Class 9 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 11 - Reflection of Light
Reflection of Light Exercise Exercise
Solution 1.a
Plane mirror - The size of the image in the plane mirror is of the same size as the object.
Concave mirror -
When an object is away from the centre of curvature the image is diminished.
when the object is at the centre of curvature the image is of the same size.
When the object is anywhere between the pole and the centre of curvature the image is magnified.
Convex mirror -
The image is always virtual, erect and diminished for all positions of the object in front of it.
Solution 1.b
- In torches, the source of light is placed at the focus of the concave mirror to obtain a parallel beam of light.
- In projector lamps, the source of light is placed at the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
- In floodlights, the source of light is placed just beyond the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
Solution 1.c
In solar devices, sunlight is used for energy. The Sun is a distant object, so the rays coming from it are parallel to the principal axis and are incident on a concave mirror. Then after reflection, they converge to a single point. So, the heat is concentrated at that point which gives better results. Hence, concave mirrors are used in solar devices.
Solution 1.d
Convex mirror is used in car as rear-view mirror because it has larger view area than a plane mirror. And it can also produce erect, virtual and diminished full image of an object.
Solution 1.e
The rays from the Sun are parallel and when these rays fall on the concave mirror, they get converged to single point on focal plane of the mirror.
Thus, a lot of heat is produced at that point. Now, if paper is placed at that point to get image of the Sun, the paper gets burnt as large amount of heat rays gets concentrated at single point.
Solution 1.f
Breaking of the spherical mirror will not change the nature of the mirror.
Solution 2
Sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors
The new Cartesian sign convention is used while considering different terms for reflection through spherical mirrors.
In this convention, the pole (P) of the mirror is taken as the origin. The principal axis of the mirror is taken as the x-axis (X'X) of the coordinate system.
The sign convention is as follows:
The object is always placed to the left of the mirror. This implies that the light from the object falls on the mirror from the left-hand side.
All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
All distances measured to the right of the origin (along +x-axis) are taken as positive, while those measured to the left of the origin (along -x-axis) are taken as negative.
Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +y-axis) are taken as positive.
Distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis (along -y-axis) are taken as negative.
Solution 3
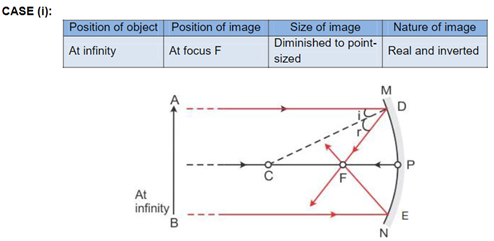
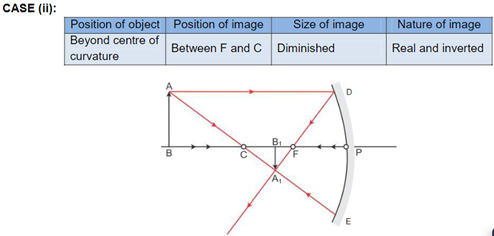
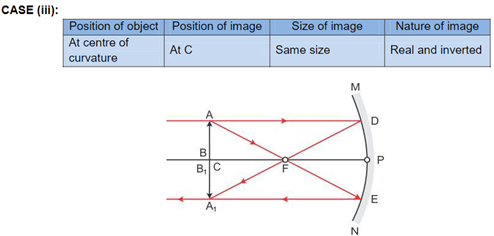
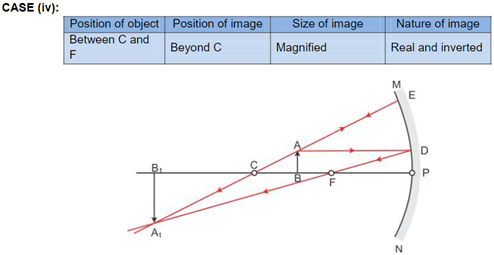
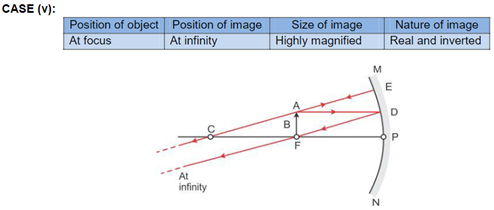
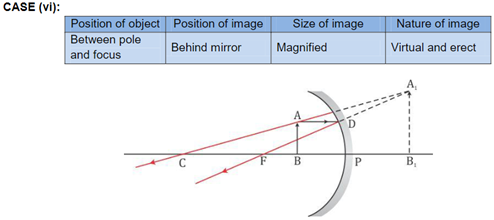
Solution 4
Periscope - Plane mirror, floodlights - concave mirror, shaving mirror - concave mirror, kaleidoscope - Plane mirror, street lights - convex mirror, head lamps of a car - concave mirror
Solution 5.a
ho = 7 cm
u = - 25 cm
f = -15 cm
Let v be the distance of the screen from the mirror so as to get clear image.
Using mirror formula,
![]()
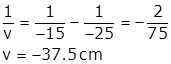
The screen should be placed a 37.5 cm from concave mirror.
Magnification is given by,
hi/ho = -(v/u)
hi = - (-37.5/-25) x 7 = -10.5 cm
The size of image is 10.5 cm and negative sign indicates that image is real and inverted.
Solution 5.b
Magnification = -v/u = 1/2,
hence, u = -2v .................(1)
where u is the mirror-to-object distance and v is mirror-to-image distance.
let f be the focal length of mirror.
we have mirror formula (1/v) + (1/u) = (1/f) ...........(2)
For convex mirror f is +ve, hence using eqn. (1) and (2),
(1/v) - [ 1/(2v)] = 1/18.... (3)
From eqn. (3), we get v = 9 cm hence u = -18 cm
hence object is at a distance 18 cm in front of mirror
Solution 5.c
u = - 30 cm
f = -10 cm
Let the image of the end of stick at point A is formed at a distance v from the mirror. Thus, using mirror formula,
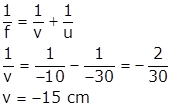
From end B,
u = -20 cm
f = - 10 cm
Let image be formed at distance v
Using mirror formula,
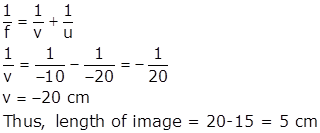
Solution 6
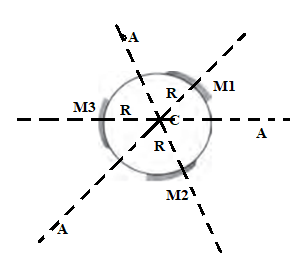
Pole is not common
Centre of curvature is common
Principal axis is not common
Radius of curvature is common

