Class 9 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 15 - Life Processes in Living Organisms
Life Processes in Living Organisms Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
Solution 2
The milk was on the stove. Rasika was engrossed watching television. She smelled something burning. She ran towards the kitchen. The milk was boiling over. She held the vessel with her bare hands but, screaming, she let it go at once. This activity was controlled by nerve cells. Special ends of dendrites in these cells collected the information, from where it was transferred to the cell body and then towards the terminal end of the axon. The chemicals produced at the terminal end passed through the minute space i.e.synapse. In this way, impulses were conducted in the body and the process of reflex action was completed by conducting the impulses from nerve to muscle cell.
Solution 3a
Root pressure
- Root pressure can be defined as a force that helps to drive fluids upward into the water-conducting vessels.
- It is generated as a result of osmotic pressure in the cells of the roots and can be demonstrated by exudation of fluid when the stem is cut off just above the ground.
- As the stem is cut off, drops of solution begin to ooze out which is an effect of root pressure.
- The effect of root pressure is also visible at night and early morning. During this time the rate of evaporation is low, as a result of which water droplets can be seen around special openings of veins near the tip of leaves of plants.
Solution 3b
Transpiration
- Transpiration is the process by which plants release the water inside it in the form of moisture or water vapour.
- Roots consume some amount of water from the soil and the rest evaporates in the atmosphere.
- Parts of plants such as stems, small pores on leaves, and flowers evaporate the water to the atmosphere.
- Several factors affect the rate of transpiration. These include internal factors such as leaf area, leaf structure and root-shoot ratio and external factors such as atmospheric humidity, temperature, wind velocity and water supply.
Importance of transpiration:
- It affects the rate of absorption of water by the roots.
- It creates a suction pressure for upward movement of water in tall trees.
- It helps in distribution of water throughout a plant.
- It helps to keep the surface of the leaves cool.
Solution 3c
Nerve cell
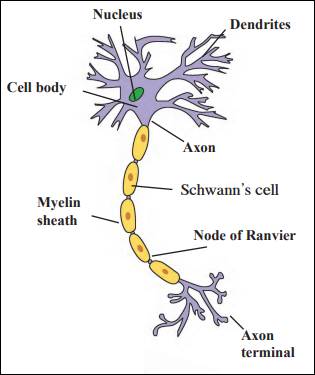
Nerve cells are also known as neurons. A neuron consists of three parts-
(i) Cell body - It contains a nucleus, cytoplasm, Nissl's granules and neurofibrils. It is also called cyton. It gives out short extensions called the dendrons, which further give rise to fibrillar extensions called dendrites.
(ii) Axon - It is a long extension of the dendron arising from the cell body. It transmits impulses away from the cell body, to the next neuron or a muscle cell.
(iii) Dendrites - These are short, branched parts arising from the cell body. They receive nerve impulses or stimulus from the previous nerve cell or muscle cell.
Nerve cells help in the conduction and transmission of nerve impulses throughout the body.
Solution 3d
Human brain
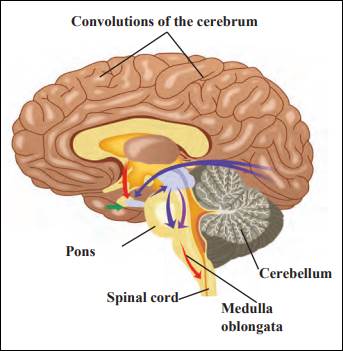
The brain is the central organ of the human nervous system. It is the main coordinating centre of the body. The brain is made of three main parts, forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.
1. Forebrain: It consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The thalamus has sensory and motor functions. Hypothalamus is involved in functions including homeostasis, emotion, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythms, and control of the autonomic nervous system.
2. Midbrain: It consists of the tectum and tegmentum. It is involved in functions such as vision, hearing, eye movement, and body movement.
3. Hindbrain: It is made of the cerebellum, pons and medulla. The cerebellum is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Pons is involved in motor control and sensory analysis. Medulla oblongata is responsible for maintaining vital body functions, such as breathing and heart rate.
Solution 3e
Reflex action
- Reflex action is a fast, involuntary unplanned sequence of actions that occurs in response to a particular stimulus. It is brought about by the spinal cord.
- Closing of eyelids when dust falls in the eyes or withdrawal of hand on touching a hot pan are few examples of reflex action.
- The nervous elements involved in carrying out the reflex actions constitute a reflex arc.
Reflex arc has the below components:
1. Sensory receptors: It is a sensory structure that responds to a specific stimulus.
2. Sensory neuron: This neuron carries sensory impulse to the grey matter of the spinal cord through the dorsal root of the spinal cord.
