Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 5: Inside the Atom
Inside the Atom Exercise Ex. 5
Solution 1
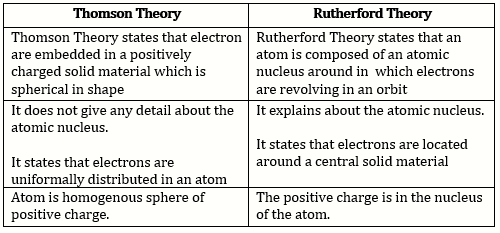
A. Difference between Thomson and Rutherford Theory are as Follows:
B. Valency of an Element
The capacity of an element of to combine with another element is known as valency.
Relationship between the number of valence electron and valency
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of an element are called valence electrons.
Helium and neon,atoms of both these gaseous element do not combine with any other atom.These elements are chemically insert,i.e their valency is zero.Helium atom contains two electrons,indicates that the outermost shell of helium has an electron octet.
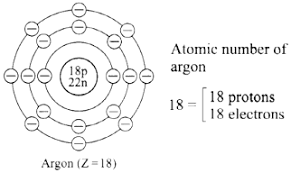
Similarly argon contains eight electrons in the valence shell,i.e argon has an electron octet.It is confirmed that the valency is zero when electron octet (or duplet) is complete.
Atoms of all the elements except insert gases have a tendency to combine with other atoms,i.e they have a nonzero valency. The molecules formed by combination with hydrogen (H2) that valency of hydrogen is 1.
The electronic configuration of hydrogen shows that there is one electron less than the complete duplet state. This number 'one' matches with the valency of hydrogen which is also one.it means that there is relationship between the valency of an element and the number of electrons in its valence shell.
C. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. The atomic number, i.e the proton number of carbon is 6 and the mass number is total number of protons and neutrons in the carbon i.e 6 protons + 6 neutrons= 12. Therefore the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
D. A particle which is a constituent of an atom hence smaller than the atom is called sub atomic particle.
An atom is formed from the nucleus and the extra nuclear part. These contain three types of subatomic particles.
The nucleus contains two types of subatomic particles together called nucleons. Protons and neutrons are the two types of nucleons or subatomic particles and electrons are subatomic particles in the extra nuclear part.
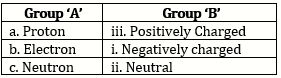
1) Proton(p): Proton is a positively charged subatomic particle in the atomic nucleus .The positive charge on the nucleus is due to the proton in it. A proton is represented by the symbol 'p'. Each proton carries a positive charge of +1e.
1e=1.6⨯10-19
When total positive charge on the nucleus is expressed in unit 'e', its magnitude is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass of the proton is approximately 1u(1 Delton).
(1u=1.66⨯10-27g)
(The mass of one hydrogen atom is also approximately 1u)
2) Neutron: Neutron is an electrically neutral subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol 'n'. The number of neutrons in the nucleus is denoted by the symbol 'N'. Atomic nuclei of all the elements except hydrogen with atomic mass 1u, contain neutrons. The mass of a neutron is approximately 1u, which is almost equal to that of a proton.
3) Electron (e-): Electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol 'e-'.Each electron carries one unit of negative charge (-1e) .Mass of an electron is 1800 times less than that of a hydrogen atom. There for the mass of an electron can be treated as a negligible. Electron in the extranuclear part revolve in the discrete orbits around the nucleus. The energy of an electron is determined by the shell in which it is present.
Solution 2
a. The scientific reason behind this is :
1. The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
2. The electrons revolve around the nucleus.
3. The mass of an electron is negligible compared to that of a proton or a neutron.
4. Hence the mass of an atom depends mainly on the number of protons and neutrons. Therefore, practically all the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
b. The reason behind this is:
1. An atom is made of two parts, viz, the nucleus and the extra nuclear part.
2. The nucleus is positively charged. The positive charge on the nucleus is due to protons.
3. The extra nuclear part of an atom is made up of negatively charged electrons.
4. In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of extra nuclear electrons.
5. The magnitude of the positive charge on the nucleus equals the magnitude of the negative charge on the electrons. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is electrically neutral.
c. The reason behind this is :
1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called Atomic Mass Number (A).
2. As protons and neutrons are whole numbers, that atomic mass number is also a whole number.
d. The reason behind this is :
1. The entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus and the positively charged nucleus at centre of an atom.
2. The negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus.
3. The total negative charge on all the electron is equal to positive charge on the nucleus. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is stable.
Solution 3
a. An atom is the smallest particle of an element which retains its chemical identity in all physical and chemical changes.
b. Atoms of the same element having the same atomic number, but atomic mass numbers are called isotopes.
c. The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by Z.
d. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called atomic mass number. It is denoted by A.
e. The substance which reduces the speed of fast moving neutrons produced in a fission is called a moderator in nuclear reactor.
Solution 4
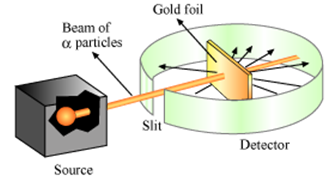
a. Ruthrford's scattering experiment :
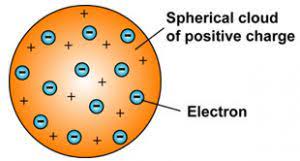
b. Thomson's atomic model :
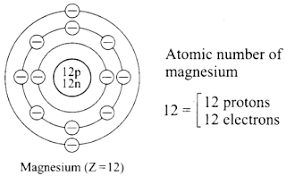
c. Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of Magnesium (Atomic number 12)
d. Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of Argon (Atomic number 18)
Solution 5
a. Subatomic particles.
b. Negative.
c. K
d. M
e. 3
Solution 6
Solution 7
1. There are 12 neutrons in the sodium
No. of neutrons = Mass no. - Atomic number
= 23-11 No. of neutrons = 12
2. Atomic mass number(A) of ACZ = 14C6 is 14
3. There are 17 protons in chlorine.
As we know, atomic number = No. of protons = No. of electrons
