Class 9 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 6 - Classification of Plants
Exercise
Classification of Plants Exercise Exercise
Solution 1

Solution 2
- Thallophyta plants have soft and fibre-like body.
- Bryophyta are called the 'amphibians' of the plant kingdom.
- In pteridophytes, asexual reproduction occurs by spores formation and sexual reproduction occurs by zygote formation.
- Male and female flowers of gymnosperms are borne on different sporophylls of the same plant.
Solution 3.a
Characteristics of Phanerogams:
- Plants which possess special structures for reproduction and produce seeds are called phanerogams.
- In these plants, after the process of reproduction, seeds are formed which contain the embryo and stored food.
- During the germination of seeds, the stored food is used for initial growth of the embryo.
- Depending on whether the seeds are enclosed in a fruit or not, phanerogams are classified into gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Solution 3.b
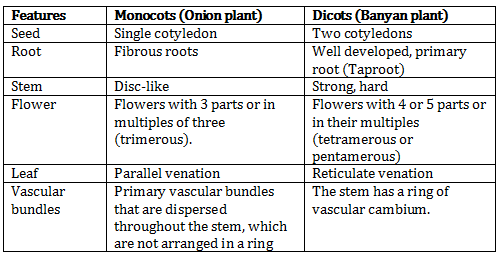
Differences between monocots and dicots:
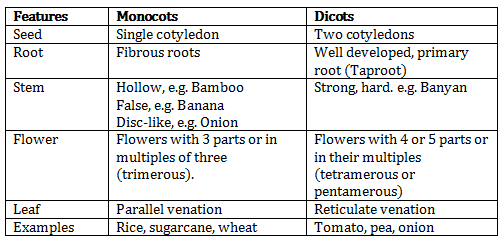
Solution 3.c
- Ferns belong to the group of plants called Pteridophyta.
- They have well-developed roots, stem and leaves but do not bear flowers and fruits.
- They have separate tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- They reproduce with the help of spores formed along the back or posterior surface of their leaves.
- They reproduce asexually by spore formation and sexually by zygote formation.
Solution 3.d
Spirogyra
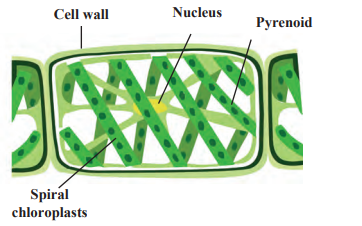
- Spirogyra belongs to division Thallophyta. Thallophytes are often called algae.
- Spirogyra grows mainly in water.
- It does not have specific parts like root, stem, leaves or flowers but are autotrophic due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- The plant body of Spirogyra is soft and fibre-like.
- It has spirally arranged chloroplasts in its cell.
Solution 3.e
Characteristics of Bryophyta:
- Bryophyta are a group of plants popularly called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they grow in moist soil but need water for reproduction.
- These plants are thalloid, multicellular and autotrophic.
- They reproduce by spore formation.
- Their plant body is flat, ribbon-like, long, without true roots, stem and leaves.
- Instead, they have stem-like or leaf-like parts and root-like rhizoids.
- They do not have specific tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- Examples: Moss (Funaria), Anthoceros, Riccia.
Solution 4
Marchantia and Funaria (Bryophyta)
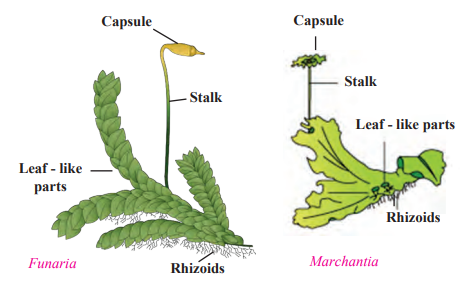
- These plants are called 'amphibians' of the plant kingdom because they grow mostly in soil and need water for reproduction.
- They do not have specific tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- Their plant body is flat, ribbon-like, long, without true roots, stem and leaves
- Instead, they have stem-like or leaf-like parts and root-like rhizoids.
Fern (Pteridophyta)

- They have well-developed roots, stem and leaves for the conduction of food and water.
- They do not bear flowers and fruits.
- They reproduce with the help of spores present along the back or posterior surface of the leaves.
Spirogyra (Thallophyta)
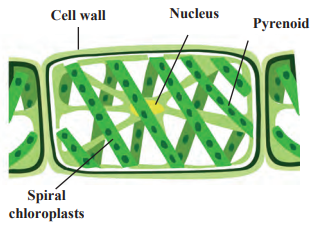
- Spirogyra belongs to division Thallophyta. Thallophytes are often called algae.
- Spirogyra grows mainly in water.
- It does not have specific parts like root, stem, leaves or flowers but are autotrophic due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- The plant body of Spirogyra is soft and fibre-like.
- It has spirally arranged chloroplasts in its cell.
Solution 5
Solution 6
Criteria for classification of plants:
- Whether they bear flowers, fruits and seeds: If plants do not bear flowers, fruits and seeds, they are non-seed bearing plants. If they bear flowers, fruits and seeds, they are seed-bearing plants.
- Presence or absence of conducting tissues: Pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms which possess conducting tissues are included in vascular plants whereas thallophytes and bryophytes which do not possess conducting tissues are included under non-vascular plants.
- Whether seeds are enclosed in fruit: Depending on whether the seeds are enclosed in fruit or not, plants are classified as gymnosperms (naked-seeds) and angiosperms (seeds enclosed in fruit).
- Number of cotyledons: Depending on the number of cotyledons in seeds, angiosperms are classified into dicotyledons (two cotyledons) and monocotyledons (single cotyledon).