3. Interneurons: One or two interneurons serve to transmit impulses from the sensory neuron to the motor neuron.
4. Motor neuron: It transmits impulse from the central nervous system to the effector organ.
5. Effector organs: It may be a muscle or gland which responds to the impulse received.
Solution 4
Solution 5a
Human endocrine glands
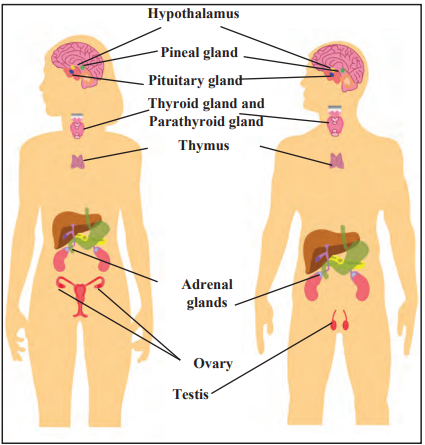
Solution 5b
Human brain
Solution 5c
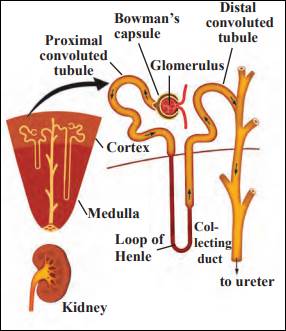
Nephron
Solution 5d
Nerve cell
Solution 5e
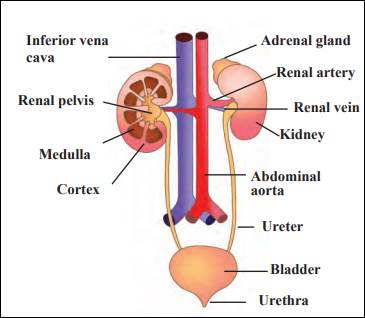
Human excretory system
Solution 6a
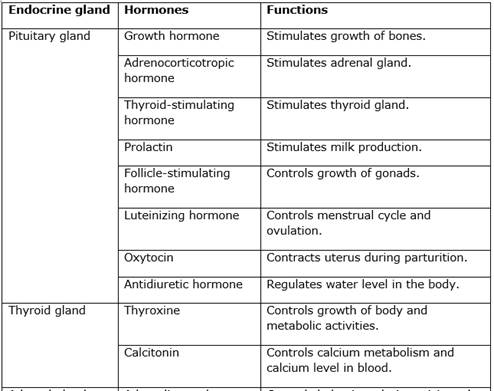
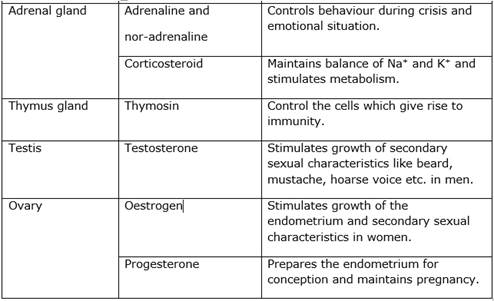
Chemical co-ordination in humans:
- In humans, chemical co-ordination is brought about with the help of certain chemical substances called hormones.
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands also called the ductless glands.
- These glands do not have any arrangement of their own to either store or carry their secretions. Therefore, the hormones are directly released into the bloodstream.
- Though the endocrine glands are present at specific locations in our body, their secretions reach all parts of the body through the blood.
- The action of hormones is very slow but long-lasting.
- Endocrine glands along with the nervous system are responsible for control and co-ordination in our body.
- These two systems help each other to control and integrate various activities of the body.
- It is very important that the hormones are secreted only in the required quantity and there is a special mechanism which controls the quantity and timing of hormone secretion.
- For example, whenever there is an increase in blood glucose level, certain cells in the pancreas get stimulated and in response, release a greater quantity of insulin, thus bringing down the sugar level to normal.
Names and functions of some hormones
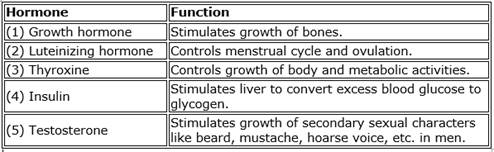
Solution 6b
Differences between the excretory system of humans and plants:
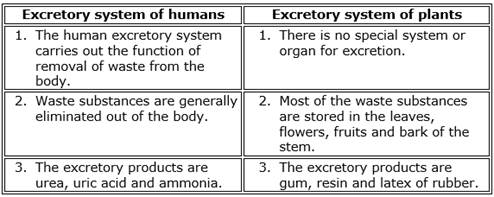
Solution 6c
Co-ordination in plants
- Plants do not have a nervous system like humans. So, the function of control and coordination in plants is performed by the chemical substances called plant hormones or phytohormones which bring about movements in plants.
