
|
800 |
|
|
|
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
To Rahul's A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being received from Rahul 60 paise in a rupee and rest amount considered as bad debt)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
12,250 |
12,250 |
Solution NUM 15
Journal
|
S.No |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Machinery A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
(Being cash paid for installation of machinery)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Charity A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods given as charity)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c) |
Interest on capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,900 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
4,900 |
|
|
(Being interest on capital charged @ 7% p.a.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
To Bad Debt Recovered A/c |
|
|
|
1,200 |
|
|
(Being cash received on from debtors which was previously written off as bad)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(e) |
Loss by Fire A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods destroyed by fire)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(f) |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Rent Outstanding A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being rent due but not paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(g) |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
900 |
|
|
|
To Interest on Drawings A/c |
|
|
|
900 |
|
|
(Being interest allowed on drawings)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(h) |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,350 |
|
|
|
Bad debts A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,650 |
|
|
|
To Sudhir Kumar |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being Sudhir kumar declared insolvent and cash received from him 45 paise in a rupee in full settlement)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(i) |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
To Commission received in Advance |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
(Being commission received in advance) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
22,500 |
22,500 |
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 94
Solution NUM 16
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
Stock A/c |
Dr. |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash and goods)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.03 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Harish A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Harish)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.05 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.08 |
Furniture A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being furniture purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.10 |
Harish A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
(Being cash paid to Harish)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.13 |
Sundry Expenses A/c |
Dr. |
|
200 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
(Being sundry expenses paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.15 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.18 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being cash deposited into Bank)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.20 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being cash withdrawn for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.22 |
Harish A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
14,700 |
|
|
To Discount Received A/c |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
(Being full payment made to Harish and discount received)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.25 |
Nitesh A/c |
Dr. |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Nitesh)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.26 |
Cartage A/c |
Dr. |
|
200 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
(Being cartage paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.27 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,500 |
|
|
(Being rent paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.29 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,800 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed A/c |
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
To Nitesh A/c |
|
|
|
7000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Nitesh and discount allowed)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being salary paid) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
3,16,900 |
3,16,900 |
Ledger
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.01 |
To Capital |
|
1,50,000 |
Nov.08 |
By Furniture |
|
5,000 |
|
|
Nov.05 |
To Sales |
|
12,000 |
Nov.10 |
By Harish |
|
15,000 |
|
|
Nov.15 |
To Sales |
|
15,000 |
Nov.13 |
By Sundry Expenses |
|
200 |
|
|
Nov.29 |
To Nitesh |
|
6,800 |
Nov.18 |
By Bank |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.20 |
By Drawings |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.22 |
By Harish |
|
14,700 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.26 |
By Cartage |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.27 |
By Rent |
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
By Salaries |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,38,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,83,800 |
|
|
|
1,83,800 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,38,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
To Balance c/d |
|
2,00,000 |
Nov.01 |
By Cash |
|
1,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.01 |
By Stock |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
2,00,000 |
|
Stock A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.01 |
To Capital |
|
50,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
Cartage A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.26 |
To Cash |
|
200 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rent A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.27 |
To Cash |
|
1,500 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
1,500 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
To Cash |
|
3,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.08 |
To Cash |
|
5,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nitesh's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.25 |
To Sales |
|
7,000 |
Nov.29 |
By Cash |
|
6,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.29 |
By Discount Allowed |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
To Balance c/d |
|
34,000 |
Nov.05 |
By Cash |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.15 |
By Cash |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.25 |
By Nitesh |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
34,000 |
|
|
|
34,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
34,000 |
|
Purchases A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.03 |
To Harish |
|
30,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Harish's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.10 |
To Cash |
|
15,000 |
Nov.03 |
By Purchases |
|
30,000 |
|
|
Nov.22 |
To Cash |
|
14,700 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.22 |
To Discount Received |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
Sundry Expenses A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.13 |
To Cash |
|
200 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.18 |
To Cash |
|
5,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Drawings A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.20 |
To Cash |
|
1,000 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Discount Received A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.30 |
To Balance c/d |
|
300 |
Nov.22 |
By Harish |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
300 |
|
