Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 17: Man made Materials
Man made Materials Exercise Exercise 17
Solution 1
a. Plasticity
b. Teflon
c. More than 100 ºC (about 240 ºC)
d. Alkali silicate or water
Solution 2
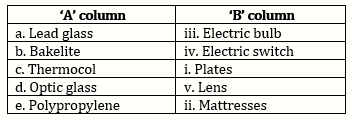
Solution 3
a. Thermocol is made from polystyrene which is also a complex thermoplastic substance.
b. PVC or polyvinyl chloride is used for making bottles, raincoat, pipes, handbags, shoes, electric cables, electric cable insulation, furniture, ropes, toys etc.
c.
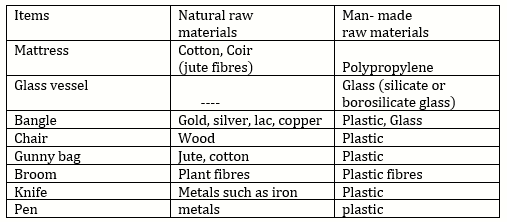
d. The main ingredients of glass are sand and silica.
e. (1) Plastics are derived from natural materials such as natural gas, oil, coal, minerals and plants
(2) The first synthetic plastics were derived from cellulose, a substance found in plants and trees. This cellulose was heated with chemicals and resulted in a plastic like material.
(3) In modern times, the different raw materials are used for making plastics, but most plastics are made from the hydro carbons present in the natural gas, oil and coal.
(4) Plastics are simply chains of like molecules linked together. These chains are called polymers. Thus, many plastics begin with "poly" such as polyethylene, polystyrene and polypropylene.
(5) Plastics is produced in factories by suitable chemical reactions.
Solution 4
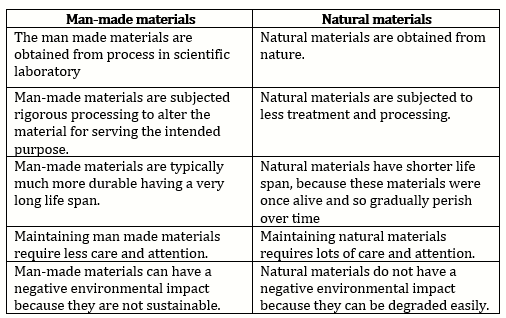
a.
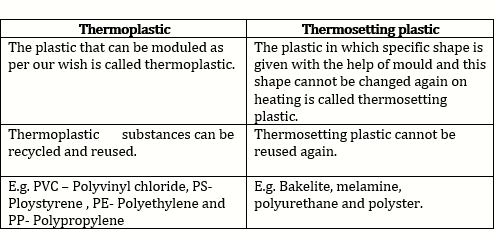
b.
Solution 5
a.
1. Plastic
- Plastic is non degradable substance. Hence if thrown in any ecosystem, it remains unchanged for many years.
- It is one of the worst environmental pollutants as its disposal is a major problem.
- If thrown in water bodies, it effects the aquatic animals. Many of turtles mistake it for algae and it the plastic. Eventually such animals die due to choking.
- In terrestrial environment, the grazing animals like cattle are affected due to plastic.
- If burnt it emits very toxic gases.
- In landfill sites, it remains unchanged for thousands of years.
2. Glass
- The glass production is carried out at high temperature of about 1500 ºC. This burning emits many hazardous gases like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, carbon dioxide. These gases cause green house effect.
- Moreover, glass being non degradebale, cause pollution.
- If broken glass piece or any waste glass material is diposed into aquatic environment, it affects animals and plants.
- Similarly, glass piece block the drainages.
- The waste glass thrown anywhere cause injury to terrestrial fauna.
3. Thermocol
- Thermocol contains carcinogenic ingredients in the form of styrene. If there is prolonged contact with thermocol, there is possibility of blood cancer like leukaemia and lymphoma.
- Thermocol is non degradable. It cannot be degraded into harmless substances easily.
- If it is burnt for destruction, it releases toxic gases in atmosphere.
- The plates and cups used for food, water, tea etc are made up of thermocol. This may effect the health. Reheating the food kept in thermocol releases styrene. This styrene may dissolve in that food, causing health problems like cancer.
(b) (1) The use of plastic should be minimum. Reducing the consumption, reusing the same plastic again and again, recycling the used plastic and making some new product are some of the measures that can be adopted.
(2) There are attempts to use plastic in making roads. Therefore plastic is bought with good price at some places.
(3) Therefore instead of disposing it anywhere, it should be collected and sold in best possible way.
(4) The better alternatives for plastics should be adopted.
(5) The awareness programmes about misuse of plastic should be arranged, so that common man can understand the dangers of using plastic.
Solution 6
a. Glass production
- Mixture of sand, soda, lime and small quantity of magnesium oxide is heated in furnace.
- At 1700 °C sand or silicon dioxide melts.
- To make the mixture melt at lesser temperature, pieces of discarded glasses are added to it.
- This addition makes the mixture to melt at lesser temperature of 850 °C.
- When all the ingredients of mixture are liquefied, then again it is heated up to 1500 °C.
- This heating is immediately followed by cooling.
- The sudden cooling causes the mixture to become homogeneous, amorphous and transparent instead of crystalline.
- For variety of glass types, different proportions of ingredients are used for heating.
b. Optic glass
- Optic glass or optical glass needs to be very clear and transparent as it is used in spectacles, lenses and other devices like microscopes.
- Optic glasses are produced from the mixture of sand, soda, limestone, barium oxide and boron.
c. Uses of plastic
- Polyvinyl chloride or PVC is used to make bottles, raincoat, pipes, handbags, shoes, electric cable insulation, furniture, ropes, toys, etc.
- Polystyrene is used in making thermo insulating parts of electric appliances like refrigerators, gears of machines, toys, protective coverings like covers of CD and DVD, etc.
- Polyethylene (PE) plastics are used for making milk bags, packing bags, flexible garden pipes, etc.
- Polypropylene (PP) is used in making parts of loudspeakers and vehicles, ropes, mattresses, laboratory appliances, etc.
- Bakelite for making cabinets of radio, T.V., telephones, electric switches, toys, plastic handles of cookers, etc.
- Melamine for making domestically useful items like cup - saucers, plates, tray, some spare parts of airplane engines, electric and sound insulating coverings, etc.
- Bakelite for making cabinets of radio, T.V., telephones, electric switches, toys, plastic handles of cookers, etc.
- Melamine for making domestically useful items like cup - saucers, plates, tray, some spare parts of airplane engines, electric and sound insulating coverings, etc.