- Plants use electrochemical impulses for transfer of information from one place to another.
- As a response to changes in the surroundings, plant hormones bring about various movements in plants.
- Plant cells change their shape by increasing or decreasing the water content and thereby, bring about the movements of plants.
- In plants, movements are mainly in the form of responses given to the stimuli.
Plants show two types of movements - growth relevant movements and growth irrelevant movements.
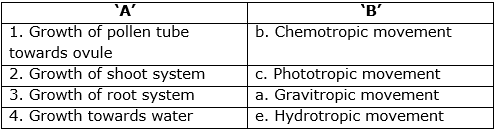
1. Growth relevant movements: Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called tropism or tropic movement.
Examples of growth-relevant movements:
- The shoot system of a plant responds to the stimulus of light i.e., it grows towards the source of light. This is called phototropic movement.
- The root system of plants responds to stimuli like gravity and water. These responses are called gravitropic movement and hydrotropic movement respectively.
- Movement shown by plants in response to specific chemicals is called chemotropic movement. For example, the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule.
2. Growth irrelevant movements: Some specific movements of the plants do not lead to plant growth. Such movements are called growth-irrelevant movements.
Examples of growth irrelevant movements:
- Closing of leaflets of touch-me-not (Mimosa) plant on touch. This movement also occurs at places other than where it has been touched.
- In the plant called Venus fly trap, when an insect comes in contact with the flower-like trap, the trap closes at once and the trapped insect is digested by the plant.
- The lotus flower opens during day-time while the tuberose flower opens at night.
Solution 7a
- Different organ systems operate together in multicellular organisms. Our body functions smoothly if there is co-ordination between different organ systems or organs and the stimuli in the surroundings.
- The systematic regulation of different life processes is called control and carrying out these life processes in proper sequence is called co-ordination.
- If any activity in the body is to be completed successfully, it is necessary that there is proper co-ordination between different systems, and organs participating at different steps of that activity.
- If due to lack of co-ordination, there is confusion at any step, the activity may not get completed. There should not be any randomness at any step.
- There should be proper co-ordination between internal activities of the body resulting from various factors like body temperature, water- level, enzyme-level, or stimuli arising in the surrounding environment.
- Proper co-ordination between various systems of an organism helps to maintain a state of equilibrium called homeostasis which is necessary for the optimal efficiency of the body.
Solution 7b
Excretion in human beings
- Removal of wastes from the body is very important. This function is carried out by the excretory system.
- The human excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, the urinary bladder and the urethra.
- Urine is formed by the kidneys by separating the wastes and unwanted excess substances from the blood.
- The functional unit of the kidney that performs the basic function of filtration is called a nephron.
- The urea produced in the liver mixes into the blood.
- When the urea-containing blood enters the glomerulus, it is filtered through capillaries and urea and other similar substances are separated from it.
- Water molecules and small molecules of some other substances can cross the semipermeable membrane of the Bowman's capsule.
- The solution accumulated in the cavity of Bowman's capsule passes into the tubular part of the nephron.
- Here, molecules of water and some other useful substances are reabsorbed into the blood.
- Urine is formed from the remaining solution which is full of waste materials.
- The urine is carried by the ureters and stored in the urinary bladder. Later, urine is eliminated out of the body through the urethra.
Solution 7c
Plants give out oxygen during photosynthesis by the process of diffusion which is useful to human beings for respiration. Some waste materials in plants like gum, resin and latex of rubber are useful to humans.
Solution 7d
Transportation system in plants
- Plants have two types of conducting tissues i.e., xylem which conducts water and phloem which conducts food.
- During transpiration, water is released into the atmosphere. As a result, water level is the epidermal layer of the leaf decreases.
- Water is brought up to the leaves through the xylem so as to compensate for the loss of water.
- Transpiration helps in absorption of water and minerals and distribution to all parts of the plant whereas root pressure preforms the important role of pushing the water up at night time.
- The food produced by the leaves is transported to each and every cell of the plant through phloem.
- When the food materials like sucrose are transported towards a part of the plant through phloem, using ATP, the water concentration in that part decreases. As a result, water enters the cell by diffusion.
- The pressure on the cell wall increases due to increase in the cellular contents.
- Due to increased pressure, food is pushed into the neighboring cells where the pressure is low.
- This process helps the phloem to transport materials as per the need of the plant.