Discount Allowed A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nov.29 |
To Nitesh |
|
200 |
Nov.30 |
By Balance c/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Solution NUM 17
Books of M/s Goel Brothers
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,65,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
1,65,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash )
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.02 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
80,000 |
|
|
(Being account opened with PNB)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
Purchase A/c |
Dr. |
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
To Tara's A/c |
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Tara)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.05 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.08 |
Naman's A/c |
Dr. |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being sale of goods to Naman)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.10 |
Tara's A/c |
Dr. |
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
|
(Being cash paid to Tara)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.15 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
11,700 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed A/c |
Dr. |
|
300 |
|
|
|
To Naman's A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Naman and discount allowed)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.16 |
Wages A/c |
Dr. |
|
200 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
(Being wages paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.18 |
Furniture A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being furniture purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.20 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
(Being cash drawn from Bank for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid through cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.23 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods drawn for household purpose)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.24 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
(Being cash withdrawn from bank)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.26 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Commision A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being commission received)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.27 |
Bank Charges A/c |
Dr. |
|
200 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
(Being bank charged paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.28 |
Insurance Premium A/c |
Dr |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being insurance premium paid through cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.29 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
(Being salary paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.30 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
3,84,400 |
3,84,400 |
Ledger
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Capital |
|
1,65,000 |
Jan.02 |
By Bank |
|
80,000 |
|
|
Jan.15 |
To Naman |
|
11,700 |
Jan.05 |
By Purchases |
|
30,000 |
|
|
Jan.24 |
To Bank |
|
6,000 |
Jan.10 |
By Tara |
|
22,000 |
|
|
Jan.26 |
To Commission |
|
1,000 |
Jan.16 |
By Wages |
|
200 |
|
|
Jan.30 |
To Sales |
|
10,000 |
Jan.18 |
By Furniture |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.29 |
By Salaries |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
49,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,93,700 |
|
|
|
1,93,700 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
49,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
1,65,000 |
Jan.01 |
By Cash |
|
1,65,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,65,000 |
|
|
|
1,65,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,65,000 |
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.02 |
To Cash |
|
80,000 |
Jan.20 |
By Drawings |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
By Rent |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.24 |
By Cash |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.27 |
By Bank charges |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.28 |
By Insurance Premium |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
63,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
80,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
63,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
Tara's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.10 |
To Cash |
|
22,000 |
Jan.04 |
By Purchases |
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
Purchases A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
To Tara |
|
22,000 |
Jan.23 |
By Purchases |
|
2,000 |
|
|
Jan.05 |
To Cash |
|
30,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
52,000 |
|
|
|
52,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
22,000 |
Jan.08 |
By Naman |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.30 |
By Cash |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
22,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
22,000 |
|
Naman's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.08 |
To Sales |
|
12,000 |
Jan.15 |
By Cash |
|
11,700 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.15 |
By Discount Allowed |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
Discount Allowed A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.15 |
To Naman |
|
300 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
Wages A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.16 |
To Cash |
|
200 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.18 |
To Cash |
|
5,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Drawings A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.20 |
To Cash |
|
4,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
6,000 |
|
|
Jan.23 |
To Purchases |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rent A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
To Bank |
|
3000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3000 |
|
|
|
3000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Commission A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
1,000 |
Jan.26 |
By Cash |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
Bank Charges A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.27 |
To Bank |
|
200 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Insurance Premium A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.28 |
To Bank |
|
3,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.29 |
To Cash |
|
7,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 95
Solution NUM 18
Books of M/s. Mohit Traders
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug .01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,10,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
1,10,000 |
|
|
(Being business commenced with cash )
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.02 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
(Being account opened with H.D.F.C)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.03 |
Furniture A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being Furniture purchased)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.07 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.08 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
42,000 |
|
|
|
To M/s Hema Trader A/c |
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from M/s Hema Trader)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.10 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.14 |
M/s Gupta Trader A/c |
Dr. |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to M/s Gupta traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.16 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.18 |
Trade Expenses A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being trade expenses paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.20 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
