Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 11: Human Body and Organ System
Human Body and Organ System Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
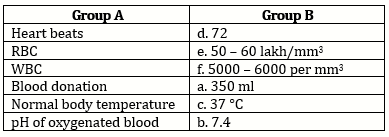
Solution 2
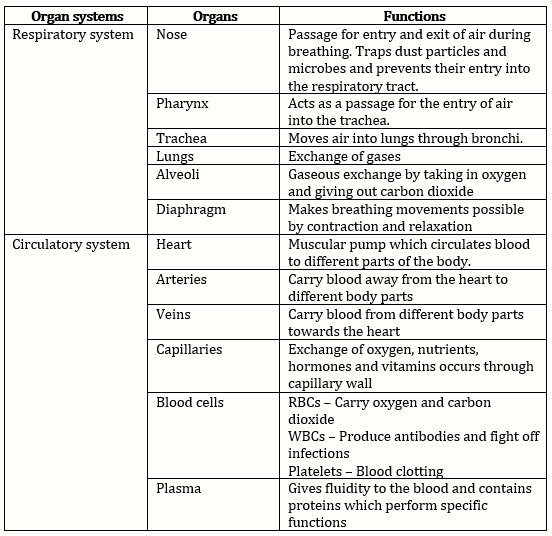
Solution 3
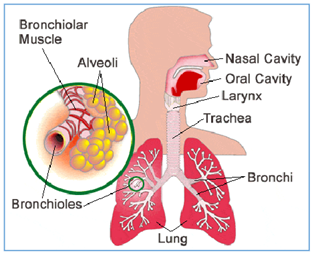
a. Respiratory system
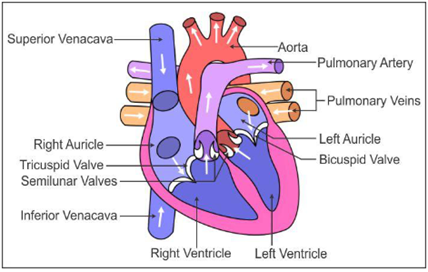
b. Internal structure of heart
Solution 4.a
- Human blood is red in colour due to the presence of haemoglobin.
- RBCs are made of an iron-containing pigment called haemoglobin.
- Presence of haemoglobin imparts red colour to blood.
Solution 4.b
- The diaphragm is a muscular partition between the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.
- When we inhale air, the ribs rise up while the diaphragm lowers down simultaneously causing a decrease in the pressure on the lungs. Thus, the air moves into lungs through the nose.
- As the ribs return to their original position, the diaphragm rises up leading to an increase in pressure inside lungs and the air moves outside the nose.
- In this way, during the process of breathing, the upward and downward movement of diaphragm occurs simultaneously.
Solution 4.c
- Blood donation is considered superior because it can save someone's life.
- Most of lives are lost due to blood loss during surgeries or accidents.
- In such cases, regular and timely blood transfusion is required.
- This requirement of blood is facilitated through blood donation.
Solution 4.d
- Person with 'O' blood group does not have any antigen on his/her RBCs.
- The 'O' type blood thus does not cause clotting reactions in the body of the recipients.
- Hence, blood group 'O' can be given to persons with any type of blood group i.e., O, A, B and AB.
- Because of this characteristic, a person with 'O' type of blood group is called universal donor.
Solution 4.e
- Food must have limited amount of salts as our body requires them in lesser quantities.
- Excessive salt consumption may lead to accumulation of water in different parts of the body such as arms and legs which may lead to oedema.
- More salt in diet means more sodium ions. These extra sodium salts cause rise in blood pressure. Such condition is called hypertension.
- This condition can be dangerous and fatal in some cases.
Solution 5.a
The functional correlation of circulatory system with respiratory, digestive and excretory system is as follows:
- During respiration, exchange of gases takes place in the lungs. The respiratory system causes diffusion of oxygen into the blood and diffusion of carbon dioxide out of the blood. Oxygen is then transported to cells of the body via the circulatory system.
- The digestive system is responsible for producing nutrients by breaking complex molecules into simpler soluble nutrients. These nutrients are absorbed in the blood in the villi of the intestine. The blood then carries these nutrients to each and every body cell during circulation.
- The excretory system is responsible for the elimination of waste products from the body. The waste products are transported by blood to the excretory system for their removal from the body.
Solution 5.b
Human blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of blood plasma and blood corpuscles suspended in it.
Composition of blood:
A. Plasma
- It is a light yellow-coloured or straw-coloured liquid.