To M/s. Gupta Traders A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from M/s Gupta traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.22 |
M/s. Hema TraderA/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchase Return A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods returned to Hema Traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.23 |
M/s Hema Traders A/c |
Dr. |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
(Being cash paid to Hema traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.25 |
Postage Stamps A/c |
Dr. |
|
100 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
(Being postage stamps purchased)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.30 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
(Being Salaries paid in cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
3,57,100 |
3,57,100 |
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.01 |
To Capital |
|
1,10,000 |
Aug.02 |
By Bank |
|
50,000 |
|
|
Aug.10 |
To Sales |
|
30,000 |
Aug.03 |
By Furniture |
|
20,000 |
|
|
Aug.20 |
To M/s. Gupta Traders |
|
12,000 |
Aug.07 |
By Purchases |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.16 |
By Rent |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.18 |
By Trade Expenses |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.23 |
By M/s Hema Traders |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.25 |
By Postage Stamps |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.30 |
By Salaries |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,900 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,52,000 |
|
|
|
1,52,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,900 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
1,10,000 |
Aug.01 |
By Cash |
|
1,10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,10,000 |
|
|
|
1,10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sept.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,10,000 |
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.02 |
To Cash |
|
50,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.03 |
To Cash |
|
20,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.07 |
To Cash |
|
30,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
72,000 |
|
|
Aug.08 |
To M/s. Hema Traders |
|
42,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
72,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
M/s Hema Traders A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.22 |
To Purchase Return |
|
2,000 |
Aug.08 |
By Purchases |
|
42,000 |
|
|
Aug.23 |
To Cash |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
42,000 |
Aug.10 |
By Cash |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.14 |
By M/s Gupta Traders |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
|
|
42,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sept.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
42,000 |
|
M/s Gupta Traders A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.14 |
To Sales |
|
12,000 |
Aug.20 |
By Cash |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
Rent A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.16 |
To Cash |
|
4,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Trade Expenses A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.18 |
To Cash |
|
1,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
Aug.22 |
By M/s. Hema Traders |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sept.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
Postage Stamps A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.25 |
To Cash |
|
100 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Aug.30 |
To Cash |
|
4,000 |
Aug.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
Sept.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Solution NUM 19
Books of M/s. Bhanu Traders
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec .01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
92,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
92,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash )
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.02 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
(Being cash deposited into Bank)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.04 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
To Himani A/c |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
(Being furniture purchased)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.06 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.08 |
Himani A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchase Return A/c |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
(Being goods returned to Himani)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.10 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.14 |
Himani A/c |
Dr. |
|
36,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
36,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque given to Himani)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.17 |
M/s Goyal Traders A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,50,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
3,50,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to M/s Goyal Traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.19 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being cash withdrawn from Bank for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.21 |
Sales Return A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,500 |
|
|
|
To M/s. Goyal Traders A/c |
|
|
|
3,500 |
|
|
(Being goods returned to M/s Goyal Traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.22 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being cash deposited into Bank)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.26 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
31,500 |
|
|
|
To M/s Goyal Traders A/c |
|
|
|
31,500 |
|
|
(Being cheque received from M/s Goyal Traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
Charity A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods given as charity)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.29 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
(Being salaries paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
Office Machine A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being office machinery purchased)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
6,94,000 |
6,94,000 |
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
r.Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Capital |
|
92,000 |
Dec.02 |
By Bank |
|
60,000 |
|
|
Dec.10 |
To Sales |
|
20,000 |
Dec.06 |
By Purchases |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.22 |
By Bank |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
By Salaries |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
By Office machine |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,12,000 |
|
|
|
1,12,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
92,000 |
Dec.01 |
By Cash |
|
92,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
92,000 |
|
|
|
92,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
92,000 |
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.02 |
To Cash |
|
60,000 |
Dec.14 |
By Himani |
|
36,000 |
|
|
Dec.22 |
To Cash |
|
20,000 |
Dec.19 |
By Drawings |
|
2,000 |
|
|
Dec.26 |
To Goyal Traders |
|
31,500 |
Dec.29 |
By Rent |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
70,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,11,500 |
|
|
|
1,11,500 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
70,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Note: For transaction on December 29, 2017, it has been assumed that the rent of Rs.3,000 is paid through cheque. If instead the rent would have been paid in cash, the cash account would have shown a credit (negative) balance and that is logically not correct.
Purchase A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.04 |
To Himani |
|
40,000 |
Dec.28 |
By Charity |
|
2,000 |
|
|
Dec.06 |
To Cash |
|
20,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
58,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
58,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Himani's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.08 |
To Purchase Return |
|
40,00 |
Dec.04 |
By Purchases |
|
40,000 |
|
|
Dec.14 |
To Bank |
|
36,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
55,000 |
Dec.10 |
By Cash |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.17 |
By M/s Goyal Traders |
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
55,000 |
|
|
|
55,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
55,000 |
|
M/s Goyal Traders A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.17 |
To Sales |
|
35,000 |
Dec.21 |
By Sales Return |
|
3,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.26 |
By Bank |
|
31,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
35,000 |
|
Purchases Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
4,000 |
Dec.08 |
By Himani |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
4,000 |
|
Drawings A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.19 |
To Bank |
|
2,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sales Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.21 |
To M/s. Goyal Traders |
|
3,500 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,500 |
|
|
|
3,500 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Charity A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
To Purchases |
|
2000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rent A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.29 |
To Cash |
|
3,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
To Cash |
|
7,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Office Machine A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
||
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
||
|
Dec.31 |
To Cash |
|
3,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
||
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
||
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
||
Recording of Transactions - I Exercise 96
Solution NUM 20
Books of Beauti Traders
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec .01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
(Being business started with cash )
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.02 |
Office Furniture A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being office furniture purchased)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.03 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
(Being opened a current account)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.05 |
Computer A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,50,,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
2,50,,000 |
|
|
(Being computer purchased and payment made through cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.06 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
To Ritika A/c |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Ritika on credit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.08 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.09 |
Karishna A/c |
Dr. |
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Karishna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.12 |
Mansi A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being cash paid to Mansi on account)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.14 |
Ritika A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases Return A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods returned to Ritika)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.15 |
Stationary A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being stationary purchased for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.16 |
Wages A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being wages paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.18 |
Sales Return A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Karishna A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods returned by Karishna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.20 |
Ritika A/c |
Dr. |
|
28,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
28,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque issued to Ritika)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.22 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Karishna A/c |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Karishna on account)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.24 |
Insurance Premium A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
4000 |
|
|
(Being insurance premium paid through cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.26 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
To Karishna A/c |
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque received from Karishna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
Rent A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being rent paid through cheque)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.29 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Meena Traders |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased on credit from Meera Traders)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
14,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
14,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
8,25,000 |
8,25,000 |
Ledger
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.01 |
To Capital |
|
2,00,000 |
Dec.02 |
By Office furniture |
|
30,000 |
|
|
Dec.02 |
To Sales |
|
30,000 |
Dec.03 |
By Bank |
|
1,00,000 |
|
|
Dec.22 |
To Krishna |
|
15,000 |
Dec.12 |
By Mansi |
|
30,000 |
|
|
Dec.30 |
To Sales |
|
14,000 |
Dec.15 |
By Stationery |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.16 |
By Wages |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
95,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,59,000 |
|
|
|
2,59,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
95,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
Balance c/d |
|
2,00,000 |
Dec.1 |
By Cash |
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
|
2,00,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
2,00,000 |
|
Office Furniture A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.2 |
To Cash |
|
30,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.03 |
To Cash |
|
1,00,000 |
Dec.05 |
By Computer |
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
Dec.26 |
To Krishna |
|
8,000 |
Dec.20 |
By Ritika |
|
28,000 |
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
1,77,000 |
Dec.24 |
By Insurance Premium |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
By Rent |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,85,000 |
|
|
|
2,85,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,77,000 |
|
Computer A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.05 |
To Bank |
|
2,50,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,50,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.06 |
To Bank |
|
60,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
80,000 |
|
|
Dec.29 |
To Meena Traders |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
80,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
80,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Ritika's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.14 |
To Purchase Return |
|
2,000 |
Dec.06 |
By Purchases |
|
60,000 |
|
|
Dec.20 |
To Bank |
|
28,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
30,000 |
|
Meena's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
20,000 |
Dec.29 |
By Purchases |
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
20,000 |
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
69,000 |
Dec.08 |
By Cash |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.09 |
By Krishna |
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.30 |
By Cash |
|
14,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
69,000 |
|
|
|
69,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
69,000 |
|
Karishna's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.09 |
To Sales |
|
25,000 |
Dec.18 |
By Sales return |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.22 |
By Cash |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.26 |