- It constitutes 55% of the total blood volume.
B. Blood Cells
- Blood cells constitute 45% of the total blood volume.
- Three kinds of cells are found in the blood - RBCs, WBCs, and platelets.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs/erythrocytes)
- RBCs are circular, disc-shaped and biconcave.
- They are produced in the bone marrow of long bones.
- Mature RBCs do not have nuclei.
- The lifespan of RBCs is 120 days.
- RBCs are made up of an iron-containing respiratory pigment called haemoglobin.
- Haemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues.
White Blood Cells (WBCs/leucocytes)
- WBCs are large, nucleated and colourless. They have a large and lobed nucleus.
- They are produced in the bone marrow, lymph glands and spleen.
- They are of five subtypes, viz. neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes and lymphocytes.
- WBCs provide immunity.
Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood platelets are minute, oval or round, non-nucleated cells.
- Platelets are formed in the bone marrow.
- They play an important role in blood clotting.
Functions of the blood:
- It transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- White blood cells destroy disease-causing microorganisms, thus help in preventing infections.
- Blood maintains the water balance in tissues and organs of the body.
- Blood platelets prevent excessive blood loss by blood clotting.
- Blood regulates the body temperature by distributing the heat in different parts of the body.
Solution 5.c
Importance and need of blood donation:
- Blood can never be synthesized artificially. There is no substitute for natural blood.
- Every healthy person possesses about 5 litres of blood in his or her body.
- Blood groups are hereditary and depend on the genes inherited from their parents.
- Blood is required in various situations like accidents, bleeding, parturition and, surgical operations.
- Blood is also transfused in case of patients suffering from anaemia, thalassaemia and cancer.
- Blood transfusion is performed only after blood group matching to avoid any fatalities for the recipient.
- Blood transfusion is carried to compensate blood shortage in the body.
- Blood donation without any expectation is always life-saving.
- Blood donated by healthy person is used to save the life of a needy person. Hence, blood donation is considered as the best donation.
Solution 6.a
Differences between arteries and veins:
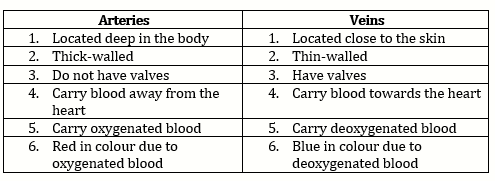
Solution 6.b
Differences between external and internal respiration:
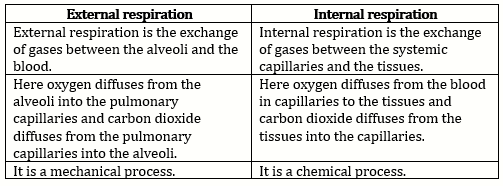
Solution 7
Parameters of blood donors that need to be taken into consideration before blood donation:
- Age - Donor should be over 18 and below 65 years of age.
- Weight - If the individual is underweight, then he/she are not allowed to donate blood as they may face dizziness and even faint after donating blood.
- Health - Donor should not be suffering from acute respiratory diseases or heart diseases. He should not have any kind of illness such as viral fever or cold at the time of blood donation.
- Haemoglobin level - Donor should have minimum level of haemoglobin of 12.5 grams.
- Pulse - Donor's pulse rate should be normal i.e., between 60 to 100 beats per minute.
- Blood pressure - Donor's blood pressure should be 90 - 119 mm Hg systolic and 60 - 79 mm Hg diastolic.
Solution 8
a. RBCs of the blood contain haemoglobin, an iron compound.
b. Diaphragm is present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
c. Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
d. pH of oxygenated blood is alkaline.
e. Production of RBCs occurs in red bone marrow.
Solution 9
a. K (All others are blood groups)
b. Blood transfusion (All others are components of blood)
c. Capillaries (All others are parts of the respiratory system while capillaries exist throughout the body)
d. Neutrophils (All others are proteins present in the plasma)
Solution 10
From the above condition, it seems that the child is suffering from a respiratory or circulatory disorder.
He has problems in breathing. Blue nails indicate that there are low levels of oxygen in the RBCs. This condition is called cyanosis.
Cyanosis is characterised by lack of oxygen in the blood due to which the skin turns bluish in colour.
Solution 11
Measures that can be taken to achieve normal blood pressure:
- Maintain healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Visit a physician and take proper medication for blood pressure control
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet containing fruits and vegetables
- Reduce the amount of salt intake
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Regularly monitor blood pressure
- Reduce stress by practicing yoga and meditation