By Bank |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
Mansi's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.12 |
To Cash |
|
30,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
Dec.14 |
By Ritika |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
Stationery A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.15 |
To Cash |
|
3,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Wages A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.16 |
To Cash |
|
1,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sales Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.18 |
To Karishna |
|
2,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Insurance Premium A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.24 |
Bank |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.31 |
Balance c/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
Rent A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Dec.28 |
To Bank |
|
3,000 |
Dec.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Solution NUM 21
Books of Sanjana
Journal
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
L.F. |
Dr. (Rs.) |
Cr. (Rs.) |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
55,000 |
|
|
|
Stock A/c |
Dr. |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
Tarun's A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Rohan's A/c |
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
To Capital A/c |
|
|
|
1,05,000 |
|
|
(Being balances brought from the last month)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.03 |
Karuna A/c |
Dr. |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold to Karuna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.06 |
Heena A/c |
Dr. |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
(Being Goods sold to Heena)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.08 |
Purchases A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
To Rupali A/c |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
(Being goods purchased from Rupali)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.10 |
Sales return A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Karuna A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being goods returned by Karuna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.14 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
13,000 |
|
|
|
To Karuna A/c |
|
|
|
13,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Karuna)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.15 |
Rohan A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque issued to Rohan)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.16 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
To Heena A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
(Being cash received from Heena)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.20 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
To Tarun A/c |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque received from Tarun)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Heena A/c |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque received from Heena)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.25 |
Rupali A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
18,000 |
|
|
(Being cash payment made to Rupali)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.26 |
Cartage A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
(Being cartage paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.27 |
Salaries A/c |
Dr. |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
To Cash A/c |
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
(Being salaries paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.28 |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
To Sales A/c |
|
|
|
7000 |
|
|
(Being goods sold for cash)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.29 |
Rupali A/c |
Dr. |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
(Being cheque issued to Rupali)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.30 |
Drawings A/c |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
To Purchases A/c |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
(Being goods drawn for personal use)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
General Expenses A/c |
Dr. |
|
500 |
|
|
|
To Cash |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
(Being general expense paid)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
2,57,500 |
2,57,500 |
Ledger
Cash A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
6,000 |
Jan.25 |
By Rupali |
|
18,000 |
|
|
Jan.04 |
To Sales |
|
10,000 |
Jan.26 |
By Cartage |
|
1,000 |
|
|
Jan.14 |
To Karuna |
|
13,000 |
Jan.27 |
By Salaries |
|
8,000 |
|
|
Jan.16 |
To Heena |
|
3,000 |
Jan.31 |
By General Expenses |
|
500 |
|
|
Jan.28 |
To Sales |
|
7,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
11,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
39,000 |
|
|
|
39,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
11,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
1,05,000 |
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,05,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,05,000 |
|
|
|
1,05,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
1,05,000 |
|
Bank A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
55,000 |
Jan.15 |
By Rohan |
|
6,000 |
|
|
Jan.20 |
To Tarun |
|
10,000 |
Jan.29 |
By Rupali |
|
12,000 |
|
|
Jan.22 |
To Heena |
|
2,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
49,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
67,000 |
|
|
|
67,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To balance b/d |
|
49,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stock A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
40,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rohan' s A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.15 |
To Bank |
|
6,000 |
Jan.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
6,000 |
|
Tarun's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
10,000 |
Jan.20 |
By Bank |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
Sales A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Balance c/d |
|
37,000 |
Jan.03 |
By Karuna |
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
By Cash |
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.06 |
By Heena |
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.28 |
By Cash |
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
37,000 |
|
|
|
37,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb.01 |
By Balance b/d |
|
37,000 |
|
Karun's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.03 |
To Sales |
|
15,000 |
Jan.10 |
By Sales Return |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.04 |
By Cash |
|
13,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
Heena's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.06 |
To Sales |
|
5,000 |
Jan.16 |
By Cash |
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.22 |
By Bank |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
Purchases A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.08 |
To Rupali |
|
30,000 |
Jan.30 |
By Drawings |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
26,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
26,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rupali's A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.25 |
To Cash |
|
18,000 |
Jan.08 |
By Purchases |
|
30,000 |
|
|
Jan.29 |
To Bank |
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
Sales Return A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.10 |
To Karuna |
|
2,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cartage A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.26 |
To Cash |
|
1,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.27 |
To Cash |
|
8,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Drawings A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.30 |
To Purchases |
|
4,000 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
General Expenses A/c
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
Date |
Particulars |
J.F. |
Amount Rs. |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
Jan.31 |
To Cash |
|
500 |
Jan.31 |
By Balance c/d |
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
Feb.01 |
To Balance b/d |
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
